
Define somaclonal variation.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: It is associated with a genetic variation that was discovered in 1981 by Larkin and Scowkraft. It is derived from any form of cell or tissue culture.
Complete answer:
The variation observed generally among the progeny of plants regenerated from callus or the phenomenon of high variability in individuals from adventitious shoots is known as somaclonal variation. The callus is a growing mass of unorganized parenchyma cells that cover the plant wound. The rearrangements of chromosomes are important for this kind of variation. The term somaclonal variation refers to outcrossing, inbreeding, vegetative, seed propagated, cultivated, and non-cultivated plants. Both qualitative and quantitative traits are the effects of such variation. The genetic variations can be phenotypic or genotypic. If it is phenotypic then it can be either genetic or epigenetic in origin. The genetic variations change in the number of chromosomes, DNA sequence, chromosome structure that is translocation, insertion, deletion, and duplication.
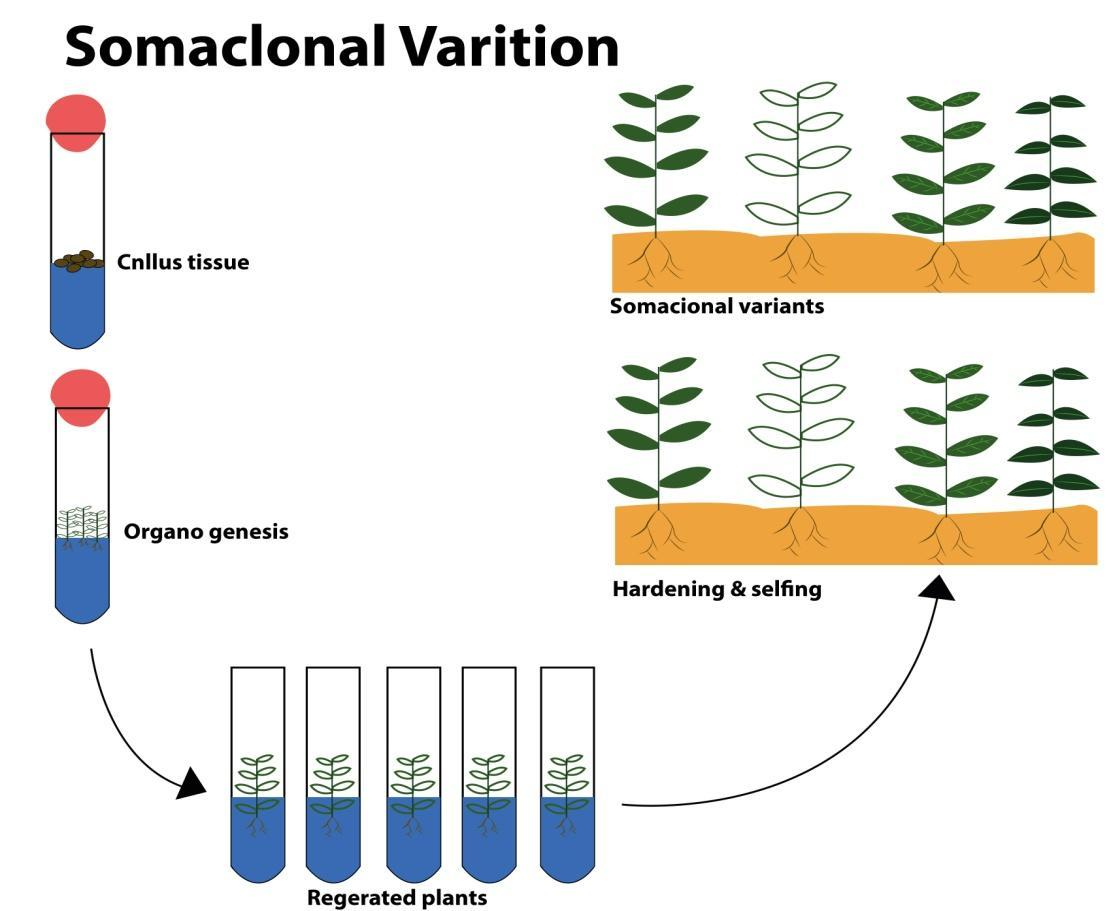
It helps in the improvement of the plant or crop. It helps in the creation of additional genetic variability which gives them better survival in nature. It is suitable for the breeding of new species. In vitro culture, the somaclonal mutants have resistance to diseases, herbicides, mineral toxicity, and have the tolerance to chemical stress. It also provides increased production of secondary metabolites.
Note: Even though somaclonal variation is such a useful way for the genetic variations it still has disadvantages as it may lead to undesirable results. Not always the selected variants are perfect. They are random and genetically unstable. It needs extended field trials and is not perfect for agronomic traits like yield, quality, etc. It also requires a clonal uniformity.
Complete answer:
The variation observed generally among the progeny of plants regenerated from callus or the phenomenon of high variability in individuals from adventitious shoots is known as somaclonal variation. The callus is a growing mass of unorganized parenchyma cells that cover the plant wound. The rearrangements of chromosomes are important for this kind of variation. The term somaclonal variation refers to outcrossing, inbreeding, vegetative, seed propagated, cultivated, and non-cultivated plants. Both qualitative and quantitative traits are the effects of such variation. The genetic variations can be phenotypic or genotypic. If it is phenotypic then it can be either genetic or epigenetic in origin. The genetic variations change in the number of chromosomes, DNA sequence, chromosome structure that is translocation, insertion, deletion, and duplication.

It helps in the improvement of the plant or crop. It helps in the creation of additional genetic variability which gives them better survival in nature. It is suitable for the breeding of new species. In vitro culture, the somaclonal mutants have resistance to diseases, herbicides, mineral toxicity, and have the tolerance to chemical stress. It also provides increased production of secondary metabolites.
Note: Even though somaclonal variation is such a useful way for the genetic variations it still has disadvantages as it may lead to undesirable results. Not always the selected variants are perfect. They are random and genetically unstable. It needs extended field trials and is not perfect for agronomic traits like yield, quality, etc. It also requires a clonal uniformity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




