
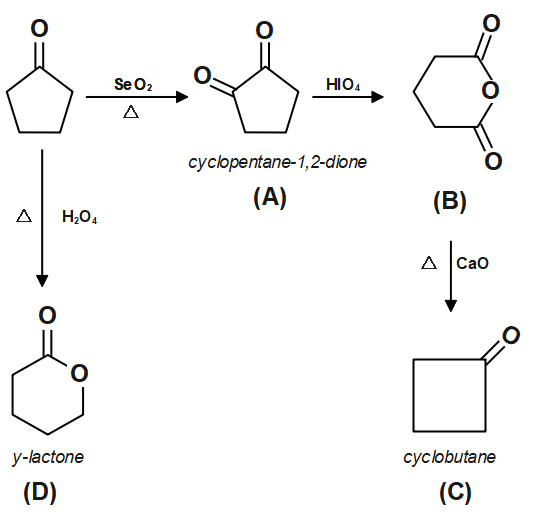
Determine the compound C and D respectively.

Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint: We know that Lactones with three- or four-membered rings $ \left( \alpha -lactones,\beta -lactones \right) $ are highly reactive, because of which isolation becomes difficult Unique laboratory methods are used for both small ring lactones, and for lactones that contain rings larger than six membered, for a reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Five membered $ \gamma -lactones $ and Six membered δ-lactones are the most stable structure because, as in every organic cycle, five and six membered rings minimize the pressure of bond angles. At room temperature, γ-lactones, along with the presence of dilute acid, are very stable. Thus, four hydroxy acids $ \left( R-CH\left( OH \right)-\left( CH \right)-COOH \right) $ instantly undergo natural esterification and cyclization to the lactone. $ .\beta -lactones $ do prevail, but can only be made by unique methods. $ \alpha -lactones $ can be detected as temporary species in mass spectrometry experiments.
By the reduction reaction, lactones get reduced to dios with the help of lithium hydride in the presence of dry ether. At first the reaction will break the ester bond of the lactone, and later it will reduce the aldehyde group $ \left( -CHO \right) $ into the alcohol group $ \left( -OH \right). $ For example, gamma lactones get reduced to the given complete reaction:
Note:
Note that when a lactone with a base is heated, it hydrolyzes the lactones into its parent compound, a straight-chained bifunctional compound. The hydrolysis-condensation reaction of lactones is reversible, just like the ester reaction. After hydrolysis, lactones offer only a single product.
Complete step by step solution:
Five membered $ \gamma -lactones $ and Six membered δ-lactones are the most stable structure because, as in every organic cycle, five and six membered rings minimize the pressure of bond angles. At room temperature, γ-lactones, along with the presence of dilute acid, are very stable. Thus, four hydroxy acids $ \left( R-CH\left( OH \right)-\left( CH \right)-COOH \right) $ instantly undergo natural esterification and cyclization to the lactone. $ .\beta -lactones $ do prevail, but can only be made by unique methods. $ \alpha -lactones $ can be detected as temporary species in mass spectrometry experiments.
By the reduction reaction, lactones get reduced to dios with the help of lithium hydride in the presence of dry ether. At first the reaction will break the ester bond of the lactone, and later it will reduce the aldehyde group $ \left( -CHO \right) $ into the alcohol group $ \left( -OH \right). $ For example, gamma lactones get reduced to the given complete reaction:

Note:
Note that when a lactone with a base is heated, it hydrolyzes the lactones into its parent compound, a straight-chained bifunctional compound. The hydrolysis-condensation reaction of lactones is reversible, just like the ester reaction. After hydrolysis, lactones offer only a single product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




