
How do you convert the following?
(i) Isopropyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol
(ii) n- Propyl alcohol to Isopropyl alcohol
(iii) Isopropyl alcohol to n- Propyl alcohol
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, first we should know the structure of the compound given in the following conversions, then note the difference between the two compounds in each conversion and observe which changes are occurring such as change in functional group or change in the number of carbon atoms. We can observe whether oxidation or reduction is happening.
Complete answer:
Let us completely understand the following conversions.
(i) Isopropyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol
First, look at the structures of isopropyl alcohol and tert-butyl alcohol.
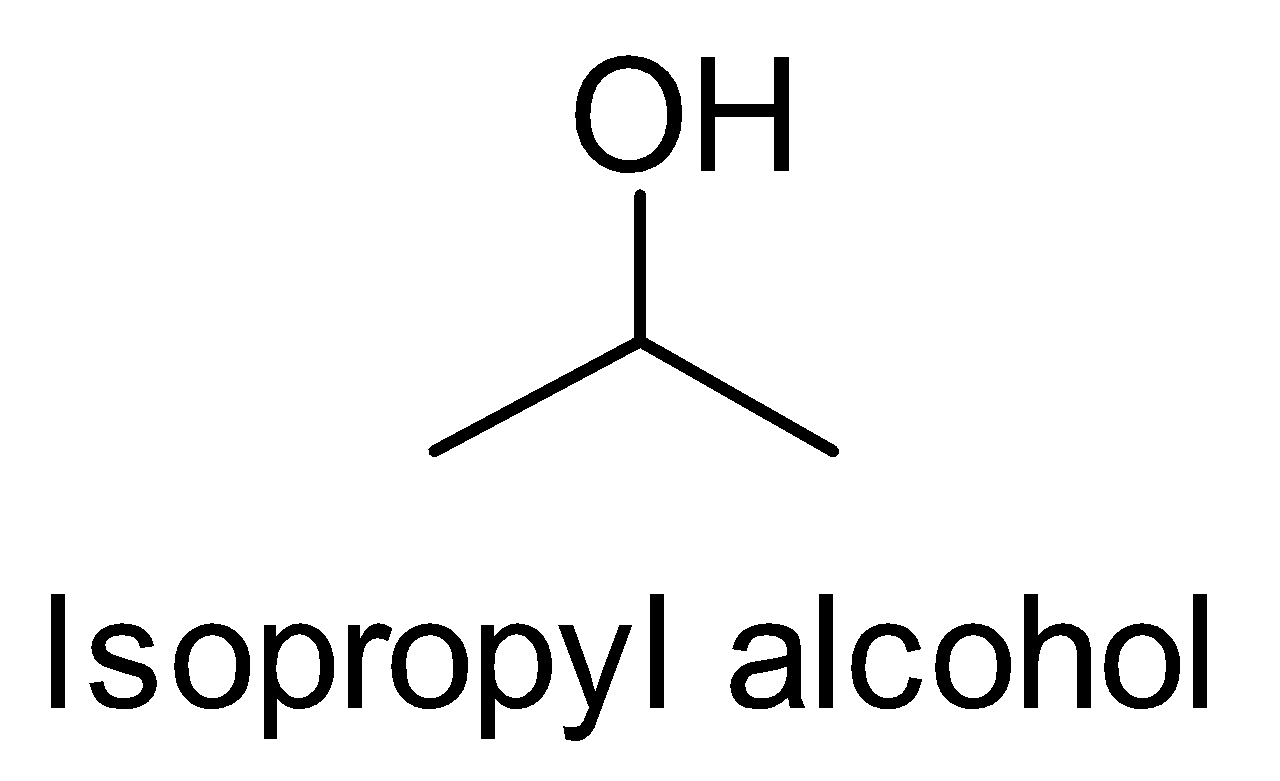
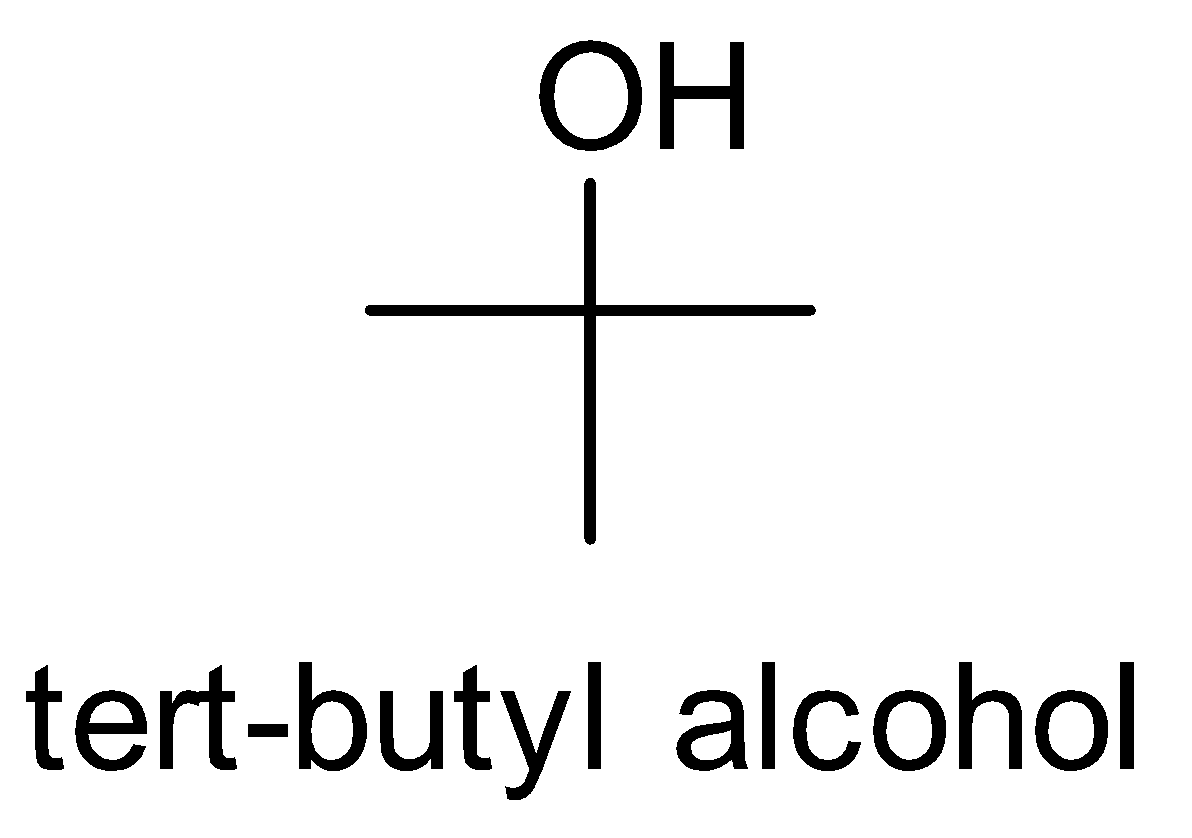
We observe that the functional group is the same but one carbon is more in tert-butyl alcohol. So we treat the isopropyl alcohol with Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis.
Reaction conversion is as follows:
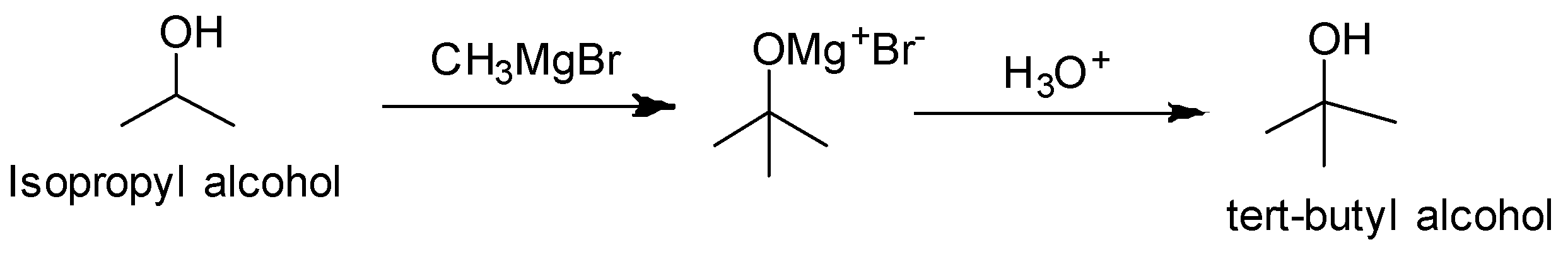
(ii) n- Propyl alcohol to Isopropyl alcohol
Let’s look at the structures of n- Propyl alcohol and Isopropyl alcohol.

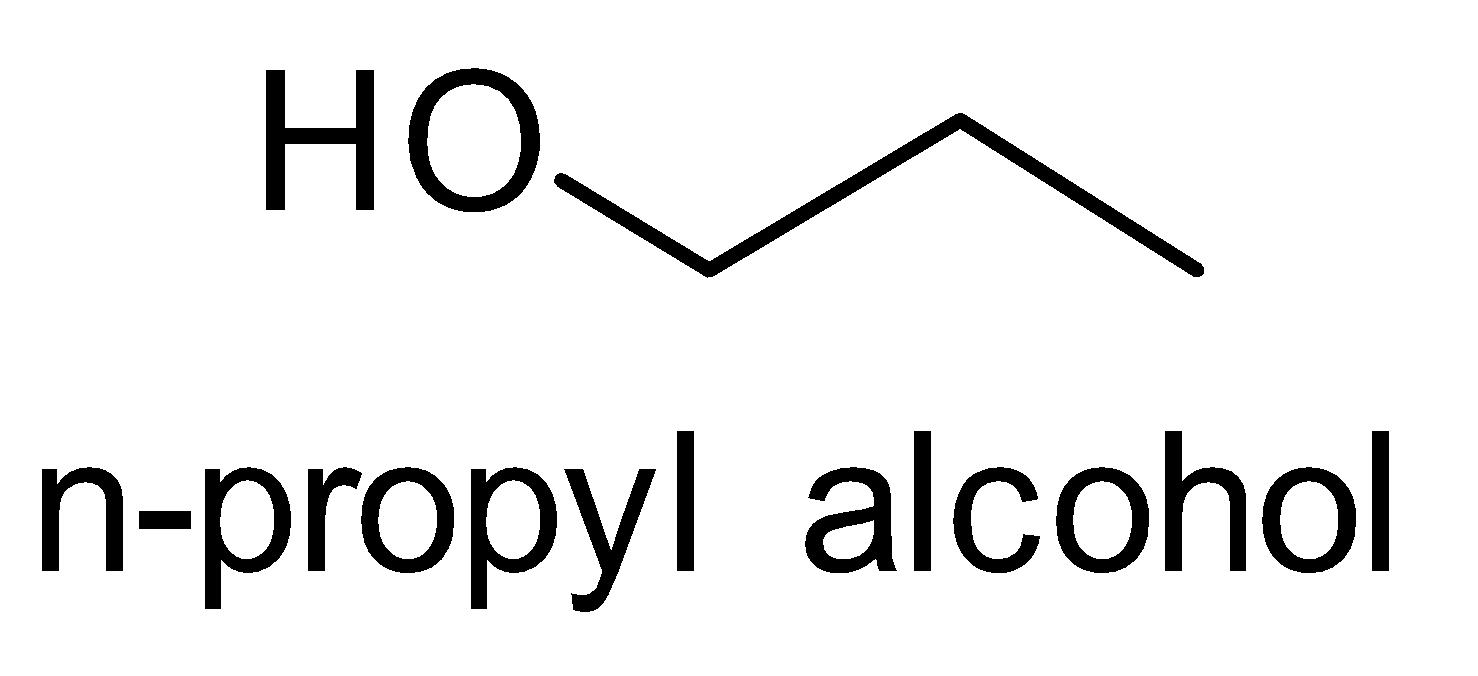
We observe that the number of carbons remains the same, only the position of the functional group i.e. hydroxyl group changes. So we treat the n-propyl alcohol with sulphuric acid followed by hydrolysis.
Reaction conversion is as follows:

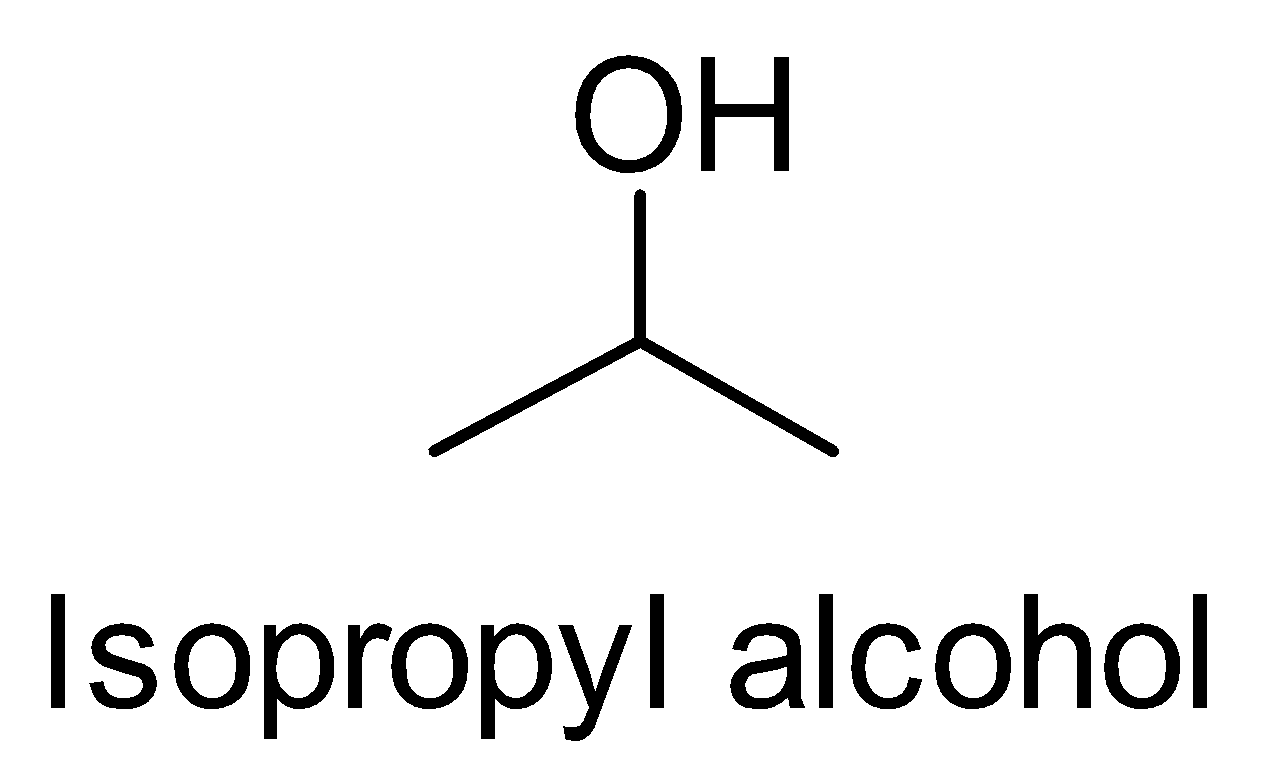
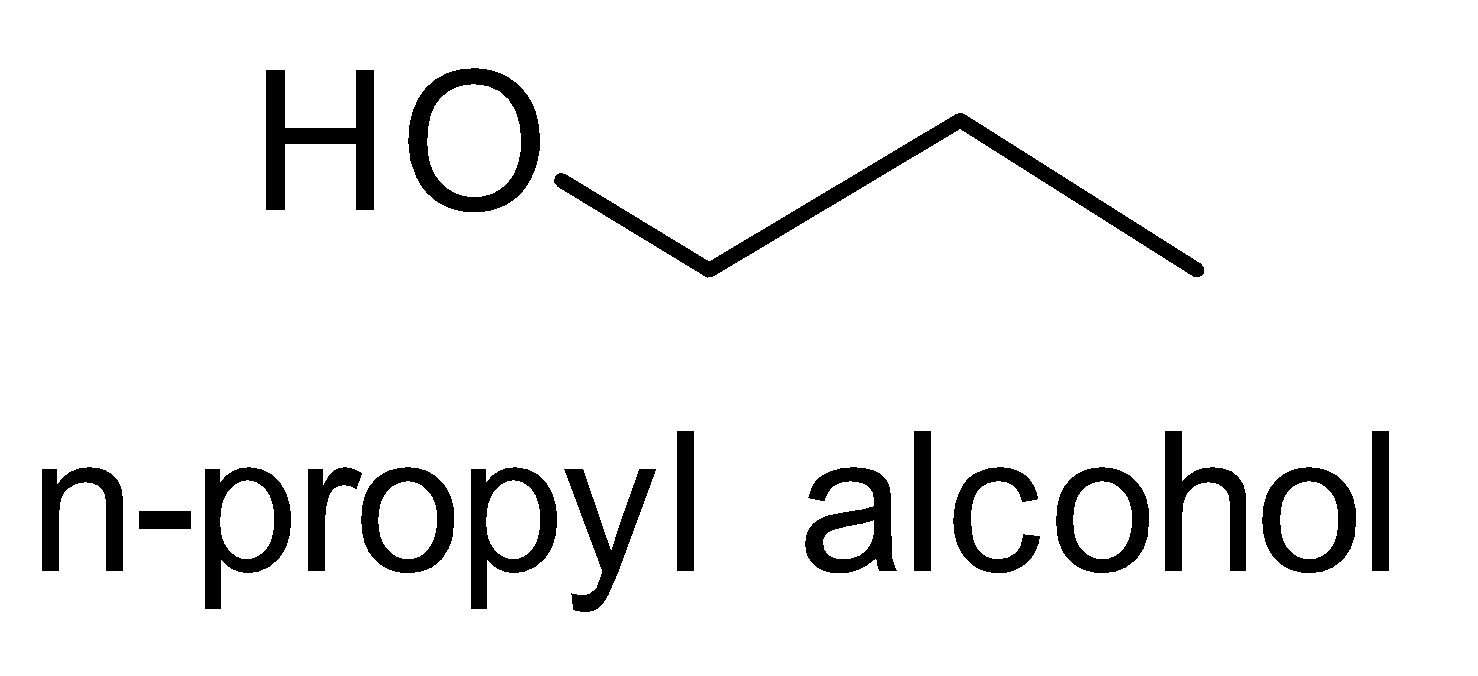
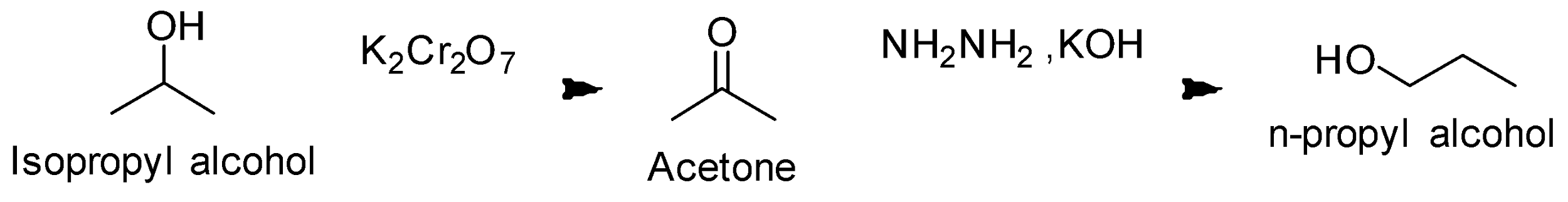
(iii) Isopropyl alcohol to n- Propyl alcohol
Let’s look at the structures of Isopropyl alcohol to n- Propyl alcohol. This conversion is the reverse of the
(ii)
Reaction conversion is as follows;
Note:
We must remember the reagents and their functions. For example- in this question, Grignard reagent is very important for the carbon –carbon bond. Here, Potassium Dichromate is also used which is a strong oxidizing agent.
Complete answer:
Let us completely understand the following conversions.
(i) Isopropyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol
First, look at the structures of isopropyl alcohol and tert-butyl alcohol.


We observe that the functional group is the same but one carbon is more in tert-butyl alcohol. So we treat the isopropyl alcohol with Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis.
Reaction conversion is as follows:

(ii) n- Propyl alcohol to Isopropyl alcohol
Let’s look at the structures of n- Propyl alcohol and Isopropyl alcohol.


We observe that the number of carbons remains the same, only the position of the functional group i.e. hydroxyl group changes. So we treat the n-propyl alcohol with sulphuric acid followed by hydrolysis.
Reaction conversion is as follows:

(iii) Isopropyl alcohol to n- Propyl alcohol
Let’s look at the structures of Isopropyl alcohol to n- Propyl alcohol. This conversion is the reverse of the
(ii)


Reaction conversion is as follows;

Note:
We must remember the reagents and their functions. For example- in this question, Grignard reagent is very important for the carbon –carbon bond. Here, Potassium Dichromate is also used which is a strong oxidizing agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




