
Define application of Resonance.
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Resonance basically defines the polarity produced in a molecule by the interaction between a lone pair and a pi bond or the interaction of two pi bonds in adjacent atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Resonance in other words means that a molecule can be drawn with multiple Lewis structures but it actually exists in a hybrid state between the various configurations. It is usually found in molecules with conjugated double bonds or in molecules having at least one lone pair and one double bond. Resonance is an important factor in deciding the stability of the compound and its energy state.
There are various rules that determines how significant a resonance structure is:
1. The rule of least charges: the resonant structure having lowest charge is the most significant one.
2. The octet principle: the resonant structures with full octet are more significant than the ones lacking in octet competition.
3. Stabilization of positive charges: resonant structures where positive charge is present on the least electronegative element are most significant.
4. Stabilization of negative charges: resonant structures where negative charge is present on the most electronegative element is most significant.
5. Covalent bonds: the most significant resonance structure has the most covalent bonds.
EXAMPLE: Resonance structure of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
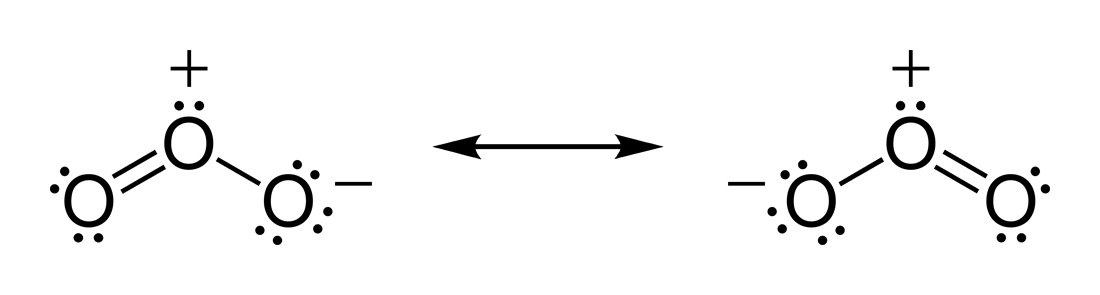
The above two species are resonance structures of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$.
Note:The rules for determining the most significant resonance structure should be kept in mind. The positive charge on less electronegative atoms and the negative charge on more electronegative atoms is the most important and basic rule while deciding the most significant resonating structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Resonance in other words means that a molecule can be drawn with multiple Lewis structures but it actually exists in a hybrid state between the various configurations. It is usually found in molecules with conjugated double bonds or in molecules having at least one lone pair and one double bond. Resonance is an important factor in deciding the stability of the compound and its energy state.
There are various rules that determines how significant a resonance structure is:
1. The rule of least charges: the resonant structure having lowest charge is the most significant one.
2. The octet principle: the resonant structures with full octet are more significant than the ones lacking in octet competition.
3. Stabilization of positive charges: resonant structures where positive charge is present on the least electronegative element are most significant.
4. Stabilization of negative charges: resonant structures where negative charge is present on the most electronegative element is most significant.
5. Covalent bonds: the most significant resonance structure has the most covalent bonds.
EXAMPLE: Resonance structure of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$

The above two species are resonance structures of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$.
Note:The rules for determining the most significant resonance structure should be kept in mind. The positive charge on less electronegative atoms and the negative charge on more electronegative atoms is the most important and basic rule while deciding the most significant resonating structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




