
Define Monozygotic and dizygotic.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Twins can be either Monozygotic or dizygotic. Monozygotic twins are conceived when a single egg is fertilized by a single sperm. Dizygotic twins are conceived when two eggs are fertilized by two different sperms. Monozygotic twins are referred to as identical twins and dizygotic twins are also referred to as fraternal twins.
Complete answer:
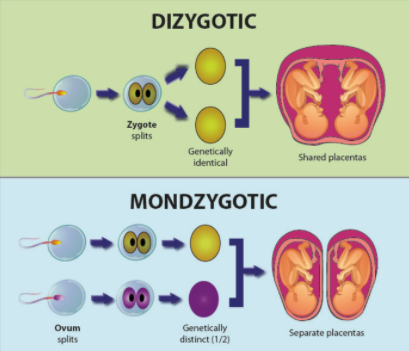
Identical twins are also known as monozygotic twins. They result from the fertilization of a single egg by a single sperm that splits in two. Identical twins share all of their genes and are always of the same sex. Such twins have nearly 100% of their genes in common. Both of them invariably have the same blood type and are of the same sex. They can be very rarely of different sex. Monozygotic twins occur when a single egg cell is fertilized by a single sperm cell and the resulting zygote splits into two in early development, leading to the formation of two separate embryos. Fraternal twins are also known as Dizygotic twins. They result from the fertilization of two different eggs by two different sperms. They do not share the same genes. They share only 50% of genes. Fraternal twins can be of three kinds; Female-Female, Male-Male, and Male-Female.
Additional Information:
-Fraternal twins are also known as non-identical twins, dissimilar twins, biovular twins, etc.
-They are the most common type of twins. Dizygotic twins may look similar or may also look very different from each other as in the Male-Female type.
-Monozygotic twins are the same sex, they share physical characteristics, and even may have similar personalities.
-Identical twins occur in 3 to 4 per 1,000 births worldwide.
Note: -Dizygotic twins are also more common for older mothers. The reason for this is that women of this age are more likely than younger women to release more than one egg during their reproductive cycle.
-Research suggests that most cases of Monozygotic twinning are not caused by genetic factors. However, a few families with a larger-than-expected number of Monozygotic twins have been reported, which indicates that genetics may play a role.
-No two people will have the same fingerprints including identical twins.
Complete answer:
Identical twins are also known as monozygotic twins. They result from the fertilization of a single egg by a single sperm that splits in two. Identical twins share all of their genes and are always of the same sex. Such twins have nearly 100% of their genes in common. Both of them invariably have the same blood type and are of the same sex. They can be very rarely of different sex. Monozygotic twins occur when a single egg cell is fertilized by a single sperm cell and the resulting zygote splits into two in early development, leading to the formation of two separate embryos. Fraternal twins are also known as Dizygotic twins. They result from the fertilization of two different eggs by two different sperms. They do not share the same genes. They share only 50% of genes. Fraternal twins can be of three kinds; Female-Female, Male-Male, and Male-Female.
Additional Information:
-Fraternal twins are also known as non-identical twins, dissimilar twins, biovular twins, etc.
-They are the most common type of twins. Dizygotic twins may look similar or may also look very different from each other as in the Male-Female type.
-Monozygotic twins are the same sex, they share physical characteristics, and even may have similar personalities.
-Identical twins occur in 3 to 4 per 1,000 births worldwide.
Note: -Dizygotic twins are also more common for older mothers. The reason for this is that women of this age are more likely than younger women to release more than one egg during their reproductive cycle.
-Research suggests that most cases of Monozygotic twinning are not caused by genetic factors. However, a few families with a larger-than-expected number of Monozygotic twins have been reported, which indicates that genetics may play a role.
-No two people will have the same fingerprints including identical twins.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




