
Derive the expression for the electric potential at any point along the axial line of an electric dipole?

Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: An electric potential is defined as the amount of work required to move a unit of electric charge from a reference to a specific point in an electric field without producing acceleration. The electric potential at a given point for a group of charges will be equal to the algebraic sum of the potentials due to individual charges. An electric dipole is an arrangement of two equal and opposite charges that are separated by a finite distance. Its units are coulomb-meter.
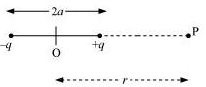
Let P be the axial point at a distance r from the center of the dipole. The Electric potential at point P is given as
$V$ = $V_1 + V_2$
Let $V_1$ and $V_2$ are the potentials at point P due to the charges $+q$ and $-q$ respectively.
$\therefore $ Then the Electric Potential, V $ = $ \[\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {(\dfrac{q}{{r - 2a}}) + (\dfrac{{ - q}}{{r + 2a}})} \right)\] $(\because V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\dfrac{q}{r})$
Here $\varepsilon _0$ is the permittivity of the vacuum, q is the charge and r is the distance
$ \Rightarrow $V $ = $ $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {\dfrac{{4aq}}{{({r^2} - 4{a^2})}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow $V $ = $ \[\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {\dfrac{{2P}}{{({r^2} - 4{a^2})}}} \right)\] $(\because qa = P/2)$
$\therefore $ The expression for the electric potential is V $ = $ $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {\dfrac{{2P}}{{{r^2} - 4{a^2}}}} \right)$
Note: 1) The electric potential for a system of point charges will be equal to the sum of the point charges of the individual potentials.
2) The electric potential is a scalar quantity and has no direction. It is also called the electric field potential or electrostatic potential or potential drop.
3) Electric potential can also be defined as potential energy per unit charge.
4) The potential at an infinite distance is often taken to be zero.
5) Dipoles are mostly found in the molecular structures which are caused by the non-uniform charge distribution of protons and electrons.
Let P be the axial point at a distance r from the center of the dipole. The Electric potential at point P is given as
$V$ = $V_1 + V_2$
Let $V_1$ and $V_2$ are the potentials at point P due to the charges $+q$ and $-q$ respectively.
$\therefore $ Then the Electric Potential, V $ = $ \[\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {(\dfrac{q}{{r - 2a}}) + (\dfrac{{ - q}}{{r + 2a}})} \right)\] $(\because V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\dfrac{q}{r})$
Here $\varepsilon _0$ is the permittivity of the vacuum, q is the charge and r is the distance
$ \Rightarrow $V $ = $ $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {\dfrac{{4aq}}{{({r^2} - 4{a^2})}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow $V $ = $ \[\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {\dfrac{{2P}}{{({r^2} - 4{a^2})}}} \right)\] $(\because qa = P/2)$
$\therefore $ The expression for the electric potential is V $ = $ $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon o}}\left( {\dfrac{{2P}}{{{r^2} - 4{a^2}}}} \right)$
Note: 1) The electric potential for a system of point charges will be equal to the sum of the point charges of the individual potentials.
2) The electric potential is a scalar quantity and has no direction. It is also called the electric field potential or electrostatic potential or potential drop.
3) Electric potential can also be defined as potential energy per unit charge.
4) The potential at an infinite distance is often taken to be zero.
5) Dipoles are mostly found in the molecular structures which are caused by the non-uniform charge distribution of protons and electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




