
Define ‘drift velocity ‘ of free electrons.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Drift velocity by the name itself suggests a velocity with which a particle is drifting in a certain direction. The velocity of electrons or particles depends upon the movement of particles. It is directly proportional to the current in the circuit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
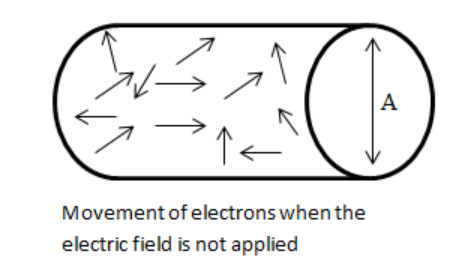
For example, if we take up the case of an electron it is easier to understand. In normal conditions when no electrical potential is applied across a piece of wire, all the electrons move in random directions and in effect giving zero average velocity.
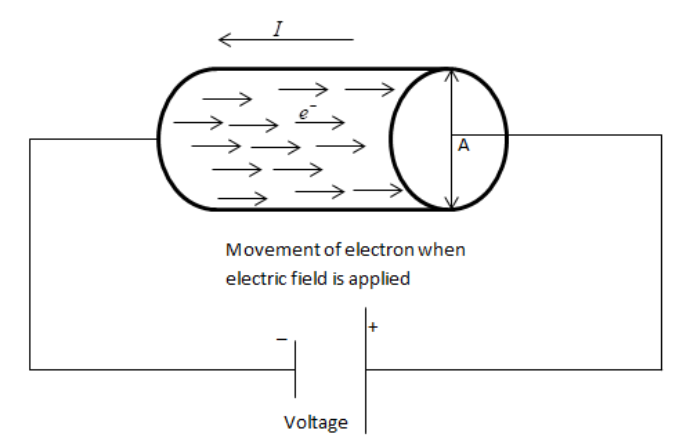
So now when we apply a potential to the piece of wire, still the electrons move in totally random directions but they have an added force acting on them due to the electric field applied which causes them to “drift” towards the side of the wire which is at a higher potential. So the net effect of this electric potential is that still the electrons move in random directions but now they also slowly move towards the higher potential side.
The average velocity of the electrons is known as “Drift Velocity”.
The formula of drift velocity is given as
${V_d} = \dfrac{I}{{nAq}}$
Where
${V_d}$ is the drift velocity of the electrons
I is the current in the wire
n is the number of electrons
q is the charge of the electrons
Note: Drift velocity of electrons varies from one material to another, though it may seem as it is constant velocity at which electrons move under influence of electric field inside a conductor, whereas it is average velocity of accelerating electrons, which constantly collide with fellow atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For example, if we take up the case of an electron it is easier to understand. In normal conditions when no electrical potential is applied across a piece of wire, all the electrons move in random directions and in effect giving zero average velocity.


So now when we apply a potential to the piece of wire, still the electrons move in totally random directions but they have an added force acting on them due to the electric field applied which causes them to “drift” towards the side of the wire which is at a higher potential. So the net effect of this electric potential is that still the electrons move in random directions but now they also slowly move towards the higher potential side.
The average velocity of the electrons is known as “Drift Velocity”.
The formula of drift velocity is given as
${V_d} = \dfrac{I}{{nAq}}$
Where
${V_d}$ is the drift velocity of the electrons
I is the current in the wire
n is the number of electrons
q is the charge of the electrons
Note: Drift velocity of electrons varies from one material to another, though it may seem as it is constant velocity at which electrons move under influence of electric field inside a conductor, whereas it is average velocity of accelerating electrons, which constantly collide with fellow atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




