
Describe the Mendel's Law of Segregation with the help of a suitable diagram.
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: During the mid-nineteenth century, the mystery behind genetics was cracked by a monk named Gregor Mendel with the help of his laws which are popularly known as Mendel law of inheritance in which three laws are included. Mendel law of segregation was one of them which is also referred to as the Law of purity of gametes. The basis of this law was formed by the monohybrid cross.
Complete answer:
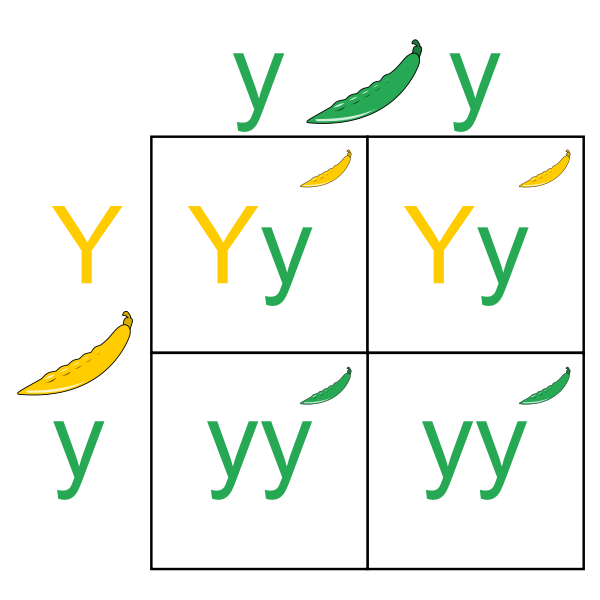
Law of segregation: This law states that 2 members of the allelic pair without being contaminated, stay together when a pair of genes are brought together in a hybrid, and the two separate from each other when gametes are formed from the hybrid, and only 1 enters each gamete as seen in monohybrid and dihybrid cross. This is the reason that the law of segregation is also described as the law of purity of gametes. Mendel made a cross between two pure plants having contrasting characters for a single plant called monohybrid cross. Pure tall and dwarf plants were crossed by Mendel. All the plants are tall hybrids that belonged to the F1 generation which were self-pollinated. The plants were both tall and dwarf of the F2 generation in approximate 3:1 ratio phenotypically and 1:2:1 genotypically.
Note:
The student might get confused about where to apply the law of segregation. When a randomly selected allele of a trait is passed by the diploid parent organism to its offspring to ensure that the offspring get one allele from each of the parents. The law is applied to determine the possibilities of a specific genotype emerging from a genetic cross.
Complete answer:
Law of segregation: This law states that 2 members of the allelic pair without being contaminated, stay together when a pair of genes are brought together in a hybrid, and the two separate from each other when gametes are formed from the hybrid, and only 1 enters each gamete as seen in monohybrid and dihybrid cross. This is the reason that the law of segregation is also described as the law of purity of gametes. Mendel made a cross between two pure plants having contrasting characters for a single plant called monohybrid cross. Pure tall and dwarf plants were crossed by Mendel. All the plants are tall hybrids that belonged to the F1 generation which were self-pollinated. The plants were both tall and dwarf of the F2 generation in approximate 3:1 ratio phenotypically and 1:2:1 genotypically.

Note:
The student might get confused about where to apply the law of segregation. When a randomly selected allele of a trait is passed by the diploid parent organism to its offspring to ensure that the offspring get one allele from each of the parents. The law is applied to determine the possibilities of a specific genotype emerging from a genetic cross.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




