
Describe the ultrastructure of the chloroplast. Add the note on the significance of photosynthesis?
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: Plant cells are eukaryotic cells found in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the realm Plantae which implies they have a film bound core. Plant cells additionally have auxiliary organelles that are not found in the creatures' cells, including the cell divider, vacuoles, plastids, e. g Chloroplast.
Complete answer:
A plant cell has an assortment of layer-bound cell organelles that perform different explicit capacities to keep up the plant cell's ordinary working. Generally, plant cells are much greater than the animal cells, coming in more comparative sizes and they are commonly cubed or rectangular fit as a fiddle. We will discuss the ultrastructure of the chloroplast in detail.
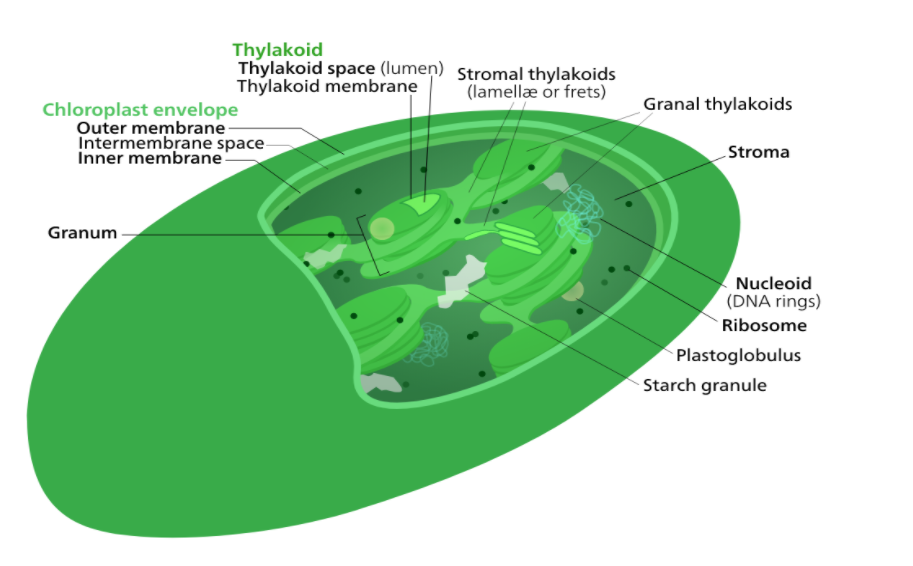
These are organelles found in plant cells and algal cells.
> They consist of two surface layers, i.e., external and inward film, and an internal layer known as the thylakoid layer has two layers.
> The external film shapes the outside covering of the chloroplast while the inward film is underneath the outer layer.
> The films are isolated by narrow membranous space, and inside the layer, there is additionally a space known as the stroma. The stroma houses the chloroplast.
> The third layer, known as the thylakoid layer, is widely collapsed, showing up of a leveled plate known as thylakoids that have enormous quantities of chlorophyll and carotenoids and the electron transport chain as the light-collecting unpredictable, utilized during photosynthesis.
> Thylakoids are heaped on the head of one another in stacks known as grana.
Functions:
> The chloroplast is the site of food union for plant cells, by a component known as photosynthesis.
> Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green color that assimilates light energy from the sun for photosynthesis.
> The photosynthesis cycle changes over water, carbon dioxide, and light energy into supplement use by the plants.
Note:
Photosynthesis is a physiological cycle that fills in power to get food and fuel for all non-photosynthetic living beings in-universe.
Organic (sugars) obtained by photosynthesis are fundamentally used to combine fats, proteins, nucleoproteins, catalysts, nutrients, cellulose, natural acids, and so forth.
Carbohydrates orchestrated during the muted response of photosynthesis become auxiliary pieces of living beings.
All the while, sun based energy is changed over into compound energy by using explicit, crude materials like CO.
Complete answer:
A plant cell has an assortment of layer-bound cell organelles that perform different explicit capacities to keep up the plant cell's ordinary working. Generally, plant cells are much greater than the animal cells, coming in more comparative sizes and they are commonly cubed or rectangular fit as a fiddle. We will discuss the ultrastructure of the chloroplast in detail.

These are organelles found in plant cells and algal cells.
> They consist of two surface layers, i.e., external and inward film, and an internal layer known as the thylakoid layer has two layers.
> The external film shapes the outside covering of the chloroplast while the inward film is underneath the outer layer.
> The films are isolated by narrow membranous space, and inside the layer, there is additionally a space known as the stroma. The stroma houses the chloroplast.
> The third layer, known as the thylakoid layer, is widely collapsed, showing up of a leveled plate known as thylakoids that have enormous quantities of chlorophyll and carotenoids and the electron transport chain as the light-collecting unpredictable, utilized during photosynthesis.
> Thylakoids are heaped on the head of one another in stacks known as grana.
Functions:
> The chloroplast is the site of food union for plant cells, by a component known as photosynthesis.
> Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green color that assimilates light energy from the sun for photosynthesis.
> The photosynthesis cycle changes over water, carbon dioxide, and light energy into supplement use by the plants.
Note:
Photosynthesis is a physiological cycle that fills in power to get food and fuel for all non-photosynthetic living beings in-universe.
Organic (sugars) obtained by photosynthesis are fundamentally used to combine fats, proteins, nucleoproteins, catalysts, nutrients, cellulose, natural acids, and so forth.
Carbohydrates orchestrated during the muted response of photosynthesis become auxiliary pieces of living beings.
All the while, sun based energy is changed over into compound energy by using explicit, crude materials like CO.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




