
Describe the female reproductive system in human beings
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The female reproductive system comprises of internal and external sex organs whose function is to reproduce new offspring. In humans, the female reproductive system is not mature at birth and develops at puberty so that it can produce gametes.
Step by step answer:The function of the external female reproductive structures called the genitals. The main external structures of the female reproductive system are described below:-
1.Labia majora: The labia majora protects the other external reproductive organs. The labia majora contain sweat and also contain oil-secreting glands. At puberty, the labia majora are covered with hair.
2. Labia minora: The labia minora is very small or up to 2 inches. They lie inside the labia majora and surround the openings to the vagina and urethra.
3. Bartholin's glands: These are located near the vaginal opening and produce a fluid secretion called mucus.
4. Clitoris: The two labia minora meet at the clitoris which is a small, sensitive protrusion. The clitoris is usually covered by a fold of skin which is called the prepuce.
The internal reproductive organs in the female include:
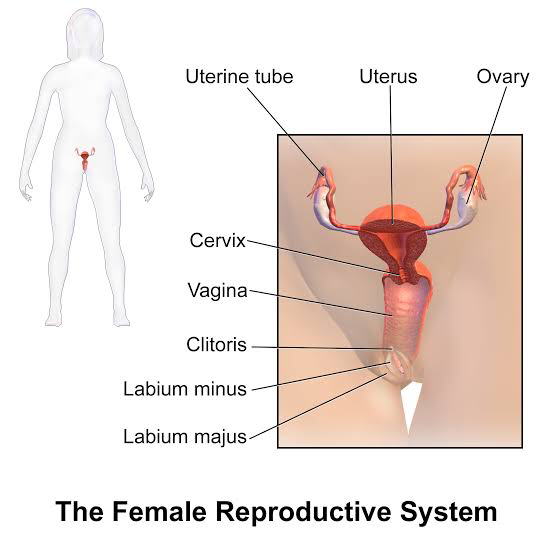
1. Vagina: The vagina is a canal that joins the cervix to the outside of the body. It is called the birth canal.
2. Uterus: The uterus is hollow and is a pear-shaped organ that behaves like a home to a fetus.
3. Ovaries: The ovaries are small and oval-shaped glands, located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries produce eggs and they also produce hormones.
4.Fallopian tube: Narrow tubes attached to the uterus and function as a tunnel for the ova to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. The fertilization of an egg by a sperm occurs in the fallopian tubes.
Note: Its functions are to produce female gametes called eggs, which secrets female sex hormones like estrogen providing a site for fertilization, giving birth to a baby, and breastfeeding the baby after birth.
Step by step answer:The function of the external female reproductive structures called the genitals. The main external structures of the female reproductive system are described below:-
1.Labia majora: The labia majora protects the other external reproductive organs. The labia majora contain sweat and also contain oil-secreting glands. At puberty, the labia majora are covered with hair.
2. Labia minora: The labia minora is very small or up to 2 inches. They lie inside the labia majora and surround the openings to the vagina and urethra.
3. Bartholin's glands: These are located near the vaginal opening and produce a fluid secretion called mucus.
4. Clitoris: The two labia minora meet at the clitoris which is a small, sensitive protrusion. The clitoris is usually covered by a fold of skin which is called the prepuce.
The internal reproductive organs in the female include:

1. Vagina: The vagina is a canal that joins the cervix to the outside of the body. It is called the birth canal.
2. Uterus: The uterus is hollow and is a pear-shaped organ that behaves like a home to a fetus.
3. Ovaries: The ovaries are small and oval-shaped glands, located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries produce eggs and they also produce hormones.
4.Fallopian tube: Narrow tubes attached to the uterus and function as a tunnel for the ova to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. The fertilization of an egg by a sperm occurs in the fallopian tubes.
Note: Its functions are to produce female gametes called eggs, which secrets female sex hormones like estrogen providing a site for fertilization, giving birth to a baby, and breastfeeding the baby after birth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




