
Derive equation of torque acting on rectangular current carrying coil kept in uniform magnetic field.
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: In this question we have been asked to derive the equation for torque for a rectangular current carrying coil placed in a uniform magnetic field. To solve this question, we shall first find the forces acting on each arm. We know that torque is given as the product of force and radius. Therefore, we will be using this to solve the given question.
Formula used:
\[\tau =rF\sin \theta \]
Complete answer:
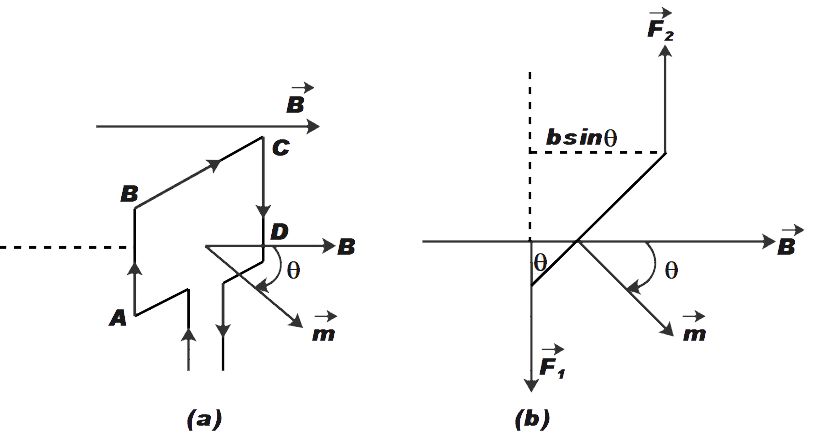
Let us consider a rectangular loop ABCD as shown in the figure (a) above. Let the dimensions of the loop be l and b. There is a steady current in the loop. This loop is placed in the uniform magnetic field as shown.
We know that,
The force on arm BC and AD be \[{{F}_{AB}}\] and \[{{F}_{AD}}\] respectively. These forces are equal and opposite and act along the axis of the coil. Therefore, these forces will cancel each other out.
Similarly,
The forces \[{{F}_{AB}}\]and \[{{F}_{CD}}\]on arm AB and CD are also equal and opposite. Since these forces are not collinear, they act as a couple.
Therefore, the magnitude of torque can be given as,
\[\tau ={{F}_{AB}}+\dfrac{b}{2}\sin \theta +{{F}_{CD}}\dfrac{b}{2}\sin \theta \]
Now, we know that
\[\left| {{F}_{AB}} \right|=\left| {{F}_{CD}} \right|=BIl\]
Therefore, we can say that,
\[\tau =BIl\times b\sin \theta \]
On solving,
We get,
\[\tau =BI(lb)\sin \theta \]
Now we know that \[A=l\times b\]
Therefore,
\[\tau =BI\times A\times \sin \theta \]
We also know that,
\[m=I\left| A \right|\]
Therefore,
\[\tau =mB\sin \theta \]
The above equation in vector form can be written as,
\[\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{m}\times \overrightarrow{B}\]
Note:
Torque is the measure of the force that causes an object to rotate around an axis. Torque is similar to force. As the force is responsible for linear acceleration, torque is responsible for the angular acceleration. The concept of torque originated when Archimedes made use of levers for moving objects. The point about which the object rotates is called pivot point.
Formula used:
\[\tau =rF\sin \theta \]
Complete answer:

Let us consider a rectangular loop ABCD as shown in the figure (a) above. Let the dimensions of the loop be l and b. There is a steady current in the loop. This loop is placed in the uniform magnetic field as shown.
We know that,
The force on arm BC and AD be \[{{F}_{AB}}\] and \[{{F}_{AD}}\] respectively. These forces are equal and opposite and act along the axis of the coil. Therefore, these forces will cancel each other out.
Similarly,
The forces \[{{F}_{AB}}\]and \[{{F}_{CD}}\]on arm AB and CD are also equal and opposite. Since these forces are not collinear, they act as a couple.
Therefore, the magnitude of torque can be given as,
\[\tau ={{F}_{AB}}+\dfrac{b}{2}\sin \theta +{{F}_{CD}}\dfrac{b}{2}\sin \theta \]
Now, we know that
\[\left| {{F}_{AB}} \right|=\left| {{F}_{CD}} \right|=BIl\]
Therefore, we can say that,
\[\tau =BIl\times b\sin \theta \]
On solving,
We get,
\[\tau =BI(lb)\sin \theta \]
Now we know that \[A=l\times b\]
Therefore,
\[\tau =BI\times A\times \sin \theta \]
We also know that,
\[m=I\left| A \right|\]
Therefore,
\[\tau =mB\sin \theta \]
The above equation in vector form can be written as,
\[\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{m}\times \overrightarrow{B}\]
Note:
Torque is the measure of the force that causes an object to rotate around an axis. Torque is similar to force. As the force is responsible for linear acceleration, torque is responsible for the angular acceleration. The concept of torque originated when Archimedes made use of levers for moving objects. The point about which the object rotates is called pivot point.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




