
Describe the male reproductive system of a man. Draw a labeled diagram of it.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: Sperm (male reproductive cell) is formed, sustained and transmitted by this mechanism and conservative fluid (semen) also produces and secretes male sex hormones.
Complete answer:
A biological network composed of organs connected to sexual reproduction is the reproductive mechanism of humans. Each of them is the male reproductive system that creates, preserves and passes sperm (male reproductive cells) and also produces and secretes male sex hormones with conservative fluid (semen). It primarily has three components:
(1) Penis: Three cylindrical spaces of erectile tissue are involved. The larger two, corpora cavernosa, lay side by side and the urethra is covered by the third sinus or corpus spongiosum. When rooms are packed with blood, the penis becomes stiff.
(2) Scrotum: The scrotum is a free, sac-like pack of skin hanging beneath the penis. Along with multiple veins and nerves, this part of the male reproductive system houses the testicles. The scrotum acts as a device of temperature control for the testicles. In order to achieve the development of sperm, it is important that the temperature of the testicles should be cooler to some extent than the amount of internal heat.
(3) Testes or Testicles: In forms that are present inside the scrotum, testicles are circular. A structure known as the spermatic cord secures these at both ends. Men have two exams. Testes have the primary function of generating testosterone (the main male sex hormone) and producing sperm. Seminiferous tubules, which are coiled tube masses, are found within the testicles. These tubes have the purpose of generating sperm cells.
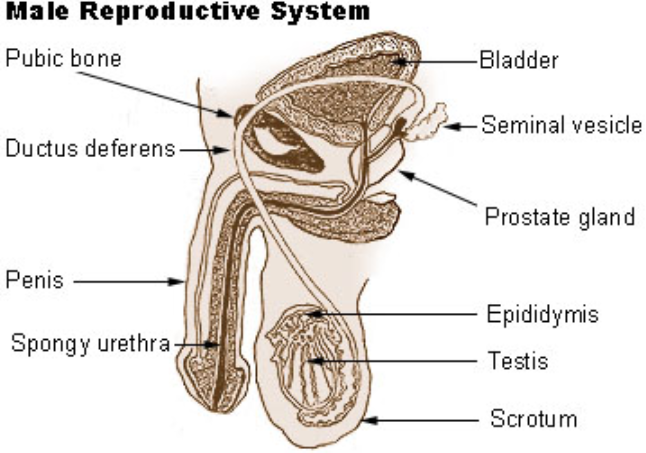
Note: There are a penis, scrotum and testicles as the parts of male reproductive system. Ejaculatory ducts, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral gland are the accessory glands.
Complete answer:
A biological network composed of organs connected to sexual reproduction is the reproductive mechanism of humans. Each of them is the male reproductive system that creates, preserves and passes sperm (male reproductive cells) and also produces and secretes male sex hormones with conservative fluid (semen). It primarily has three components:
(1) Penis: Three cylindrical spaces of erectile tissue are involved. The larger two, corpora cavernosa, lay side by side and the urethra is covered by the third sinus or corpus spongiosum. When rooms are packed with blood, the penis becomes stiff.
(2) Scrotum: The scrotum is a free, sac-like pack of skin hanging beneath the penis. Along with multiple veins and nerves, this part of the male reproductive system houses the testicles. The scrotum acts as a device of temperature control for the testicles. In order to achieve the development of sperm, it is important that the temperature of the testicles should be cooler to some extent than the amount of internal heat.
(3) Testes or Testicles: In forms that are present inside the scrotum, testicles are circular. A structure known as the spermatic cord secures these at both ends. Men have two exams. Testes have the primary function of generating testosterone (the main male sex hormone) and producing sperm. Seminiferous tubules, which are coiled tube masses, are found within the testicles. These tubes have the purpose of generating sperm cells.

Note: There are a penis, scrotum and testicles as the parts of male reproductive system. Ejaculatory ducts, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral gland are the accessory glands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




