
Coulomb’s law for electrostatic force between two point charges and Newton’s law for gravitational force between two stationary point masses, both have inverse-square dependence on the distance between the charges/masses. (a) Compare the strength of these forces by determining the ratio of their magnitudes (i) for an electron and a proton and (ii) for two protons. (b) Estimate the accelerations of electron and proton due to the electrical force of their mutual attraction when they are $1{A^\circ }\,( = {10^{ - 10}}m)\;apart?\;({m_p} = 1.67 \times {10^{ - 27}}\,kg,\,\;{m_e} = 9.11 \times {10^{ - 31}}kg) $.
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: Concept of natural gravitational force and electric force. By finding the ratio of the forces in different cases, the strengths can be compared easily.According to Coulomb’s law, the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. It acts along the line joining the two charges considered to be point charges.
Formula used:
1. Gravitational force
${F_g} = G\dfrac{{{m_1}\,{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where ${m_1}$and${m_2}$ are masses of two bodies separated by a distance $r$.
G is the gravitational constant.
2. Electrostatic force
${F_e} = K\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where ${q_1}$and${q_2}$ are masses of two bodies separated by a distance $r$.
K is a constant.
Complete step by step solution:
Gravitational Force – According to universal law of gravitation each and every object in this universe attracts another object with a force given by
${F_g} = G\;\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
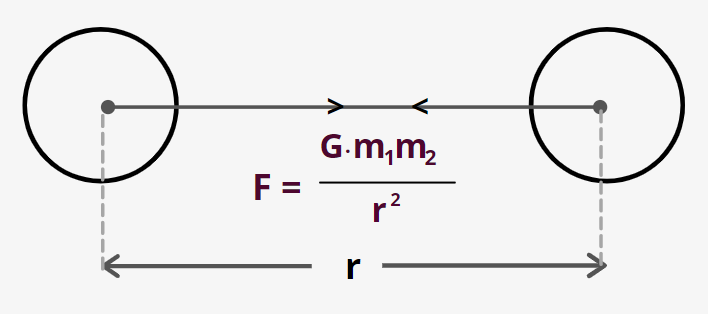
Where ${m_1}\;and\,\;{m_2}$ are two particles separated by a distance of r.
- It follows inverse square law
- Gravitational force is always attractive in nature
- G is the universal gravitational constant and $G = 6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}$
- Coulomb’s law: According to Coulomb’s s law, two charge particles of charges ${q_1}\;and\;{q_2}$ and separated by a distance r exerts an electrostatic force on each other given by
${F_e}\; = \;K\;\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
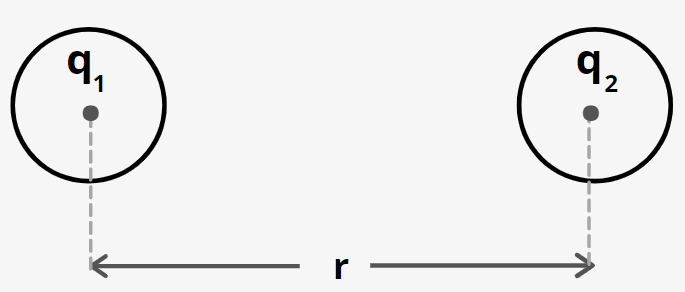
where k is a constant.
- The value of k is
$K = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}\;N{m^2}/{C^2}$
- It can be attractive or repulsive
- For similar charges, it is repulsive
- For opposite charges, it is attractive in nature.
(a) (i) Ratio of Coulomb force to gravitational force for an electron and a proton Here,
\[
{q_1} = e = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}\;c \\
{q_2} = p = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}\;c \\
\]
Mass of electron \[({m_1}) = \;9.1\; \times \;{10^{ - 31}}kg\]
Mass of proton \[({m_2}) = 1.67\; \times \;{10^{ - 27}}kg\]
Required ratio $({r_1}) = \;\dfrac{{{F_e}}}{{{F_g}}}\; = \;\dfrac{{K\;\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}{{G\dfrac{{{m_1}\,m{}_2}}{{{r^2}}}}}$
${r_1}\; = \;\dfrac{{K\; \times \;{q_1}\; \times \;{q_2}}}{{G\; \times \;{m_1}\; \times \;{m_2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{9\, \times \,{{10}^9}\, \times \,(1.6\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 19}})\, \times \,(1.6\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 19}})}}{{6.67\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 11}}\, \times \,9.1\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 31}}\, \times \,1.67\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 27}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{2.27\; \times \;{{10}^{39}}}}{1}$
(ii) Ratio of Coulomb force to gravitational force of two protons is
\[{r_2}\; = \;\dfrac{{K\; \times \;\dfrac{{{q_1} \times {q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}{{G\; \times \;\dfrac{{{m_1} \times {m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}\]
Here,
\[{q_1} = {q_2} = p = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}C\]
Mass of proton ${m_1} = {m_2} = 1.67 \times {10^{ - 27}}kg$
So, ${r_2} = \dfrac{{K\,q_1^2}}{{G\,m_1^2}}$
${r_2} = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}})}}{{6.67 \times {{10}^{ - 11}} \times {{(1.67 \times {{10}^{ - 27}})}^2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{1.24 \times {{10}^{36}}}}{1}$
(b) Coulomb force between electron and proton is given by
$F = K\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Here
\[{q_1} = e = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}c\]
\[{q_2} = p = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}c\]
\[r = 1{A^\circ } = {10^{ - 10}}m\]
So,
$F = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}) \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}) \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}})}}{{{{({{10}^{ - 10}})}^2}}}$
$F = 2.304 \times {10^{ - 8}}N$
Now, according to Newton’s second law, $F = ma\;\; \Rightarrow \;\;a = F/m$.
So, acceleration of electron will be
\[{a_1} = {\dfrac{F}{m}_1}\] Where m$ = $ mass of electron $({m_1} = 9.1 \times {10^{ - 31}}kg)$
$\implies {a_1} = \dfrac{{2.30\,4 \times {{10}^{ - 8}}}}{{9.1 \times {{10}^{ - 31}}}}$
$\implies {a_1} = 2.5 \times {10^{22}}\,m/{s^2}$
The acceleration for proton is given by
\[{a_2} = {\dfrac{F}{m}_2}\]
Where ${m_2} = $ mass of proton, $({m_2} = 1.67 \times {10^{ - 27}}kg)$
So,
${a_2} = \dfrac{{2.304 \times {{10}^{ - 8}}}}{{1.67 \times {{10}^{ - 27}}}}$
$\therefore {a_2} = 1.4 \times {10^{19}}m/{s^2}$.
Note:
Remember although charges on both electron and proton are equal but they are equal only in magnitude but opposite in their polarity. Also proton is heavier than that of electrons although both have the same charges.Moreover,a French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb in 1785 coined a tangible relationship in mathematical form between two bodies that have been electrically charged. He published an equation for the force causing the bodies to attract or repel each other which is known as Coulomb’s law or Coulomb’s inverse-square law.
Formula used:
1. Gravitational force
${F_g} = G\dfrac{{{m_1}\,{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where ${m_1}$and${m_2}$ are masses of two bodies separated by a distance $r$.
G is the gravitational constant.
2. Electrostatic force
${F_e} = K\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where ${q_1}$and${q_2}$ are masses of two bodies separated by a distance $r$.
K is a constant.
Complete step by step solution:
Gravitational Force – According to universal law of gravitation each and every object in this universe attracts another object with a force given by
${F_g} = G\;\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$

Where ${m_1}\;and\,\;{m_2}$ are two particles separated by a distance of r.
- It follows inverse square law
- Gravitational force is always attractive in nature
- G is the universal gravitational constant and $G = 6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}$
- Coulomb’s law: According to Coulomb’s s law, two charge particles of charges ${q_1}\;and\;{q_2}$ and separated by a distance r exerts an electrostatic force on each other given by
${F_e}\; = \;K\;\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
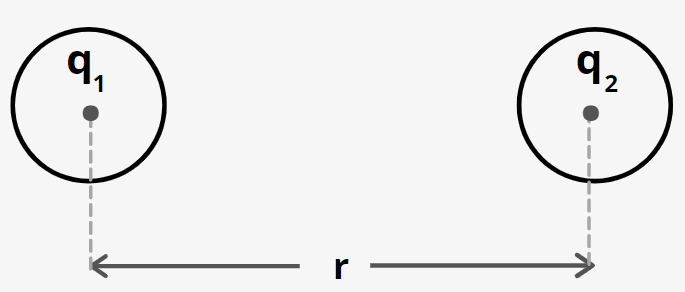
where k is a constant.
- The value of k is
$K = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}\;N{m^2}/{C^2}$
- It can be attractive or repulsive
- For similar charges, it is repulsive
- For opposite charges, it is attractive in nature.
(a) (i) Ratio of Coulomb force to gravitational force for an electron and a proton Here,
\[
{q_1} = e = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}\;c \\
{q_2} = p = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}\;c \\
\]
Mass of electron \[({m_1}) = \;9.1\; \times \;{10^{ - 31}}kg\]
Mass of proton \[({m_2}) = 1.67\; \times \;{10^{ - 27}}kg\]
Required ratio $({r_1}) = \;\dfrac{{{F_e}}}{{{F_g}}}\; = \;\dfrac{{K\;\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}{{G\dfrac{{{m_1}\,m{}_2}}{{{r^2}}}}}$
${r_1}\; = \;\dfrac{{K\; \times \;{q_1}\; \times \;{q_2}}}{{G\; \times \;{m_1}\; \times \;{m_2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{9\, \times \,{{10}^9}\, \times \,(1.6\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 19}})\, \times \,(1.6\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 19}})}}{{6.67\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 11}}\, \times \,9.1\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 31}}\, \times \,1.67\, \times \,{{10}^{ - 27}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{2.27\; \times \;{{10}^{39}}}}{1}$
(ii) Ratio of Coulomb force to gravitational force of two protons is
\[{r_2}\; = \;\dfrac{{K\; \times \;\dfrac{{{q_1} \times {q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}{{G\; \times \;\dfrac{{{m_1} \times {m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}\]
Here,
\[{q_1} = {q_2} = p = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}C\]
Mass of proton ${m_1} = {m_2} = 1.67 \times {10^{ - 27}}kg$
So, ${r_2} = \dfrac{{K\,q_1^2}}{{G\,m_1^2}}$
${r_2} = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}})}}{{6.67 \times {{10}^{ - 11}} \times {{(1.67 \times {{10}^{ - 27}})}^2}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{1.24 \times {{10}^{36}}}}{1}$
(b) Coulomb force between electron and proton is given by
$F = K\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Here
\[{q_1} = e = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}c\]
\[{q_2} = p = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}c\]
\[r = 1{A^\circ } = {10^{ - 10}}m\]
So,
$F = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}) \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}) \times (1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}})}}{{{{({{10}^{ - 10}})}^2}}}$
$F = 2.304 \times {10^{ - 8}}N$
Now, according to Newton’s second law, $F = ma\;\; \Rightarrow \;\;a = F/m$.
So, acceleration of electron will be
\[{a_1} = {\dfrac{F}{m}_1}\] Where m$ = $ mass of electron $({m_1} = 9.1 \times {10^{ - 31}}kg)$
$\implies {a_1} = \dfrac{{2.30\,4 \times {{10}^{ - 8}}}}{{9.1 \times {{10}^{ - 31}}}}$
$\implies {a_1} = 2.5 \times {10^{22}}\,m/{s^2}$
The acceleration for proton is given by
\[{a_2} = {\dfrac{F}{m}_2}\]
Where ${m_2} = $ mass of proton, $({m_2} = 1.67 \times {10^{ - 27}}kg)$
So,
${a_2} = \dfrac{{2.304 \times {{10}^{ - 8}}}}{{1.67 \times {{10}^{ - 27}}}}$
$\therefore {a_2} = 1.4 \times {10^{19}}m/{s^2}$.
Note:
Remember although charges on both electron and proton are equal but they are equal only in magnitude but opposite in their polarity. Also proton is heavier than that of electrons although both have the same charges.Moreover,a French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb in 1785 coined a tangible relationship in mathematical form between two bodies that have been electrically charged. He published an equation for the force causing the bodies to attract or repel each other which is known as Coulomb’s law or Coulomb’s inverse-square law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




