
How do you determine the area to the left of $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ and to the right of $x=-1$ ?
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: We have been given two functions and we have to find the area enclosed by those functions. The left boundary of the area enclosed is $x=-1$ and the area is contained by the function $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$. We shall first plot these two functions on the same cartesian plane and find their two points of intersections. Then we shall perform definite integration on the function $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ taking the two points of intersections as the limits.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given are two functions $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ and $x=-1$ where one function is straight-line parallel to the y-axis and the other function is parabolic in nature.
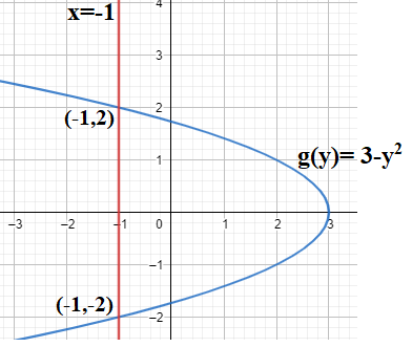
Here, we see that the points of intersection of these two functions are $\left( -1,2 \right)$ and $\left( -1,-2 \right)$.
Thus, the required region is the shaded region in the graph below.
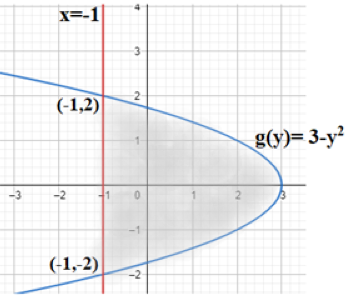
In order to find the enclosed area, we shall integrate $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ from $y=2$ to $y=-2$.
$A=\int\limits_{-2}^{2}{3-{{y}^{2}}.dy}$
From the basic properties of integration, we know that $\int{3.dy=3y}+C$ and $\int{{{y}^{n}}.dy=\dfrac{{{y}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+C$. We shall use these properties to integrate our function.
$\Rightarrow A=\left. 3y-\dfrac{{{y}^{3}}}{3} \right|_{-2}^{2}$
Now, we will apply the upper limit of the integral equal to 2 and the lower limit of the integral equal to -2.
$\Rightarrow A=3\left( 2 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}}{3}-\left( 3\left( -2 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}}{3} \right)$
Since ${{2}^{3}}=2\times 2\times 2=8$, thus substituting ${{2}^{3}}=8$, we get
$\Rightarrow A=6-\dfrac{8}{3}-\left( -6-\dfrac{\left( -8 \right)}{3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow A=6-\dfrac{8}{3}+6-\dfrac{8}{3}$
$\Rightarrow A=12-\dfrac{16}{3}$
$\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{20}{3}$
Therefore, the area to the left of $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ and to the right of $x=-1$ is $\dfrac{20}{3}$ square units.
Note: Definite integral of a function $f\left( y \right)$ is the area bound under the graph of function, $x=f\left( y \right)$and above the y-axis which is bound between two bounds as $y=a$ and $y=b$. Here, $a=$ -2 and $b=$2. The best thing about integral calculus is that the one of the two boundaries of the area to be found is a curve and the other boundary is the y-axis when the function is being integrated with respect to $dy$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given are two functions $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ and $x=-1$ where one function is straight-line parallel to the y-axis and the other function is parabolic in nature.

Here, we see that the points of intersection of these two functions are $\left( -1,2 \right)$ and $\left( -1,-2 \right)$.
Thus, the required region is the shaded region in the graph below.

In order to find the enclosed area, we shall integrate $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ from $y=2$ to $y=-2$.
$A=\int\limits_{-2}^{2}{3-{{y}^{2}}.dy}$
From the basic properties of integration, we know that $\int{3.dy=3y}+C$ and $\int{{{y}^{n}}.dy=\dfrac{{{y}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+C$. We shall use these properties to integrate our function.
$\Rightarrow A=\left. 3y-\dfrac{{{y}^{3}}}{3} \right|_{-2}^{2}$
Now, we will apply the upper limit of the integral equal to 2 and the lower limit of the integral equal to -2.
$\Rightarrow A=3\left( 2 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}}{3}-\left( 3\left( -2 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}}{3} \right)$
Since ${{2}^{3}}=2\times 2\times 2=8$, thus substituting ${{2}^{3}}=8$, we get
$\Rightarrow A=6-\dfrac{8}{3}-\left( -6-\dfrac{\left( -8 \right)}{3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow A=6-\dfrac{8}{3}+6-\dfrac{8}{3}$
$\Rightarrow A=12-\dfrac{16}{3}$
$\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{20}{3}$
Therefore, the area to the left of $g\left( y \right)=3-{{y}^{2}}$ and to the right of $x=-1$ is $\dfrac{20}{3}$ square units.
Note: Definite integral of a function $f\left( y \right)$ is the area bound under the graph of function, $x=f\left( y \right)$and above the y-axis which is bound between two bounds as $y=a$ and $y=b$. Here, $a=$ -2 and $b=$2. The best thing about integral calculus is that the one of the two boundaries of the area to be found is a curve and the other boundary is the y-axis when the function is being integrated with respect to $dy$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




