
How many copies of DNA samples are produced in the PCR technique after 6-cycles?
(a) 4
(b) 32
(c) 64
(d) 16
Answer
532.6k+ views
Hint: From a single DNA sample, after completion of one cycle two copies of that DNA is produced which increases in the later cycles.
Complete answer:
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technique that is used to make millions of copies of a sample DNA very rapidly. After the completion of each cycle, two copies of DNA samples are produced. So, that means after the second cycle, it will produce 4 copies of DNA sample, then after the third cycle, 8 copies are produced, after the fourth cycle, 16 copies are produced, after the fifth cycle, 32 copies are produced, and lastly, after the sixth cycle, 64 copies of DNA samples are produced.
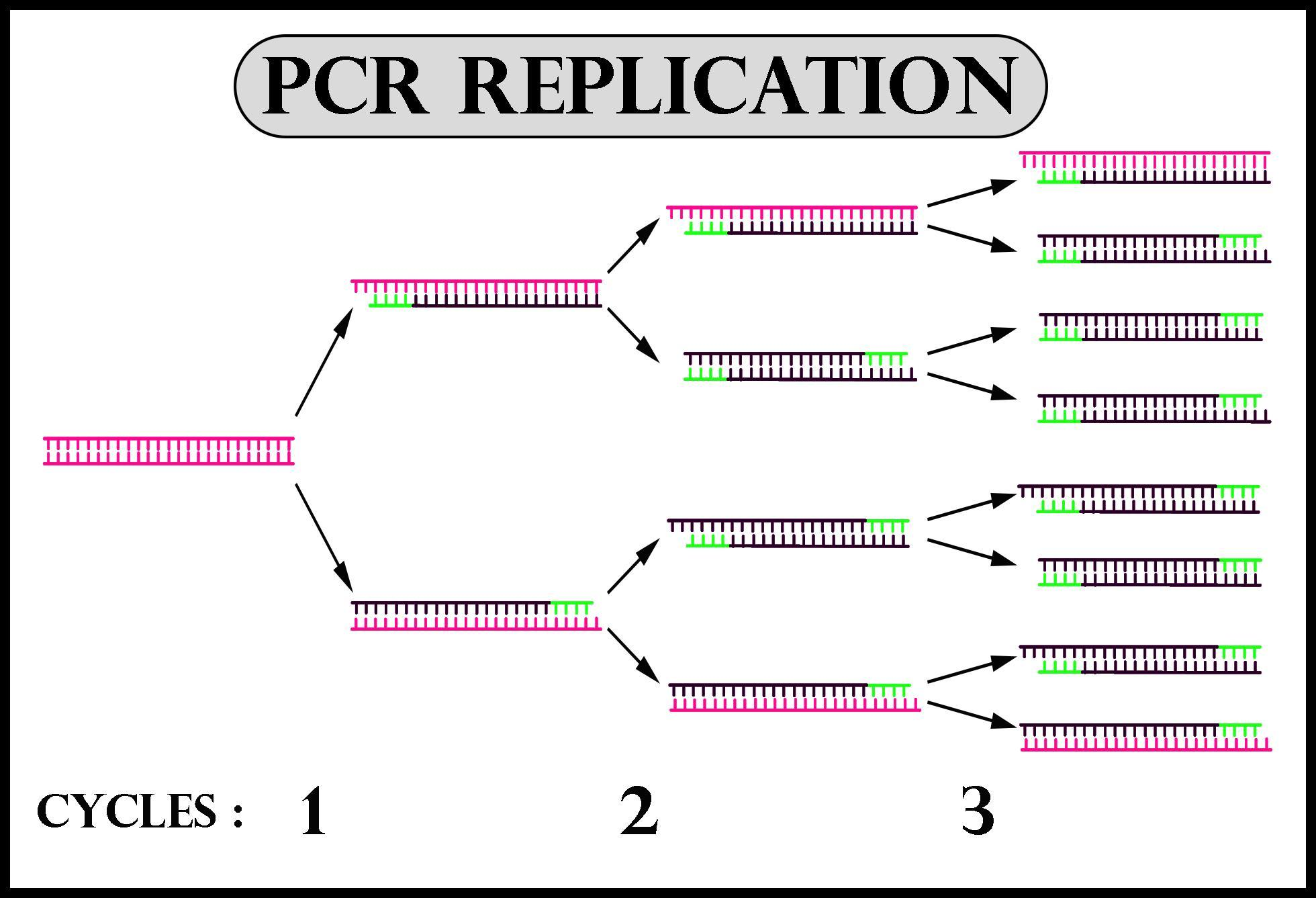
- The PCR technique is very conventional, as it allows scientists to take a very small amount of DNA samples.
- It is used in making copies of those species which are extinct or are endangered to study afterward.
- The PCR technique is based on thermal cycling which involves the heating and cooling of reactants at various temperatures.
- It has two main reagents: primers (short single- stranded DNA fragments that are a complementary sequence to the target DNA), and DNA polymerase.
- The DNA polymerase is heat stable, that is Taq polymerase which is extracted from the bacteria Thermus aquaticus.
So, the correct answer is ‘64’.
Note: The Polymerase Chain Reaction was invented by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation in 1984. It has wide applications which include DNA cloning, gene mutagenesis, gene cloning, diagnosis of hereditary diseases, amplifying the ancient DNA, used in the analysis of genetic fingerprints in forensic science and paternity testing, and the detection of pathogens that are causing infectious diseases.
Complete answer:
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technique that is used to make millions of copies of a sample DNA very rapidly. After the completion of each cycle, two copies of DNA samples are produced. So, that means after the second cycle, it will produce 4 copies of DNA sample, then after the third cycle, 8 copies are produced, after the fourth cycle, 16 copies are produced, after the fifth cycle, 32 copies are produced, and lastly, after the sixth cycle, 64 copies of DNA samples are produced.

- The PCR technique is very conventional, as it allows scientists to take a very small amount of DNA samples.
- It is used in making copies of those species which are extinct or are endangered to study afterward.
- The PCR technique is based on thermal cycling which involves the heating and cooling of reactants at various temperatures.
- It has two main reagents: primers (short single- stranded DNA fragments that are a complementary sequence to the target DNA), and DNA polymerase.
- The DNA polymerase is heat stable, that is Taq polymerase which is extracted from the bacteria Thermus aquaticus.
So, the correct answer is ‘64’.
Note: The Polymerase Chain Reaction was invented by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation in 1984. It has wide applications which include DNA cloning, gene mutagenesis, gene cloning, diagnosis of hereditary diseases, amplifying the ancient DNA, used in the analysis of genetic fingerprints in forensic science and paternity testing, and the detection of pathogens that are causing infectious diseases.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




