
Describe the working of sound signals reaching the brain with the help of a figure of the human ear.
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: You could firstly give the basic mechanism of hearing by human ear. Then you could give an appropriate diagram in which all the basic parts are neatly marked. After that you could explain step by step what happens to the sound signals after entering the outer ear and also specify when and where the conversions take place.
Complete solution:
The basic mechanism of hearing is the conversion of sound waves into electrical signals.
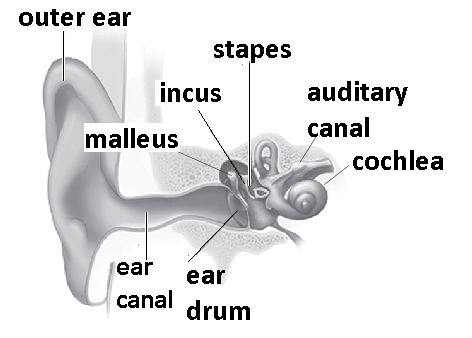
The sound waves reach the eardrum from the outer ear via the ear canal. The eardrum then suffers from vibrations as the result of these sound waves. These vibrations are then passed to the three tiny bones called malleus, incus and stapes that are present in the middle ear.
The function of these tiny bones is amplification. These amplified vibrations are then transferred to cochlea. The fluid that is present in the cochlea is rippled by these vibrations and thus a traveling wave is formed along the basilar membrane that forms the partition of cochlea. Then we have the hair cells which are actually the sensory cells that ride this wave.
Then we have stereocilia that are minute hair like projections that bends as the result of hair cells bumping onto it. At their tip, there are pore like channels present that opens up due to this bending. This causes the chemicals to rush into the cells thereby resulting in the creation of electrical signal. This electrical signal is then perceived by the brain after being carried by the auditory nerve. There, these electric signals are again turned into sound waves for us to recognize.
Note:
Cochlea which forms the inner ear is observed to be a snail like structure. The basilar membrane is that membrane that runs throughout the cochlea forming partition and thereby dividing it into upper and lower parts. The key hearing structures namely the hair cells and stereocilia are present on this basilar membrane.
Complete solution:
The basic mechanism of hearing is the conversion of sound waves into electrical signals.

The sound waves reach the eardrum from the outer ear via the ear canal. The eardrum then suffers from vibrations as the result of these sound waves. These vibrations are then passed to the three tiny bones called malleus, incus and stapes that are present in the middle ear.
The function of these tiny bones is amplification. These amplified vibrations are then transferred to cochlea. The fluid that is present in the cochlea is rippled by these vibrations and thus a traveling wave is formed along the basilar membrane that forms the partition of cochlea. Then we have the hair cells which are actually the sensory cells that ride this wave.
Then we have stereocilia that are minute hair like projections that bends as the result of hair cells bumping onto it. At their tip, there are pore like channels present that opens up due to this bending. This causes the chemicals to rush into the cells thereby resulting in the creation of electrical signal. This electrical signal is then perceived by the brain after being carried by the auditory nerve. There, these electric signals are again turned into sound waves for us to recognize.
Note:
Cochlea which forms the inner ear is observed to be a snail like structure. The basilar membrane is that membrane that runs throughout the cochlea forming partition and thereby dividing it into upper and lower parts. The key hearing structures namely the hair cells and stereocilia are present on this basilar membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




