
Crossing over in diploid organisms is responsible for
(a) Dominance of gene
(b) Linkage between genes
(c) Segregation of alleles
(d) Recombination of alleles
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: This is a process by which the genetic elements from two separate organisms are brought together in a single unit and refers to the movement of genetic information from one nucleic acid to another. This also contributes to a population’s genetic diversity.
Complete step by step answer:
Genetic recombination through sexual reproduction is a crucial means of variation in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes don’t have the same process of sexual reproduction. Recombination occurs between homologous DNA sequences from two different sources. Significance of crossing over:
- Produces a new combination of traits
- Through crossing over segments of homologous chromosomes are interchanged and hence provide the origin of new characters and genetic variation.
- Crossing over plays a really important role within breeding to enhance the varieties of plants and animals.
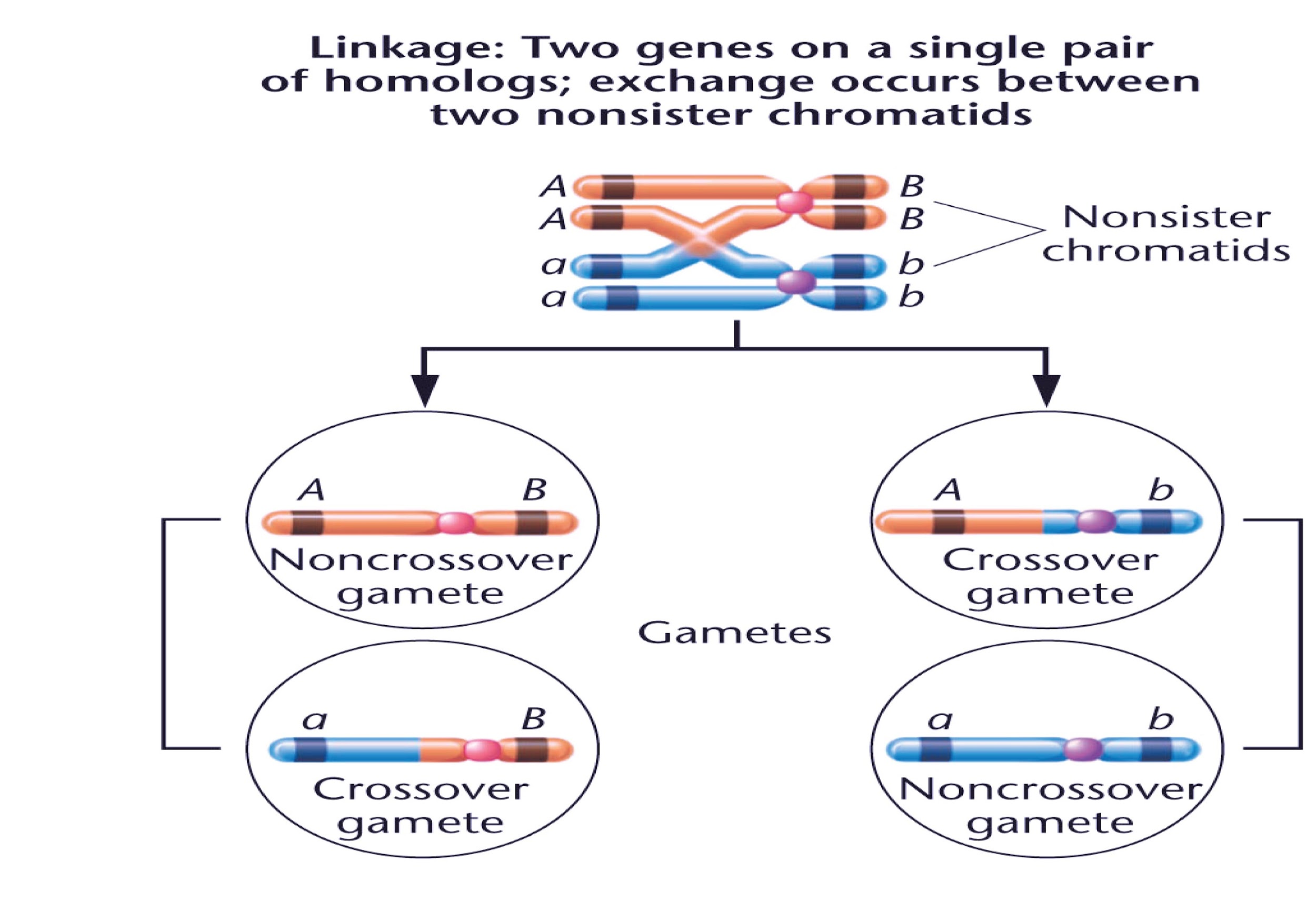
So, the correct answer is ‘(d) Recombination of alleles.’
Additional Information: Genetic recombination is of three types:
- Homologous recombination
Recombination can occur between similar molecules of DNA, that is in homologous recombination or dissimilar molecules as in non- homologous joining (NHEJ)
- Site- specific recombination
Specialized recombination and site- specific recombination, first characterized in prokaryotes SSR is liable for the integration of the phage genome onto the bacterial chromosome.
- DNA transposition
Transposition allows one DNA sequence to be inserted into another without relying on sequence homology.
Note:
- More the distance between two genes on the same chromosome, higher the frequency of crossing over.
- Single crossing over, chromosomal crossover is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that leads to recombinant chromosomes. It is among the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs during prophase I of meiosis that’s pachytene during a process called synapsis.
Complete step by step answer:
Genetic recombination through sexual reproduction is a crucial means of variation in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes don’t have the same process of sexual reproduction. Recombination occurs between homologous DNA sequences from two different sources. Significance of crossing over:
- Produces a new combination of traits
- Through crossing over segments of homologous chromosomes are interchanged and hence provide the origin of new characters and genetic variation.
- Crossing over plays a really important role within breeding to enhance the varieties of plants and animals.

So, the correct answer is ‘(d) Recombination of alleles.’
Additional Information: Genetic recombination is of three types:
- Homologous recombination
Recombination can occur between similar molecules of DNA, that is in homologous recombination or dissimilar molecules as in non- homologous joining (NHEJ)
- Site- specific recombination
Specialized recombination and site- specific recombination, first characterized in prokaryotes SSR is liable for the integration of the phage genome onto the bacterial chromosome.
- DNA transposition
Transposition allows one DNA sequence to be inserted into another without relying on sequence homology.
Note:
- More the distance between two genes on the same chromosome, higher the frequency of crossing over.
- Single crossing over, chromosomal crossover is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that leads to recombinant chromosomes. It is among the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs during prophase I of meiosis that’s pachytene during a process called synapsis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




