
Describe the terrestrial telescope based on the following points.
(i) Labeled Ray diagram.
(ii) Derivation of formula for magnifying power, when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Terrestrial telescope is a refracting type telescope used to see erect images of distant earthly objects. In order to answer this question perfectly, students must have knowledge about how to construct ray diagrams.
Complete step by step answer:
The terrestrial telescope is a refracting type telescope used to see erect images of distant earthly objects. It uses an additional convex lens between the objective and eyepiece for obtaining an erect image.
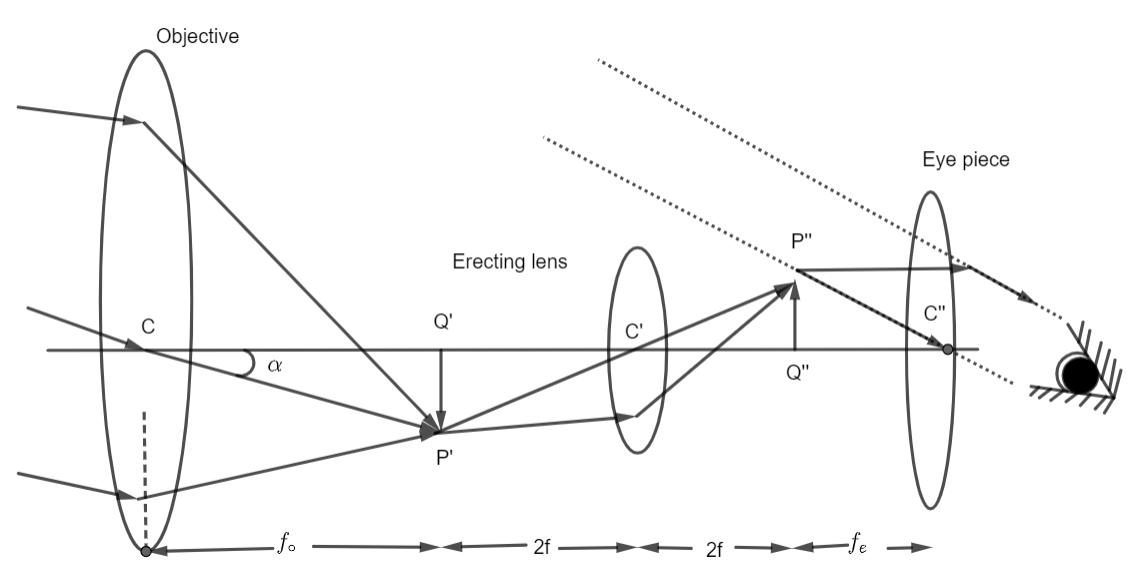
The construction of a terrestrial telescope is quite similar to that of an astronomical telescope. The only difference is the introduction of a third convex lens $\left( {{L_f}} \right)$ known as field lens or erecting lens. This lens is kept in between the objective and erecting lens.
${f_ \circ } + zf$ is the objective and erecting lens.
Where ${f_o}$ is the focal length of the objective and similarly, ${f_u}$the focal length of the erecting lens. The following ray diagram shows a terrestrial telescope:
Derivation for magnifying power, when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision:
As the object is situated far away, so the image formed on the objective is equal to the visual angle formed on the eyepiece.
Because these $\alpha {\text{ and }}\beta $ angles are very small. Therefore, $\tan \alpha \approx \alpha {\text{ and }}\tan \beta \approx \beta $
$\therefore m = \dfrac{\beta }{\alpha } = \dfrac{{\tan \beta }}{{\tan \alpha }} \approx \alpha $
From the above figure, we have:
$\eqalign{
& \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{PQ}}{{OQ}} = \dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{OQ'}} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right) \cr
& {\text{and}}\tan \beta = \dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{Q'O}} \cr
& {\text{Putting values of tan}}\alpha {\text{ and tan}}\beta {\text{ in equation}}\left( 1 \right),{\text{we get:}} \cr
& {\text{m = }}\dfrac{{\dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{Q'O'}}}}{{\dfrac{{ - P'Q'}}{{OQ}}}} \cr
& {\text{or }}m = \dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{Q'O}} \times \dfrac{{OQ}}{{P'}}Q' \cr
& = - \dfrac{{OQ}}{{O'Q'}} \cr
& {\text{but}},OQ = {f_ \circ }{\text{ and }}O'Q' = - {u_e} \cr
& \therefore m = \dfrac{{ - {f_ \circ }}}{{ - {u_e}}} = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{u_e}}}\left[ {{\text{by sign convention}}} \right] \cr} $
When image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision,
$\eqalign{
& {u_e} = {f_e}\left( {1 + \dfrac{D}{{{f_e}}}} \right) \cr
& \therefore m = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{f_e}}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{f_e}}}{D}} \right) \cr} $
The above equation gives a formula for magnifying power, when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
Note: A terrestrial telescope must not be confused with an astronomical telescope. A terrestrial telescope is also used to see distant objects but it produces a non-inverted image. Thus it is only used to observe the objects on the earth’s surface. While the latter is used for distant celestial bodies.
Complete step by step answer:
The terrestrial telescope is a refracting type telescope used to see erect images of distant earthly objects. It uses an additional convex lens between the objective and eyepiece for obtaining an erect image.

The construction of a terrestrial telescope is quite similar to that of an astronomical telescope. The only difference is the introduction of a third convex lens $\left( {{L_f}} \right)$ known as field lens or erecting lens. This lens is kept in between the objective and erecting lens.
${f_ \circ } + zf$ is the objective and erecting lens.
Where ${f_o}$ is the focal length of the objective and similarly, ${f_u}$the focal length of the erecting lens. The following ray diagram shows a terrestrial telescope:
Derivation for magnifying power, when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision:
As the object is situated far away, so the image formed on the objective is equal to the visual angle formed on the eyepiece.
Because these $\alpha {\text{ and }}\beta $ angles are very small. Therefore, $\tan \alpha \approx \alpha {\text{ and }}\tan \beta \approx \beta $
$\therefore m = \dfrac{\beta }{\alpha } = \dfrac{{\tan \beta }}{{\tan \alpha }} \approx \alpha $
From the above figure, we have:
$\eqalign{
& \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{PQ}}{{OQ}} = \dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{OQ'}} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right) \cr
& {\text{and}}\tan \beta = \dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{Q'O}} \cr
& {\text{Putting values of tan}}\alpha {\text{ and tan}}\beta {\text{ in equation}}\left( 1 \right),{\text{we get:}} \cr
& {\text{m = }}\dfrac{{\dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{Q'O'}}}}{{\dfrac{{ - P'Q'}}{{OQ}}}} \cr
& {\text{or }}m = \dfrac{{P'Q'}}{{Q'O}} \times \dfrac{{OQ}}{{P'}}Q' \cr
& = - \dfrac{{OQ}}{{O'Q'}} \cr
& {\text{but}},OQ = {f_ \circ }{\text{ and }}O'Q' = - {u_e} \cr
& \therefore m = \dfrac{{ - {f_ \circ }}}{{ - {u_e}}} = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{u_e}}}\left[ {{\text{by sign convention}}} \right] \cr} $
When image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision,
$\eqalign{
& {u_e} = {f_e}\left( {1 + \dfrac{D}{{{f_e}}}} \right) \cr
& \therefore m = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{f_e}}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{f_e}}}{D}} \right) \cr} $
The above equation gives a formula for magnifying power, when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
Note: A terrestrial telescope must not be confused with an astronomical telescope. A terrestrial telescope is also used to see distant objects but it produces a non-inverted image. Thus it is only used to observe the objects on the earth’s surface. While the latter is used for distant celestial bodies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




