
Define current density. Write an expression which connects current density with drift speed.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Think from the basics, current is nothing but amount of charge passing through a cross-sectional area in unit time and current density is nothing but a quantity which expresses how much current is flowing through a unit area.
Formula Used:
The relation between current density and drift velocity
$J=ne{{v}_{d}}$
Where
$J=$ Current density
${{v}_{d}}=$ Drift velocity
Complete step by step answer:
Current density:- The amount of electric current flowing perpendicularly to the unit cross section area.
$J=\dfrac{i}{A}$
Where $J$ is the current density.
$i$ is the current in the conductor.
$A$ is the cross section area.
Relation between current density and drift velocity:- The strength of the electric current in a conductor is measured by the magnitude of electric charge flowing per second through a cross section area of the conductor. If the charge carried by the free electron passing through a section of the wire in $t$ second be $q$, then strength of current in the wire is
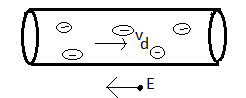
$i=\dfrac{q}{t}$ ….(1)
Suppose area of cross section A, and number of free ${{e}^{-}}$ per unit volume of the wire is n.
The number of electrons passing per second through a cross section of the wire will be $nA{{v}_{d}}t$.
In $t$ second, $nA{{v}_{d}}t$ electrons will pass.
Charge on the electrons ${{e}^{-}}$
Then charge passing through any cross section of wire in $t$ second will be.
$q=\left( nA{{v}_{d}}t \right)\times e$
Substituting the value of $q$ in equation (1)
$i=\dfrac{neA{{v}_{d}}t}{t}$
$i=neA{{v}_{d}}$ ……………(2)
We know that
$J=\dfrac{i}{A}$
$J=\dfrac{neA{{v}_{d}}}{A}$
$J=ne{{v}_{d}}$
This is the relation between current density and drift velocity and written in vector form
$\overrightarrow{J}=-ne\overrightarrow{{{v}_{d}}}$
$\left( - \right)$ sign signifies that electron move in the direction $-\overrightarrow{J.}$
Note: Current flows in the direction of motion of a positive charge but since electrons are negatively charged, current flow and direction of motion of electrons is opposite to each other.
Formula Used:
The relation between current density and drift velocity
$J=ne{{v}_{d}}$
Where
$J=$ Current density
${{v}_{d}}=$ Drift velocity
Complete step by step answer:
Current density:- The amount of electric current flowing perpendicularly to the unit cross section area.
$J=\dfrac{i}{A}$
Where $J$ is the current density.
$i$ is the current in the conductor.
$A$ is the cross section area.
Relation between current density and drift velocity:- The strength of the electric current in a conductor is measured by the magnitude of electric charge flowing per second through a cross section area of the conductor. If the charge carried by the free electron passing through a section of the wire in $t$ second be $q$, then strength of current in the wire is

$i=\dfrac{q}{t}$ ….(1)
Suppose area of cross section A, and number of free ${{e}^{-}}$ per unit volume of the wire is n.
The number of electrons passing per second through a cross section of the wire will be $nA{{v}_{d}}t$.
In $t$ second, $nA{{v}_{d}}t$ electrons will pass.
Charge on the electrons ${{e}^{-}}$
Then charge passing through any cross section of wire in $t$ second will be.
$q=\left( nA{{v}_{d}}t \right)\times e$
Substituting the value of $q$ in equation (1)
$i=\dfrac{neA{{v}_{d}}t}{t}$
$i=neA{{v}_{d}}$ ……………(2)
We know that
$J=\dfrac{i}{A}$
$J=\dfrac{neA{{v}_{d}}}{A}$
$J=ne{{v}_{d}}$
This is the relation between current density and drift velocity and written in vector form
$\overrightarrow{J}=-ne\overrightarrow{{{v}_{d}}}$
$\left( - \right)$ sign signifies that electron move in the direction $-\overrightarrow{J.}$
Note: Current flows in the direction of motion of a positive charge but since electrons are negatively charged, current flow and direction of motion of electrons is opposite to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




