
Define the following: Thermionic emission and dual nature of radiation
Answer
584.7k+ views
HintFor getting the solution to this question just concentrate on the word “thermionic emission”. This means, we have to think, what happens when we provide thermal energy to any metal.
Now for, dual nature of radiation, we have to think the two in which radiation exists.
Complete step-by-step solution:Thermionic Emission: The phenomenon of the emission of electrons, from the surface of the metal when it's heated is called thermionic emission. These electrons are called thermions. The number of electrons emitted depends on the temperature at which the metal is heated. Thermionic emission is the thermally
Induced flow of charge carriers from a surface or over a potential-energy barrier.
This occurs because the thermal energy given to the carrier overcomes the work function of the material. After emission, a charge that is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the total charge emitted is initially left behind in the emitting region. But if the emitter is connected to a battery, the charge left behind is neutralized by charge supplied by the battery as the emitted charge carriers move away from the emitter, and finally the emitter will be in the same state as it was before emission.
The number of electrons emitted per second from a surface depends on the following three factors:
The nature of the metal surface: smaller the work function of the surface, higher is the rate of emission of electrons from its surface and vice versa.
The temperature of the surface: larger the temperature of the metal, higher is the rate of emission of electrons from the affected metal surface.
The surface area : greater the affected surface area of the metal emitting the electrons, larger is the rate of emission of electrons.
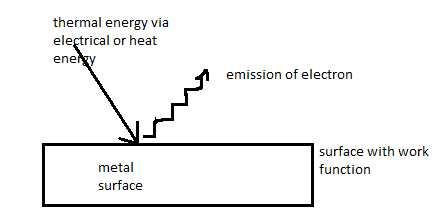
When thermal energy provided exceeds work function, thermal emission starts.
Dual Nature of Radiation:
Sometimes it behaves like a particle (called a photon), which explains how light travels in straight lines
Sometimes it behaves like a wave, which explains how light bends (or diffracts) around an object
Light also shows interference properties.
Note:- Remember thermionic emission is only possible in metal surfaces. And emission varies from metal to metal with varying intensity of thermal energy provided.
Now for, dual nature of radiation, we have to think the two in which radiation exists.
Complete step-by-step solution:Thermionic Emission: The phenomenon of the emission of electrons, from the surface of the metal when it's heated is called thermionic emission. These electrons are called thermions. The number of electrons emitted depends on the temperature at which the metal is heated. Thermionic emission is the thermally
Induced flow of charge carriers from a surface or over a potential-energy barrier.
This occurs because the thermal energy given to the carrier overcomes the work function of the material. After emission, a charge that is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the total charge emitted is initially left behind in the emitting region. But if the emitter is connected to a battery, the charge left behind is neutralized by charge supplied by the battery as the emitted charge carriers move away from the emitter, and finally the emitter will be in the same state as it was before emission.
The number of electrons emitted per second from a surface depends on the following three factors:
The nature of the metal surface: smaller the work function of the surface, higher is the rate of emission of electrons from its surface and vice versa.
The temperature of the surface: larger the temperature of the metal, higher is the rate of emission of electrons from the affected metal surface.
The surface area : greater the affected surface area of the metal emitting the electrons, larger is the rate of emission of electrons.

When thermal energy provided exceeds work function, thermal emission starts.
Dual Nature of Radiation:
Sometimes it behaves like a particle (called a photon), which explains how light travels in straight lines
Sometimes it behaves like a wave, which explains how light bends (or diffracts) around an object
Light also shows interference properties.
Note:- Remember thermionic emission is only possible in metal surfaces. And emission varies from metal to metal with varying intensity of thermal energy provided.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




