
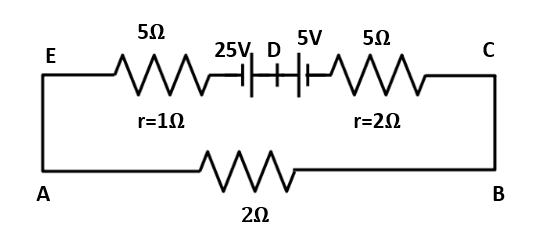
What is the current in the following circuit?
a) $\dfrac{3}{5}$ A from E to C through D.
b) $\dfrac{4}{3}$ A from E to C through D.

Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: The value of current is the same by any component in a series system. The total resistance of any series circuit is equivalent to the sum of the separate resistances. The supply voltage in a line circuit is equivalent to the sum of the unique voltage falls.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given circuit, the two voltages joined with same terminal.
So, net voltage will be:
$V = (25 – 5 )V$
$\implies V = 20 V$
There are three resistances having two resistances with internal resistance.
$r_{1} = 1 \Omega$; $r_{2} = 1 \Omega$
$R_{1} = 5 \Omega$
$R_{2} = 5 \Omega$
$R_{3} = 2 \Omega$
Total resistance is equal to the sum of all resistances.
$ R_{total} = r_{1} + r_{2} + R_{1} + R_{2} + R_{3}$
$\implies R_{total} = 1 + 2 + 5 + 5 + 2$
$\implies R_{total} = 15 \Omega$
We need to calculate the current.
$\text{Current} = \dfrac{\text{voltage}}{\text{resistance}}$
$I = \dfrac{20}{15} A$
$\implies I = \dfrac{4}{3} A$
This current will go from E to B through D.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: The value of current in a series line is the same by any component in the system. This is because there is only one way for current flow in a series circuit. Because electric charge passes through conductors, the flow rate at any time in the circuit must be equivalent to the specific point in time.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given circuit, the two voltages joined with same terminal.
So, net voltage will be:
$V = (25 – 5 )V$
$\implies V = 20 V$
There are three resistances having two resistances with internal resistance.
$r_{1} = 1 \Omega$; $r_{2} = 1 \Omega$
$R_{1} = 5 \Omega$
$R_{2} = 5 \Omega$
$R_{3} = 2 \Omega$
Total resistance is equal to the sum of all resistances.
$ R_{total} = r_{1} + r_{2} + R_{1} + R_{2} + R_{3}$
$\implies R_{total} = 1 + 2 + 5 + 5 + 2$
$\implies R_{total} = 15 \Omega$
We need to calculate the current.
$\text{Current} = \dfrac{\text{voltage}}{\text{resistance}}$
$I = \dfrac{20}{15} A$
$\implies I = \dfrac{4}{3} A$
This current will go from E to B through D.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: The value of current in a series line is the same by any component in the system. This is because there is only one way for current flow in a series circuit. Because electric charge passes through conductors, the flow rate at any time in the circuit must be equivalent to the specific point in time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




