
What is the correct product in the given reaction?
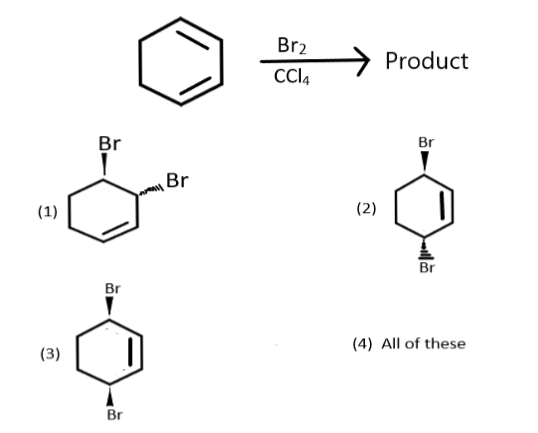

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: As we all know that bromine is much more soluble in chloroform than water so in bromination reaction when bromine interacts with chloroform a dipole-dipole interaction arises and bromine dissociates into cation and anion which acts as electrophile and nucleophile respectively.
Complete Step by step answer: We all know that bromine is much more soluble in chloroform than water so during bromination reaction when bromine interacts with chloroform a dipole-dipole interaction arises and bromine dissociates into cation and anion which acts as electrophile and nucleophile respectively.
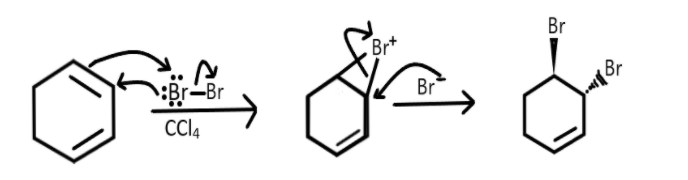
This is an example of electrophilic addition reaction. As we know that when bromine reacts with double bonds containing compounds it results in reduction of these bonds and addition of bromine to both the carbons to give a dibromide compounds. Similarly when it will react with the given reactant then the formation of intermediate will take place and one bromine will be attached with the carbon atoms on first and second position and the remaining bromine will then act as a nucleophile and attack the carbon on second position leading to the formation of a dibromide compound, which we can show as the following:
Therefore the correct answer is (1).
Note: Benzene will only react with halogen in the presence of halogen carrier like $FeC{l_3}$ which acts as a catalyst but when benzene is reacted with $B{r_2}$/$CC{l_4}$ it will not form any product due to the delocalised electrons of benzene which are spread over all six atoms of carbon and thus has lower pi-electron density to polarise the bromine whereas a cyclohexane will react like a typical alkene with the bromine atoms when added across the double bond and take part in the electrophilic addition reaction like every other alkene. It also changes its orange colour when reacting with cyclohexane but when reacted with benzene bromine’s orange colour remains as such and no reaction takes place.
Complete Step by step answer: We all know that bromine is much more soluble in chloroform than water so during bromination reaction when bromine interacts with chloroform a dipole-dipole interaction arises and bromine dissociates into cation and anion which acts as electrophile and nucleophile respectively.
This is an example of electrophilic addition reaction. As we know that when bromine reacts with double bonds containing compounds it results in reduction of these bonds and addition of bromine to both the carbons to give a dibromide compounds. Similarly when it will react with the given reactant then the formation of intermediate will take place and one bromine will be attached with the carbon atoms on first and second position and the remaining bromine will then act as a nucleophile and attack the carbon on second position leading to the formation of a dibromide compound, which we can show as the following:

Therefore the correct answer is (1).
Note: Benzene will only react with halogen in the presence of halogen carrier like $FeC{l_3}$ which acts as a catalyst but when benzene is reacted with $B{r_2}$/$CC{l_4}$ it will not form any product due to the delocalised electrons of benzene which are spread over all six atoms of carbon and thus has lower pi-electron density to polarise the bromine whereas a cyclohexane will react like a typical alkene with the bromine atoms when added across the double bond and take part in the electrophilic addition reaction like every other alkene. It also changes its orange colour when reacting with cyclohexane but when reacted with benzene bromine’s orange colour remains as such and no reaction takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




