
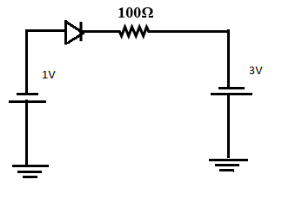
What is the current through an ideal p-n junction diode as shown in the figure below?
1) Zero
2) 10mA
3) 20mA
4) 50mA

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint:A diode is a two terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction.
To find the current in the above circuit we will apply KVL(Kirchhoff's Voltage law) and Ohm's law as current will flow in one direction only through the diode(diode is connected in forward biased).
Using the above criteria in mind we will find the current through the diode.
Complete step by step solution:
Let's discuss Diode in more detail before proceeding for the calculation of the solution.
Diode is a passive two terminal device that conducts current in one direction only. Generally when the diode is ideal, for silicon diode potential drop is taken as 0.7V and for Germanium diode potential drop is taken as 0.3V. Diode provides a low resistance path when forward biased and high resistance when reversed biased. By forward bias we mean that Anode of the diode is connected to the positive terminal of the external battery connected in the circuit.
When the cathode of the diode is connected to the positive terminal then the diode is said to be reversed biased.
Now we will do the calculation of the solution:
Total potential of the circuit is taken as;
$ \Rightarrow V = - 1 - ( - 3) $
$ \Rightarrow V = 2V $
(We have subtracted the two voltages given in the circuit)
Diode given is ideal then no losses; therefore resistance of the circuit is 100 ohm.
Current is given as:
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{2}{{100}} $
(Substituted the value of voltage and resistor)
$I = 20mA$ (We have divided and multiplied the equation by 10)
Thus option 3 is correct.
Note:Diodes are the electronic component used in almost each and every electronic gadgets such as limiters, clippers, gates, computer systems as logic gates, clampers, power supply systems such as rectifiers and inverters, television systems as phase detectors, limiters clampers, radar circuits as gain control circuits, parameter amplifiers etc.
To find the current in the above circuit we will apply KVL(Kirchhoff's Voltage law) and Ohm's law as current will flow in one direction only through the diode(diode is connected in forward biased).
Using the above criteria in mind we will find the current through the diode.
Complete step by step solution:
Let's discuss Diode in more detail before proceeding for the calculation of the solution.
Diode is a passive two terminal device that conducts current in one direction only. Generally when the diode is ideal, for silicon diode potential drop is taken as 0.7V and for Germanium diode potential drop is taken as 0.3V. Diode provides a low resistance path when forward biased and high resistance when reversed biased. By forward bias we mean that Anode of the diode is connected to the positive terminal of the external battery connected in the circuit.
When the cathode of the diode is connected to the positive terminal then the diode is said to be reversed biased.
Now we will do the calculation of the solution:
Total potential of the circuit is taken as;
$ \Rightarrow V = - 1 - ( - 3) $
$ \Rightarrow V = 2V $
(We have subtracted the two voltages given in the circuit)
Diode given is ideal then no losses; therefore resistance of the circuit is 100 ohm.
Current is given as:
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{2}{{100}} $
(Substituted the value of voltage and resistor)
$I = 20mA$ (We have divided and multiplied the equation by 10)
Thus option 3 is correct.
Note:Diodes are the electronic component used in almost each and every electronic gadgets such as limiters, clippers, gates, computer systems as logic gates, clampers, power supply systems such as rectifiers and inverters, television systems as phase detectors, limiters clampers, radar circuits as gain control circuits, parameter amplifiers etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




