
Describe pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint:Pulmonary and systemic circulation are both parts of the circulatory system or the cardiovascular system. The difference is that the pulmonary system involves heart and lungs while the systemic circulation involves lungs and all other body systems.
Complete answer:
The cardiovascular system is an organ system present in animals. It permits circulation of blood which carries out transport of nutrients, gases, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body. Its function is to provide nourishment to the cells in the body and helps in fighting diseases, it also stabilizes temperature and pH, by maintaining homeostasis. The lymphatic system is a major part of the circulatory system which circulates lymph. The passage of lymph is much longer than that of blood. The cardiovascular system includes the blood, heart, and blood vessels. On an average, an adult human contains roughly 4.7 to 5.7 litres of blood, which forms approximately around 7% of their total body weight. Plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are components of the blood.
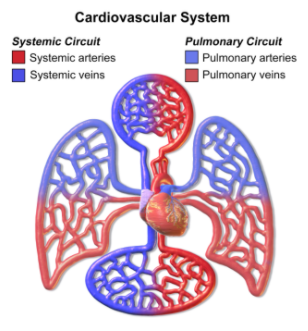
The blood circulatory system has two components, a pulmonary circulation which forms a loop between the lungs where blood is oxygenated and heart and a systemic circulation which forms a loop initiating from heart, moving through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. The systemic circulation can also be divided into two parts, a macrocirculation and a microcirculation.
Note:Systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation may sound different but are a part of the same system. Do not get confused by their names.The blood circulatory system has two components, a pulmonary circulation which forms a loop between the lungs where blood is oxygenated and heart and a systemic circulation which forms a loop initiating from heart, moving through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood.
Complete answer:
The cardiovascular system is an organ system present in animals. It permits circulation of blood which carries out transport of nutrients, gases, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body. Its function is to provide nourishment to the cells in the body and helps in fighting diseases, it also stabilizes temperature and pH, by maintaining homeostasis. The lymphatic system is a major part of the circulatory system which circulates lymph. The passage of lymph is much longer than that of blood. The cardiovascular system includes the blood, heart, and blood vessels. On an average, an adult human contains roughly 4.7 to 5.7 litres of blood, which forms approximately around 7% of their total body weight. Plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are components of the blood.

The blood circulatory system has two components, a pulmonary circulation which forms a loop between the lungs where blood is oxygenated and heart and a systemic circulation which forms a loop initiating from heart, moving through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. The systemic circulation can also be divided into two parts, a macrocirculation and a microcirculation.
| S. no | Pulmonary circulation | Systemic circulation |
| 1 | Carry deoxygenated blood from heart to the lungs. | Carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. |
| 2 | Carry oxygenated blood towards the heart. | Carry deoxygenated blood towards the heart. |
| 3 | Vessels involved are pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein. | Vessels involved are inferior and superior vena cava, aorta, and numerous small blood vessels. |
Note:Systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation may sound different but are a part of the same system. Do not get confused by their names.The blood circulatory system has two components, a pulmonary circulation which forms a loop between the lungs where blood is oxygenated and heart and a systemic circulation which forms a loop initiating from heart, moving through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




