
Describe Haber process for the manufacture of ammonia?
Answer
523.9k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the problem we will first understand what is the Haber process for the manufacture of aluminium by the help of simple processes and steps involved in the manufacture process. We will understand the reactions involved with the help of chemical reactions. Also we will understand the significance of Haber process and the uses of Haber process.
Complete step by step solution: The Haber process is one of the most important processes in the manufacture of ammonia.
In this Haber process ammonia is formed by the use of atmospheric nitrogen on reaction with hydrogen. A metal is used as a catalyst in this process while maintaining high temperature and pressure.
The raw materials involved in the Haber process are:
Nitrogen is supplied from the air.
Water and natural supplies the required hydrogen for the process and the energy required for the heat as reactants.
Iron is used as the catalyst in this process which does not get used up.
The chemical reaction involved in Haber process is as follows:
${N_2}\left( g \right) + 3{H_2}\left( g \right) \to 2N{H_3}\left( g \right)$
Nitrogen is obtained in the reaction by removing nitrogen from the soil by liquefaction, and hydrogen is obtained by steam reforming from natural gas.
$C{H_4}\left( g \right) + {H_2}O \to {H_2}\left( g \right) + CO\left( g \right)$
Let us understand the Haber process by the help of the diagram.
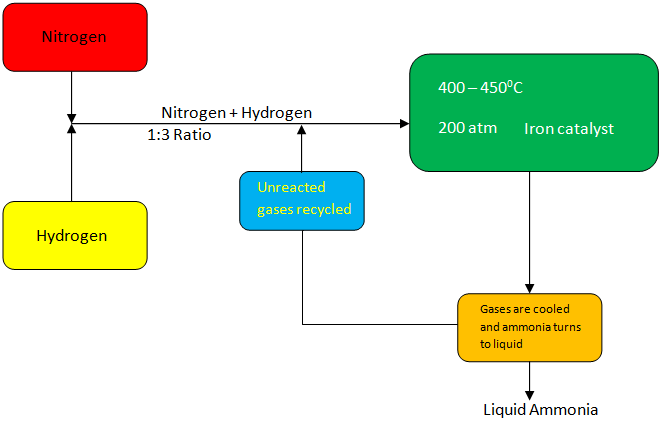
In the Haber method, as seen in the diagram, we take nitrogen gas from the air and mix it with a hydrogen atom from natural gas in the ratio 1:3 by volume.
Gasses are passed through four catalyst fields, with each pass refrigerated. It is achieved to maintain stable equilibrium.
Though different oxidation rates are observed in-pass where unreacted gases are recycled.
The iron catalyst is usually used in the process, and the whole operation is done by maintaining a temperature of about ${400^0}C - {450^0}C$ and a pressure of 150 – 200 atm.
The process also includes phases such as shift transfer, elimination of carbon dioxide, steam change and methanation.
The ammonia gas is cooled down at the final step of the cycle to create a liquid solution and is then extracted and deposited in storage containers.
There are different uses of ammonia in our day to day life so the Haber process is very important in production of ammonia.
Note: In order to solve such problems students must remember the reactions involved in such processes and also should remember the diagram for easy understanding and remembering of the process. Scientists are also trying to develop a new process and also trying to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases in the production of ammonia. The most important thing in this process is that nitrogen is taken from the environment which reduces the cost of production.
Complete step by step solution: The Haber process is one of the most important processes in the manufacture of ammonia.
In this Haber process ammonia is formed by the use of atmospheric nitrogen on reaction with hydrogen. A metal is used as a catalyst in this process while maintaining high temperature and pressure.
The raw materials involved in the Haber process are:
Nitrogen is supplied from the air.
Water and natural supplies the required hydrogen for the process and the energy required for the heat as reactants.
Iron is used as the catalyst in this process which does not get used up.
The chemical reaction involved in Haber process is as follows:
${N_2}\left( g \right) + 3{H_2}\left( g \right) \to 2N{H_3}\left( g \right)$
Nitrogen is obtained in the reaction by removing nitrogen from the soil by liquefaction, and hydrogen is obtained by steam reforming from natural gas.
$C{H_4}\left( g \right) + {H_2}O \to {H_2}\left( g \right) + CO\left( g \right)$
Let us understand the Haber process by the help of the diagram.

In the Haber method, as seen in the diagram, we take nitrogen gas from the air and mix it with a hydrogen atom from natural gas in the ratio 1:3 by volume.
Gasses are passed through four catalyst fields, with each pass refrigerated. It is achieved to maintain stable equilibrium.
Though different oxidation rates are observed in-pass where unreacted gases are recycled.
The iron catalyst is usually used in the process, and the whole operation is done by maintaining a temperature of about ${400^0}C - {450^0}C$ and a pressure of 150 – 200 atm.
The process also includes phases such as shift transfer, elimination of carbon dioxide, steam change and methanation.
The ammonia gas is cooled down at the final step of the cycle to create a liquid solution and is then extracted and deposited in storage containers.
There are different uses of ammonia in our day to day life so the Haber process is very important in production of ammonia.
Note: In order to solve such problems students must remember the reactions involved in such processes and also should remember the diagram for easy understanding and remembering of the process. Scientists are also trying to develop a new process and also trying to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases in the production of ammonia. The most important thing in this process is that nitrogen is taken from the environment which reduces the cost of production.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




