
Derive the formula $ \omega = \dfrac{{D\lambda }}{d} $ for fringe width in Young's double-slit experiment. The symbols used have their usual meanings.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint
In Young's double-slit experiment, we have two slits separated by a distance. Two coherent sources will produce an interference pattern. This will create alternate bright and dark fringes. The separation between the two consecutive bright fringes is called the fringe width.
Complete step by step answer
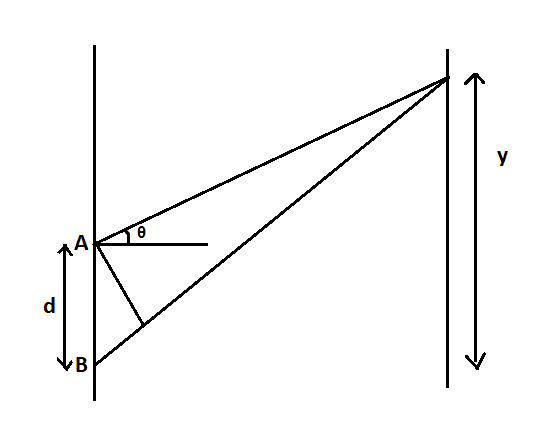
As shown in the figure, there will be two rays of light from the two slits A and B. The rays will have a path difference. The path difference can be written as,
$\Rightarrow d\sin \theta = n\lambda $ ………………………………………………..equation
Where $ \theta $ is the angle between the incident ray and the normal. $ d $ is the distance between the slits, $ n $ is an integer that stands for the order of the fringes, and $ \lambda $ is the wavelength of the light.
We know that, for small angles $ \sin \theta \approx \theta $
Then we can write equation as,
$\Rightarrow d\theta = n\lambda $
From this we get $ \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{d} $
Let the screen be placed at a distance $ D $ and let $ y $ be the position of maxima
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{D} = \tan \theta $
For small angle $ \tan \theta \approx \theta $
Hence we can write the above equation as
$\Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{y}{D} $
From this equation we get,
$\Rightarrow y = D\theta $
Substituting the expression for $ \theta $ from equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} $
The fringe width can be written as the difference between two maxima,
For an $ {n^{th}} $ order fringe, $ {Y_n} = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} $
And the $ {\left( {n + 1} \right)^{th}} $ order fringe, $ {Y_{n + 1}} = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda D}}{d} $
Let $ \omega $ be the separation between two consecutive bright or dark fringe then
The fringe width can be written as,
$\Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{{\left( {n + 1} \right)\lambda D}}{d} - \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}\left( {n + 1 - n} \right) $
Therefore we get,
$\Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{{D\lambda }}{d} $
Note
The width of the fringes is inversely proportional to the separation between the slits, i.e. when the separation between the slits $ \left( d \right) $ increases, the fringe width will decrease. The separation between the slits and the screen is directly proportional to the fringe width i.e. when the separation between the slits and the screen $ \left( D \right) $ increases the fringe width increases.
In Young's double-slit experiment, we have two slits separated by a distance. Two coherent sources will produce an interference pattern. This will create alternate bright and dark fringes. The separation between the two consecutive bright fringes is called the fringe width.
Complete step by step answer

As shown in the figure, there will be two rays of light from the two slits A and B. The rays will have a path difference. The path difference can be written as,
$\Rightarrow d\sin \theta = n\lambda $ ………………………………………………..equation
Where $ \theta $ is the angle between the incident ray and the normal. $ d $ is the distance between the slits, $ n $ is an integer that stands for the order of the fringes, and $ \lambda $ is the wavelength of the light.
We know that, for small angles $ \sin \theta \approx \theta $
Then we can write equation as,
$\Rightarrow d\theta = n\lambda $
From this we get $ \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{d} $
Let the screen be placed at a distance $ D $ and let $ y $ be the position of maxima
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{D} = \tan \theta $
For small angle $ \tan \theta \approx \theta $
Hence we can write the above equation as
$\Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{y}{D} $
From this equation we get,
$\Rightarrow y = D\theta $
Substituting the expression for $ \theta $ from equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} $
The fringe width can be written as the difference between two maxima,
For an $ {n^{th}} $ order fringe, $ {Y_n} = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} $
And the $ {\left( {n + 1} \right)^{th}} $ order fringe, $ {Y_{n + 1}} = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda D}}{d} $
Let $ \omega $ be the separation between two consecutive bright or dark fringe then
The fringe width can be written as,
$\Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{{\left( {n + 1} \right)\lambda D}}{d} - \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}\left( {n + 1 - n} \right) $
Therefore we get,
$\Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{{D\lambda }}{d} $
Note
The width of the fringes is inversely proportional to the separation between the slits, i.e. when the separation between the slits $ \left( d \right) $ increases, the fringe width will decrease. The separation between the slits and the screen is directly proportional to the fringe width i.e. when the separation between the slits and the screen $ \left( D \right) $ increases the fringe width increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




