
Define electric flux. Write its S.I. unit.
“Gauss’s law in electrostatics is true for any closed surface, no matter what its shape or size is”. Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
Answer
532.7k+ views
Hint:- Electric field, electric field lines and the electric flux are all linked with each other and are defined and used in different forms to understand the concept of electrostatics more deeply and easily. We will see their definitions and units as we proceed further.
Step By Step Answer:
Electric flux - Electric flux is the measure of number of electric field lines passing through any surface .It is a scalar quantity.
It's S.I unit is volt meters.
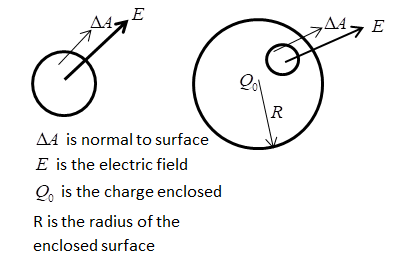
Gauss Law- It is defined as the total flux linked within a closed surface is equal to the $\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ times the total charge enclosed by that surface.
Mathematically it is defined as
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Where
$q = $ Charge enclosed in the surface
${\varepsilon _0} = $permittivity of the vacuum.
The Gaussian surface can be of any shape and size because it’s only the amount of flux coming out of the charge distribution on which we have to concentrate and these will be the same if allowed to pass through any shape and size of surface. It's like a cloud coming out from any three dimensional surface.We use this gauss law in order to find the magnitude of the electric field at any point due to charge distribution.
Note- We mostly choose a surface on which the rays of flux remain either parallel or perpendicular and identical at all points that will be easy to carry integration easily and thus we mostly choose cylindrical or spherical surfaces . We are free to choose any type of Gaussian surface but integration of cylindrical and spherical surfaces becomes very easy.
Step By Step Answer:
Electric flux - Electric flux is the measure of number of electric field lines passing through any surface .It is a scalar quantity.
It's S.I unit is volt meters.

Gauss Law- It is defined as the total flux linked within a closed surface is equal to the $\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ times the total charge enclosed by that surface.
Mathematically it is defined as
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Where
$q = $ Charge enclosed in the surface
${\varepsilon _0} = $permittivity of the vacuum.
The Gaussian surface can be of any shape and size because it’s only the amount of flux coming out of the charge distribution on which we have to concentrate and these will be the same if allowed to pass through any shape and size of surface. It's like a cloud coming out from any three dimensional surface.We use this gauss law in order to find the magnitude of the electric field at any point due to charge distribution.
Note- We mostly choose a surface on which the rays of flux remain either parallel or perpendicular and identical at all points that will be easy to carry integration easily and thus we mostly choose cylindrical or spherical surfaces . We are free to choose any type of Gaussian surface but integration of cylindrical and spherical surfaces becomes very easy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which country did Danny Casey play for class 12 english CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




