
Describe the various types of placentations found in flowering plants.
Answer
348.3k+ views
Hint: Flowering plants, which are also known as angiosperms, use a sexual method of reproduction. Reproduction in plants rotates around the flower, which has both the female and the male gametes. All parts of a flower help in the process of reproduction, even though some of them are sterile.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Placentation indicates the structure, kind, formation and or arrangement of placentas. The area of the ovary wall in which the ovules are connected in a flower is known as the placenta. Several kinds of placentations found in flowering plants are
Marginal placentation The placenta makes a ridge along through the ventral suture of the ovary, ovules are borne on the ridge to form two rows. Example: Pea
Axile placentation The placenta is axial, and ovules are connected to it in a multilocular ovary. Example: Lemon
Parietal placentation Ovules evolve on the peripheral or on the inner wall of the ovary. It is single-chambered, but because of the development of a false septum, it turns into two-chambered. Example: Mustard
Basal placentation The placenta evolves at the base of the ovary in which a single ovule is connected to it. Example: Marigold
Free central placentation On the middle axis ovules are borne and septa are not present. Example: Primrose
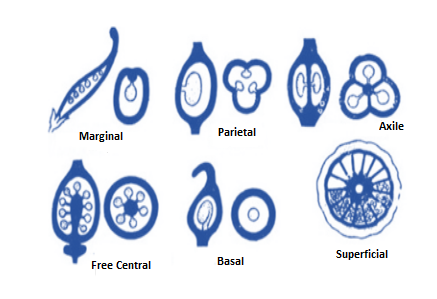
Image:Placentation Types
Note: Placentation is the layout of ovules in the ovary of a plant. The function of placentation is to transmit respiratory gases, nutrients, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in certain cases to eliminate waste from the embryo.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Placentation indicates the structure, kind, formation and or arrangement of placentas. The area of the ovary wall in which the ovules are connected in a flower is known as the placenta. Several kinds of placentations found in flowering plants are
Marginal placentation The placenta makes a ridge along through the ventral suture of the ovary, ovules are borne on the ridge to form two rows. Example: Pea
Axile placentation The placenta is axial, and ovules are connected to it in a multilocular ovary. Example: Lemon
Parietal placentation Ovules evolve on the peripheral or on the inner wall of the ovary. It is single-chambered, but because of the development of a false septum, it turns into two-chambered. Example: Mustard
Basal placentation The placenta evolves at the base of the ovary in which a single ovule is connected to it. Example: Marigold
Free central placentation On the middle axis ovules are borne and septa are not present. Example: Primrose

Image:Placentation Types
Note: Placentation is the layout of ovules in the ovary of a plant. The function of placentation is to transmit respiratory gases, nutrients, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in certain cases to eliminate waste from the embryo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE




