
Define LASER under the following points:
(A) A Meaning
(B) Basic Principle
(C) Uses
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint:In LASER light is emitted in the form of radiations and the electrons either absorb the energy or lose energy. Since each atom has electrons moving in the orbitals, the gain or loss of energy by electrons results in shifting of electrons from a lower energy to a higher energy or vice versa. If they gain energy, they get excited and jump to a higher energy level and if they lose energy they fall back into their respective orbital or ground state.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Step I:
Meaning: LASER means ‘ Light Amplification By Stimulated Emission Of Radiation’. Laser means a device which excites atoms in order to emit light at a wavelength and produces a very narrow beam of light at high radiation.
Step II:
Basic Principle: Lasers work on the basic principle of emission or jumping of electrons from ground state to higher level and then coming back from higher state to ground state. It is done in three ways:
- Stimulated Absorption : In which the electron absorbs photons and jumps to a higher energy level.
-Stimulated Emission: In which an electron when reacts with a photon, loses energy and falls back to a lower energy level.
-Spontaneous Emission: In which photons are not interacted with electrons. But the electron in higher energy states falls back to a lower level and emits energy in a random direction in the form of photons.
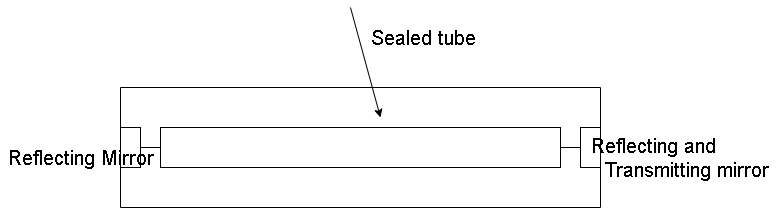
Step III:
Uses: Lasers are used in different fields. Since very high intensity of light is produced so they are used in:
-Cutting hard metals like diamonds.
-In the treatment of the retina.
-To detect and destroy the rockets of the enemy at night.
-To control rockets, spaceships and satellites.
Note:
It is to be noted that light emitted from a laser does not grow if it is at a distance away from the laser. Also the laser light should not be very close to the retina of the eye, otherwise it can result in a blind spot or burn.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Step I:
Meaning: LASER means ‘ Light Amplification By Stimulated Emission Of Radiation’. Laser means a device which excites atoms in order to emit light at a wavelength and produces a very narrow beam of light at high radiation.
Step II:
Basic Principle: Lasers work on the basic principle of emission or jumping of electrons from ground state to higher level and then coming back from higher state to ground state. It is done in three ways:
- Stimulated Absorption : In which the electron absorbs photons and jumps to a higher energy level.
-Stimulated Emission: In which an electron when reacts with a photon, loses energy and falls back to a lower energy level.
-Spontaneous Emission: In which photons are not interacted with electrons. But the electron in higher energy states falls back to a lower level and emits energy in a random direction in the form of photons.

Step III:
Uses: Lasers are used in different fields. Since very high intensity of light is produced so they are used in:
-Cutting hard metals like diamonds.
-In the treatment of the retina.
-To detect and destroy the rockets of the enemy at night.
-To control rockets, spaceships and satellites.
Note:
It is to be noted that light emitted from a laser does not grow if it is at a distance away from the laser. Also the laser light should not be very close to the retina of the eye, otherwise it can result in a blind spot or burn.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




