
Derive lens formula\[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint – Start by describing how a convex lens interacts with different incident rays and use this to draw a diagram as shown in the solution. Then use simple geometrical calculations to derive the lens formula.
Complete step by step answer:
Before deriving the lens formula, we have to know two properties of a convex lens:
(i)An incident ray perpendicular to the principal axis, after exiting the lens, will pass through the focus.
(ii)An incident light ray that passes through the optical center of the lens, will pass through without undergoing any refraction.
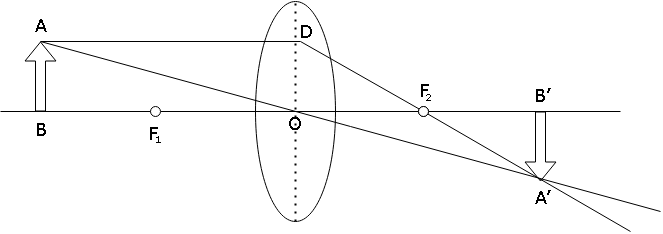
Using both of these conditions, we construct the following diagram and use it to derive the lens formula.The object is placed at a distance $u$from the optical center, $f$is the focal length of the lens and\[v\] is the distance of image formed from the optical center.
By Cartesian sign convention, we know:
Distance of object$(OB) = - u$
Distance of image$(OB') = + v$
Focal Length$(O{F_1} = O{F_2}) = + f$
Now,$\because \angle ABO = \angle A'B'O = 90^\circ $
And $\because \angle AOB = \angle A'OB' = 90^\circ $(Vertically Opposite Angles)
$\therefore \Delta ABO \sim \Delta A'B'O$
$\therefore \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{OB'}}$(Equation 1)
$\therefore \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{O{F_2}}}{{{F_2}B'}}$($becauseOD = AB,$ Opposite sides of $\square ABOD$ are equal)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{O{F_2}}}{{OB' - O{F_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{f}{{v - f}}$(Equation 2)
Substituting, the value of$\dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}}$ in equation 1 with Cartesian sign convention, we get
$ - \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{v}{{v - f}}$
$ \Rightarrow - u(v - f) = vf$
$ \Rightarrow - uv + uf = vf$
Dividing both sides by$uvf$,
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{{uv}}{{uvf}} + \dfrac{{uf}}{{uvf}} = \dfrac{{vf}}{{uvf}}$
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{u}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
This equation is known as the ‘lens formula’.
Lens formula is to obviously among other things make lenses. From spectacles to the contacts you wear, everything is designed keeping the lens formula in mind
Note - The lens formula can also be easily derived by using concave lens instead of convex lens. The process of making the diagram and using geometrical calculations to reach the solution. The only difference is that the image formed will be virtual instead of real that does not change anything.
Complete step by step answer:
Before deriving the lens formula, we have to know two properties of a convex lens:
(i)An incident ray perpendicular to the principal axis, after exiting the lens, will pass through the focus.
(ii)An incident light ray that passes through the optical center of the lens, will pass through without undergoing any refraction.

Using both of these conditions, we construct the following diagram and use it to derive the lens formula.The object is placed at a distance $u$from the optical center, $f$is the focal length of the lens and\[v\] is the distance of image formed from the optical center.
By Cartesian sign convention, we know:
Distance of object$(OB) = - u$
Distance of image$(OB') = + v$
Focal Length$(O{F_1} = O{F_2}) = + f$
Now,$\because \angle ABO = \angle A'B'O = 90^\circ $
And $\because \angle AOB = \angle A'OB' = 90^\circ $(Vertically Opposite Angles)
$\therefore \Delta ABO \sim \Delta A'B'O$
$\therefore \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{OB'}}$(Equation 1)
$\therefore \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{O{F_2}}}{{{F_2}B'}}$($becauseOD = AB,$ Opposite sides of $\square ABOD$ are equal)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{O{F_2}}}{{OB' - O{F_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{f}{{v - f}}$(Equation 2)
Substituting, the value of$\dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}}$ in equation 1 with Cartesian sign convention, we get
$ - \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{v}{{v - f}}$
$ \Rightarrow - u(v - f) = vf$
$ \Rightarrow - uv + uf = vf$
Dividing both sides by$uvf$,
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{{uv}}{{uvf}} + \dfrac{{uf}}{{uvf}} = \dfrac{{vf}}{{uvf}}$
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{u}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
This equation is known as the ‘lens formula’.
Lens formula is to obviously among other things make lenses. From spectacles to the contacts you wear, everything is designed keeping the lens formula in mind
Note - The lens formula can also be easily derived by using concave lens instead of convex lens. The process of making the diagram and using geometrical calculations to reach the solution. The only difference is that the image formed will be virtual instead of real that does not change anything.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




