
Derive an expression for an equivalent focal length of two thin lenses kept in contact.
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: Focal length is the distance over which the parallel rays either converge or diverge. For convex lenses, the focal length is positive and for concave length it is negative. Focal length varies with sign depending on the nature of the lens and the mirror.
Complete solution:
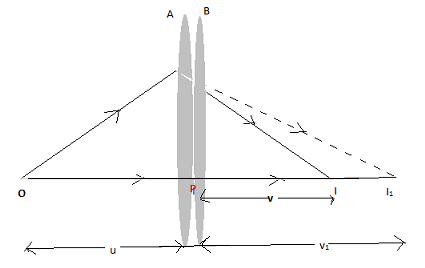
Let us consider two lenses A and B of focal length $f_1$ and $f_2$ which are placed in contact with each other. The object is placed at a point O beyond the focus of the first lens A. $I_1$ is the image produced by the first lens which is real. Since it is a real image, it serves as a virtual object for the second lens B producing the final image at $I$. The direction of the rays emerging from the first lens gets changed according to the angle at which strikes the second lens. We assume that the optical centers of the lenses are coincident as the lenses are very thin. Let this central point be represented by P.
Therefore, For the image formed by lens A, we get
$\dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}}\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 1 \right)$
Similarly, for the image formed by lens B, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 2 \right)$
On adding $($1 ) and $($2 ), we get
\[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}\]
If the two lenses are considered as equal to a single lens of focal length f, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{{{f_2} + {f_1}}}{{{f_1}{f_2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{{f_1}{f_2}}}{{{f_1} + {f_2}}}\]
The expression is \[f = \dfrac{{{f_1}{f_2}}}{{{f_1} + {f_2}}}\].
Note: 1) The focal length of the mirror is the distance between the pole and the focus of the mirror.
2) Focal length of the mirror is a measure of the power of the mirror.
3) Thin lenses have the same focal length on either side.
Complete solution:

Let us consider two lenses A and B of focal length $f_1$ and $f_2$ which are placed in contact with each other. The object is placed at a point O beyond the focus of the first lens A. $I_1$ is the image produced by the first lens which is real. Since it is a real image, it serves as a virtual object for the second lens B producing the final image at $I$. The direction of the rays emerging from the first lens gets changed according to the angle at which strikes the second lens. We assume that the optical centers of the lenses are coincident as the lenses are very thin. Let this central point be represented by P.
Therefore, For the image formed by lens A, we get
$\dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}}\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 1 \right)$
Similarly, for the image formed by lens B, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 2 \right)$
On adding $($1 ) and $($2 ), we get
\[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}\]
If the two lenses are considered as equal to a single lens of focal length f, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{{{f_2} + {f_1}}}{{{f_1}{f_2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{{f_1}{f_2}}}{{{f_1} + {f_2}}}\]
The expression is \[f = \dfrac{{{f_1}{f_2}}}{{{f_1} + {f_2}}}\].
Note: 1) The focal length of the mirror is the distance between the pole and the focus of the mirror.
2) Focal length of the mirror is a measure of the power of the mirror.
3) Thin lenses have the same focal length on either side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




