
How do you determine if a molecule has a polar covalent bond based on the Lewis dot structure?
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: The covalent bond is formed by the mutual sharing of the electrons between the two atoms to form a molecule. In the Lewis structure, the valence electrons are placed in the form of small dots on the atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
The chemical bond is defined as the bond which joined the two atoms to form a compound. The chemical bond helps to keep the molecule or compound intact.
The polar covalent bond is formed between the two atoms by the mutual sharing of valence electrons by the two atoms.
The Lewis dot structure is the representation of the valence electrons surrounding the electrons. The valence electrons are shown using small dots and are placed on the atoms of the molecule.
In the Lewis structure, when we circle around both the atoms, we can see that it represents the stable inert gas structure.
When we draw the Lewis structure, if both the atoms are stable even after the sharing of valence electrons they form covalent bonds between the atoms.
Let's take the example of carbon dioxide, the chemical formula of carbon dioxide is $C{O_2}$. It is formed from one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the electronic configuration is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^2}$. The valence electrons of carbon is 4. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and the electronic configuration of oxygen is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^4}$. The valence electrons of oxygen is 6. The total valence electrons of carbon dioxide is 16.
The Lewis structure of carbon dioxide is shown below.
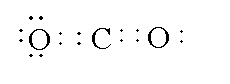
If you draw a circle around the carbon atom it will give a stable structure containing 8 electrons. The two pairs of valence electrons form a double bond between the carbon and two oxygen atoms.
Note:
The single covalent bond is formed by sharing one electron by each atom. The double covalent bond is formed when two valence electrons are shared by each atom. In double bonds one pi-bond and one sigma bond is present.
Complete step by step answer:
The chemical bond is defined as the bond which joined the two atoms to form a compound. The chemical bond helps to keep the molecule or compound intact.
The polar covalent bond is formed between the two atoms by the mutual sharing of valence electrons by the two atoms.
The Lewis dot structure is the representation of the valence electrons surrounding the electrons. The valence electrons are shown using small dots and are placed on the atoms of the molecule.
In the Lewis structure, when we circle around both the atoms, we can see that it represents the stable inert gas structure.
When we draw the Lewis structure, if both the atoms are stable even after the sharing of valence electrons they form covalent bonds between the atoms.
Let's take the example of carbon dioxide, the chemical formula of carbon dioxide is $C{O_2}$. It is formed from one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the electronic configuration is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^2}$. The valence electrons of carbon is 4. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and the electronic configuration of oxygen is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^4}$. The valence electrons of oxygen is 6. The total valence electrons of carbon dioxide is 16.
The Lewis structure of carbon dioxide is shown below.
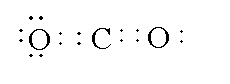
If you draw a circle around the carbon atom it will give a stable structure containing 8 electrons. The two pairs of valence electrons form a double bond between the carbon and two oxygen atoms.
Note:
The single covalent bond is formed by sharing one electron by each atom. The double covalent bond is formed when two valence electrons are shared by each atom. In double bonds one pi-bond and one sigma bond is present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




