
Describe the compound microscope based on the following headings: 1) Labelled ray diagram of image formation. 2) Magnifying power when final image is formed at least distance of distinct vision
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: In this question we have been asked to draw a labelled ray diagram of image formation of a compound microscope. We have also been asked to calculate the magnifying power when the final image is formed at least distance of distinct vision. Therefore, we shall first draw a labelled ray diagram. We shall use the magnification formula and the lens formula to calculate the magnifying power.
Formula Used: \[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Complete answer:
The compound microscope consists of two lenses as shown in the figure below. The first lens forms an inverted image as shown. The final image is observed through the ocular lens also known as eye piece. The following ray diagram shows the formation of an image by a compound microscope.
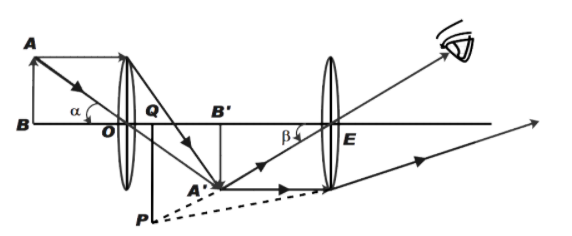
The magnifying power of a microscope is the ratio of angle subtended by image to the angle subtended by image placed at least distance of distinct vision.
Therefore, from above diagram,
\[m=\dfrac{\beta }{\alpha }\] …………….. (1)
\[\therefore \alpha =\dfrac{AB}{D}\] ……………… (2)
Where, D is the least distance of distinct vision i.e. distance between point O and Point B
Now, angle made by image PQ can be given by,
\[\beta =\dfrac{PQ}{EQ}=\dfrac{A'B'}{EB'}\]
Let, \[{{u}_{e}}\] be the distance between image and eyes piece
Therefore,
\[\beta =\dfrac{A'B'}{{{u}_{e}}}\] ……………. (3)
Now, from (1), (2) and (3)
We get,
\[m=\dfrac{A'B'}{AB}\times \dfrac{D}{{{u}_{e}}}\]
From the diagram above we can say that,
\[\dfrac{A'B'}{AB}=\dfrac{OB'}{OB}\]
Therefore,
\[m=\dfrac{OB'}{OB}\times \dfrac{D}{{{u}_{e}}}\]
OB and OB’ is the distance of object and image from point O
Therefore,
\[m=\dfrac{{{v}_{o}}}{-{{u}_{o}}}\times \left( \dfrac{-D}{-{{u}_{e}}} \right)\] …………………. (4)
On solving,
\[m=\dfrac{{{v}_{o}}D}{{{u}_{o}}{{u}_{e}}}\]
Now, from lens formula we know,
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
The lens formula for given microscope can be written by,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{-{{v}_{e}}}-\dfrac{1}{-{{u}_{e}}}\]
We know that \[{{v}_{e}}\] is the distance D
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{-D}+\dfrac{1}{{{u}_{e}}}\]
Rearranging the terms
We get,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{u}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{e}}}+\dfrac{1}{D}\]
On solving,
\[\dfrac{D}{{{u}_{e}}}=\dfrac{D}{{{f}_{e}}}+1\] …………….. (5)
Now, from (4) and (5)
We get,
\[m=\dfrac{-{{v}_{o}}}{{{u}_{o}}}\left( 1+\dfrac{D}{{{f}_{e}}} \right)\]
Therefore, the magnification power of compound microscope is given by, \[m=\dfrac{-{{v}_{o}}}{{{u}_{o}}}\left( 1+\dfrac{D}{{{f}_{e}}} \right)\].
Note:
The optical instrument that uses two lenses to obtain higher magnification of an image is known as compound microscope. A compound microscope provides two dimensional images. Magnification is the property by which the image size is enlarged. The compound microscopes are therefore used to view specimens as small as blood cells. The name compound microscope comes from the lens system of the microscope, that consists of a primary objective lens compounded with eyepiece or ocular lens.
Formula Used: \[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Complete answer:
The compound microscope consists of two lenses as shown in the figure below. The first lens forms an inverted image as shown. The final image is observed through the ocular lens also known as eye piece. The following ray diagram shows the formation of an image by a compound microscope.

The magnifying power of a microscope is the ratio of angle subtended by image to the angle subtended by image placed at least distance of distinct vision.
Therefore, from above diagram,
\[m=\dfrac{\beta }{\alpha }\] …………….. (1)
\[\therefore \alpha =\dfrac{AB}{D}\] ……………… (2)
Where, D is the least distance of distinct vision i.e. distance between point O and Point B
Now, angle made by image PQ can be given by,
\[\beta =\dfrac{PQ}{EQ}=\dfrac{A'B'}{EB'}\]
Let, \[{{u}_{e}}\] be the distance between image and eyes piece
Therefore,
\[\beta =\dfrac{A'B'}{{{u}_{e}}}\] ……………. (3)
Now, from (1), (2) and (3)
We get,
\[m=\dfrac{A'B'}{AB}\times \dfrac{D}{{{u}_{e}}}\]
From the diagram above we can say that,
\[\dfrac{A'B'}{AB}=\dfrac{OB'}{OB}\]
Therefore,
\[m=\dfrac{OB'}{OB}\times \dfrac{D}{{{u}_{e}}}\]
OB and OB’ is the distance of object and image from point O
Therefore,
\[m=\dfrac{{{v}_{o}}}{-{{u}_{o}}}\times \left( \dfrac{-D}{-{{u}_{e}}} \right)\] …………………. (4)
On solving,
\[m=\dfrac{{{v}_{o}}D}{{{u}_{o}}{{u}_{e}}}\]
Now, from lens formula we know,
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
The lens formula for given microscope can be written by,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{-{{v}_{e}}}-\dfrac{1}{-{{u}_{e}}}\]
We know that \[{{v}_{e}}\] is the distance D
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{-D}+\dfrac{1}{{{u}_{e}}}\]
Rearranging the terms
We get,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{u}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{e}}}+\dfrac{1}{D}\]
On solving,
\[\dfrac{D}{{{u}_{e}}}=\dfrac{D}{{{f}_{e}}}+1\] …………….. (5)
Now, from (4) and (5)
We get,
\[m=\dfrac{-{{v}_{o}}}{{{u}_{o}}}\left( 1+\dfrac{D}{{{f}_{e}}} \right)\]
Therefore, the magnification power of compound microscope is given by, \[m=\dfrac{-{{v}_{o}}}{{{u}_{o}}}\left( 1+\dfrac{D}{{{f}_{e}}} \right)\].
Note:
The optical instrument that uses two lenses to obtain higher magnification of an image is known as compound microscope. A compound microscope provides two dimensional images. Magnification is the property by which the image size is enlarged. The compound microscopes are therefore used to view specimens as small as blood cells. The name compound microscope comes from the lens system of the microscope, that consists of a primary objective lens compounded with eyepiece or ocular lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




