
Derive an expression for the bandwidth of interference fringes in Young’s double slit experiment.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: In order to derive this expression first we will understand what Young's double slit experiment is. This experiment states that when a monochromatic light is passed through two narrow slits illuminates a distant screen; a characteristic pattern of bright and dark fringes is observed which is caused by the superposition of overlapping light waves originating from the two slits.
Complete step-by-step answer:
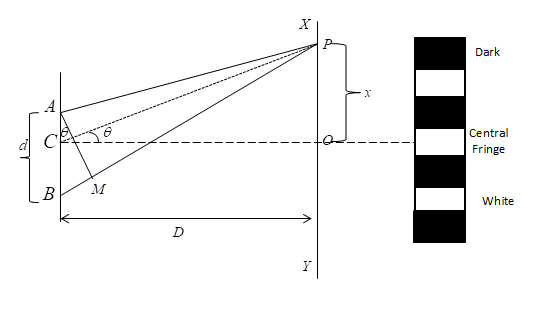
Let d be the distance between the two coherent sources AB. Also XY is the screen placed parallel to the source at a distance D. C is the midpoint of AB
Construction- Draw AM perpendicular to PB.
The path difference S = BP-AP
Therefore AP = MP
Also, BP-AP = BP-MP = BM
For constructive interference path difference must be equal to $n\lambda $
$
BP - AP = n\lambda \\
n = 0,1,2,3........ \\
$
From the diagram above
\[B{P^2} - A{P^2} = \left[ {{D^2} + {{\left( {x + \dfrac{d}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right] - \left[ {{D^2} + {{\left( {x - \dfrac{d}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right]\]
Solving the above equation, we get
$
B{P^2} - A{P^2} = 2xd \\
\left( {BP - AP} \right)\left( {BP + AP} \right) = 2xd \\
$
Approximately, OC = AP = BP = D
$
\left( {BP - AP} \right)2D = 2xd \\
BP - AP = \dfrac{{xd}}{D} = n\lambda \\
$
For n fringes, it is given as
${x_n} = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d}$
Where n = 0, 1 , 2 ,3 ……………. And depending upon the positive value of integers gives bright fringes and negative integers give dark fringes.
Now, since the fringes are equally spaced the distance between two consecutive bright or consecutive dark fringes gives the fringe width.
$
\beta = {x_{n + 1}} - {x_n} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{\left( {n + 1} \right)\lambda D}}{d} - \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d} \\
$
Where $\beta $ is the bandwidth of the fringe
Note- The above expression for fringes can also be derived without taking the assumptions and the results we get will be the same. The assumption we made here is D should be large, the distance between the two sources is very small. This experiment helps in understanding the waves theory of light.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let d be the distance between the two coherent sources AB. Also XY is the screen placed parallel to the source at a distance D. C is the midpoint of AB
Construction- Draw AM perpendicular to PB.
The path difference S = BP-AP
Therefore AP = MP
Also, BP-AP = BP-MP = BM
For constructive interference path difference must be equal to $n\lambda $
$
BP - AP = n\lambda \\
n = 0,1,2,3........ \\
$
From the diagram above
\[B{P^2} - A{P^2} = \left[ {{D^2} + {{\left( {x + \dfrac{d}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right] - \left[ {{D^2} + {{\left( {x - \dfrac{d}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right]\]
Solving the above equation, we get
$
B{P^2} - A{P^2} = 2xd \\
\left( {BP - AP} \right)\left( {BP + AP} \right) = 2xd \\
$
Approximately, OC = AP = BP = D
$
\left( {BP - AP} \right)2D = 2xd \\
BP - AP = \dfrac{{xd}}{D} = n\lambda \\
$
For n fringes, it is given as
${x_n} = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d}$
Where n = 0, 1 , 2 ,3 ……………. And depending upon the positive value of integers gives bright fringes and negative integers give dark fringes.
Now, since the fringes are equally spaced the distance between two consecutive bright or consecutive dark fringes gives the fringe width.
$
\beta = {x_{n + 1}} - {x_n} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{\left( {n + 1} \right)\lambda D}}{d} - \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d} \\
$
Where $\beta $ is the bandwidth of the fringe
Note- The above expression for fringes can also be derived without taking the assumptions and the results we get will be the same. The assumption we made here is D should be large, the distance between the two sources is very small. This experiment helps in understanding the waves theory of light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




