
Convert the following:
1.Chlorobenzene to Aniline
2.${{{C}}_{{2}}}{{{H}}_{{5}}}{{Br}}$ to ethyl acetate
3. Chloropropane to fluoropropane
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Chlorobenzene is converted into benzene followed by nitration gives a nitrobenzene. By the reduction of nitrobenzene given aniline. Halides are converted into alcohols then oxidation gives acetates. Alkanes are converted into Alkenes by dehydrogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
The chlorobenzene is reacted with alcoholic potassium hydroxide at approximately $400^oC$ to give phenol which is passed via zinc dust to form benzene.
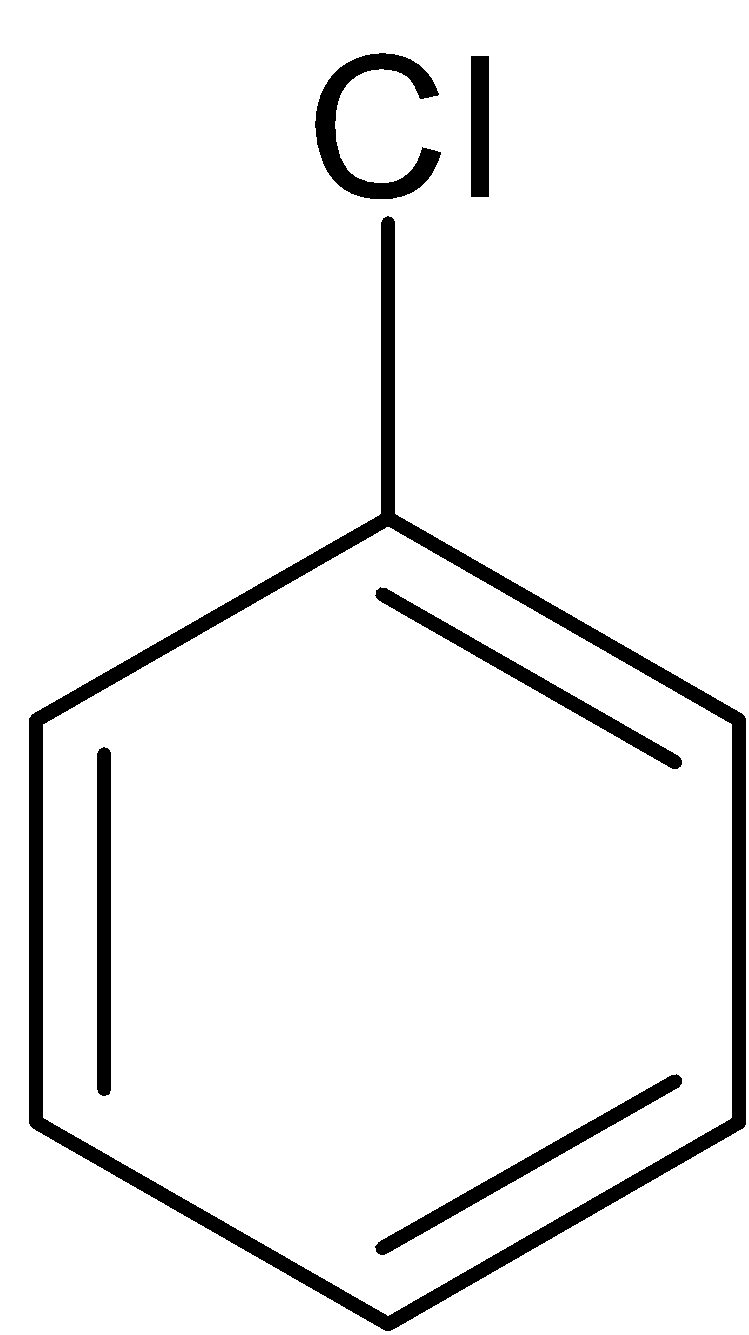 $\xrightarrow[{{{40}}{{{0}}^ \circ }{{C}}}]{{{{alc}}{{.KOH}}}}$
$\xrightarrow[{{{40}}{{{0}}^ \circ }{{C}}}]{{{{alc}}{{.KOH}}}}$
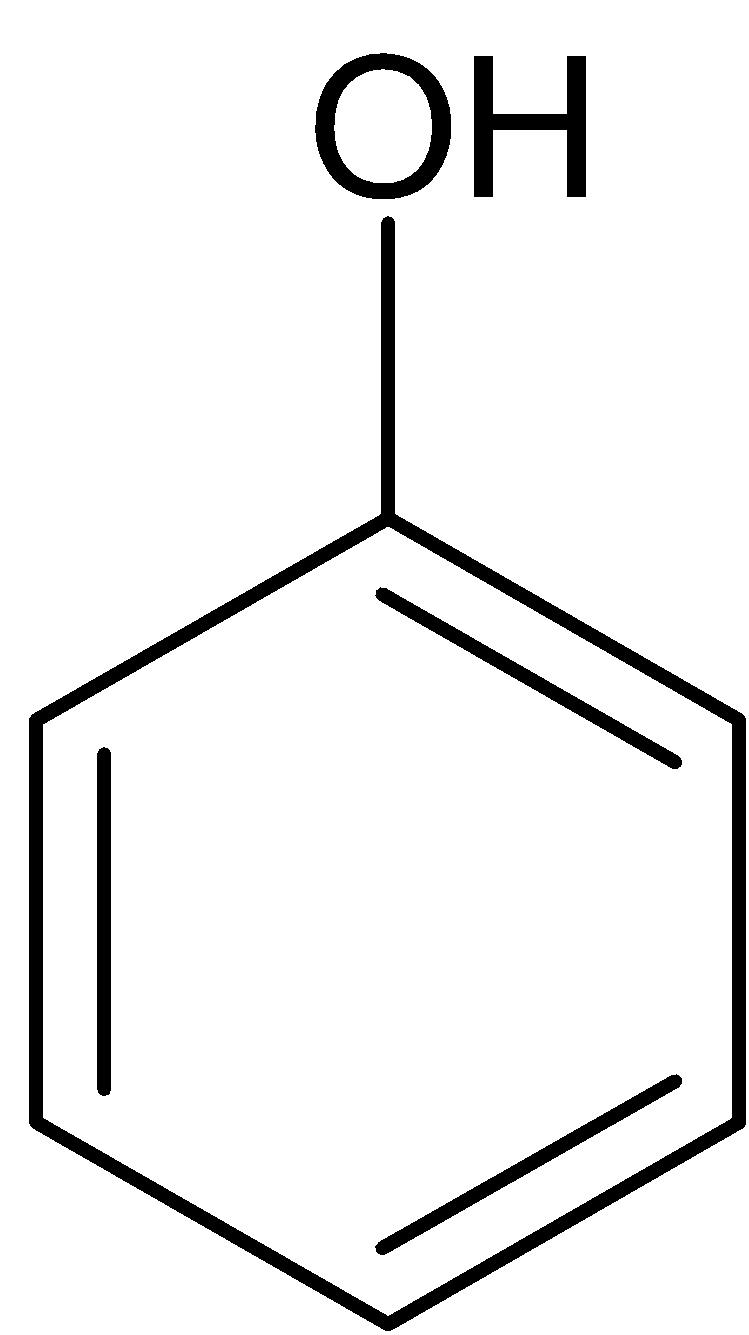 $\xrightarrow{{{{Zn}}}}$
$\xrightarrow{{{{Zn}}}}$
Step 2:
The benzene is further reacted with sulfuric acid and nitric acid (nitration reaction), to form nitrobenzene which is treated with hydrochloric acid in presence of tin catalyst to form aniline.
 $\xrightarrow{{{{{H}}_2}{{S}}{{{O}}_4} + {{HN}}{{{O}}_3}}}$
$\xrightarrow{{{{{H}}_2}{{S}}{{{O}}_4} + {{HN}}{{{O}}_3}}}$
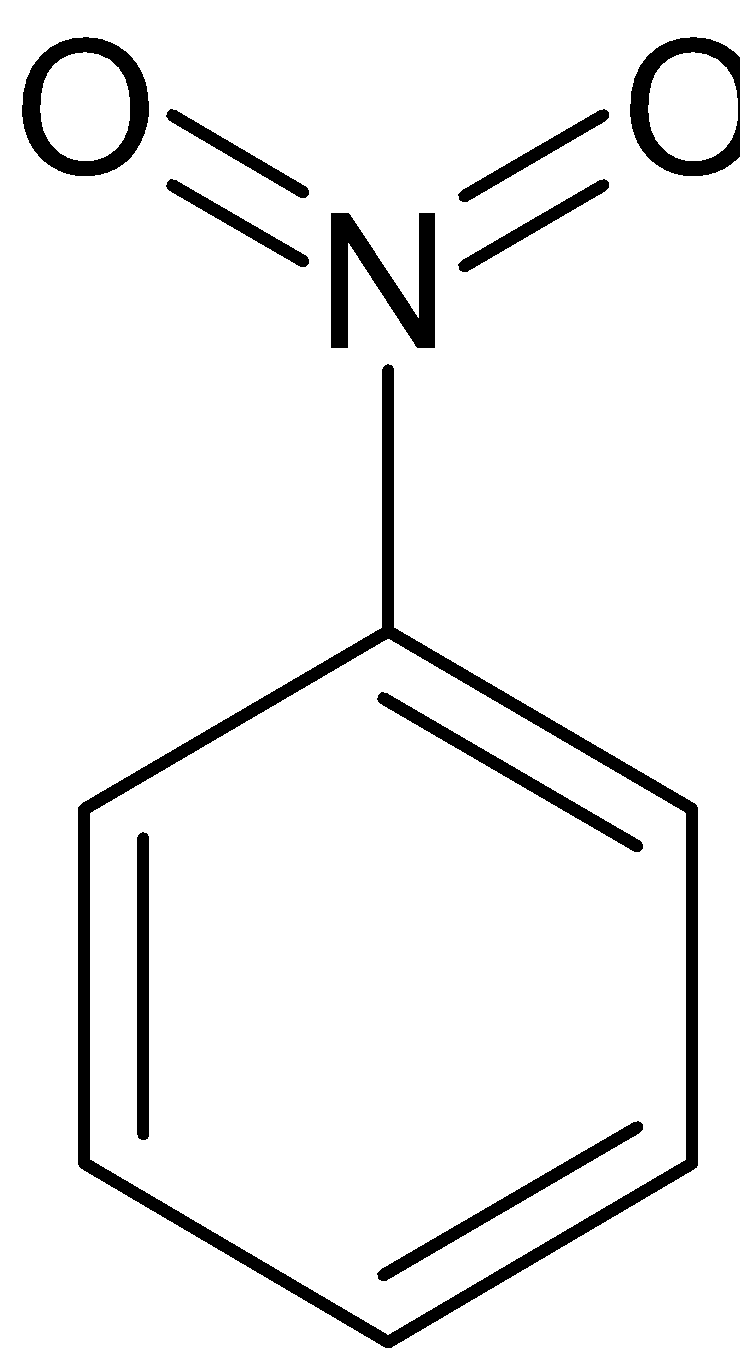 $\xrightarrow{{{{Sn}} + {{HCl}}}}$
$\xrightarrow{{{{Sn}} + {{HCl}}}}$
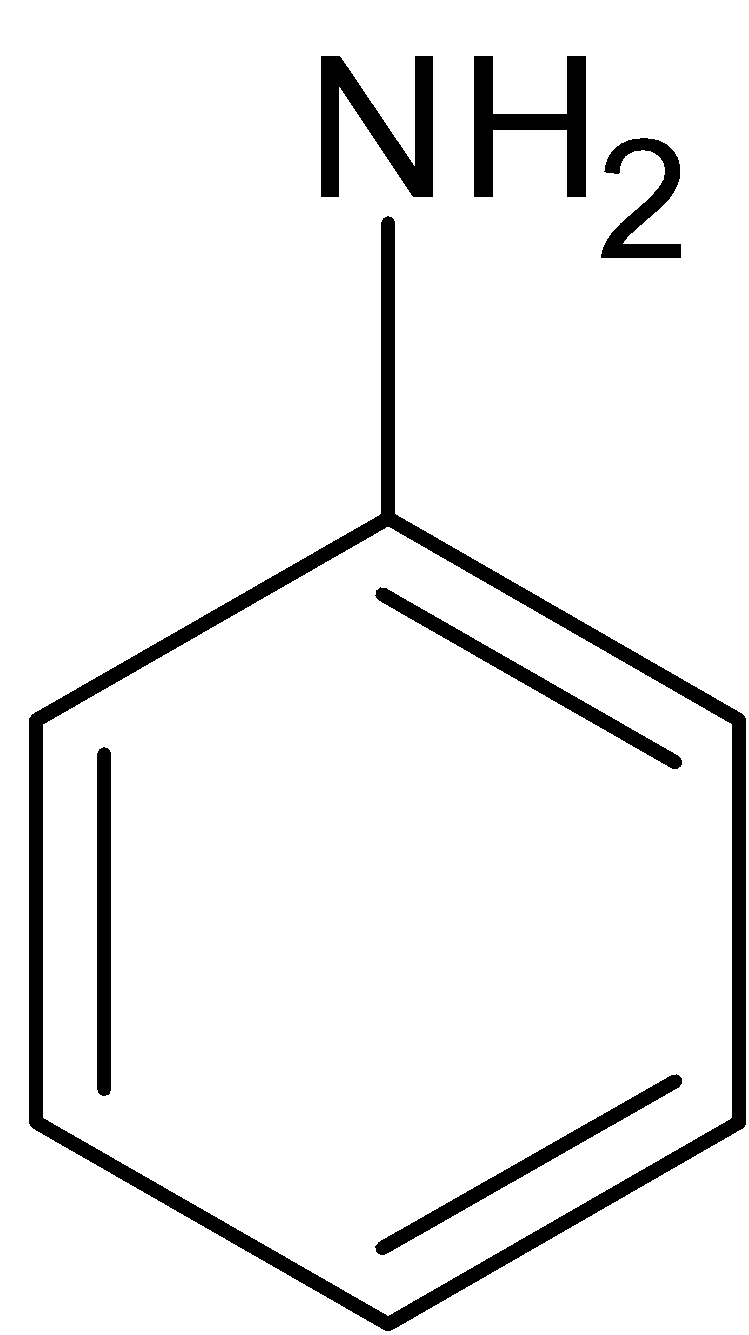
Conversion ${{{C}}_{{2}}}{{{H}}_{{5}}}{{Br}}$to ethyl acetate:
Step 1:
The ethyl bromide reacts with aqueous potassium hydroxide to form ethyl alcohol.
Reaction involved:
${{{C}}_2}{{{H}}_5}{{Br + aq}}{{. KOH}} \to {{{C}}_2}{{{H}}_5}{{OH + HBr}}$
Step 2:
Then, the formed acid is oxidized in presence of ${{KMn}}{{{O}}_4}$to produce acetic acid or ethyl acetate.
${{{C}}_2}{{{H}}_5}{{OH}}\xrightarrow[{\left[ {{O}} \right]}]{{{{KMn}}{{{O}}_4}}}{{C}}{{{H}}_3}{{COOH}}$
Chloropropane to fluoropropane:
Step 1:
Chloropropane is first converted to propene by the use of alcoholic potassium hydroxide, which is a beta-elimination reaction.
${{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{Cl + alc}}{{.KOH}} \to {{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_6} + {{HCl}}$
Step 2:
Propene is converted to bromopropane by the addition of HBr in the presence of peroxide.
It follows Anti-Markovnikov's rule:
${{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_6}\xrightarrow[{{{peroxide}}}]{{{{HBr}}}}{{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{Br}}$
Step 3:
Alkyl fluoride is formed when an alkyl halide is treated with a fluorine compound namely \[{{AgF,Sb}}{{{F}}_{{3}}}{{,H}}{{{g}}_{{2}}}{{{F}}_{{2}}}{{ etc}}\].This is a Swartz reaction.
${{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{Br + AgF}} \to {{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{F + AgBr}}$
Additional Information:
-Aniline is an organic compound having phenyl groups attached to an amino group. It is a commodity chemical that is industrially important, as well as a highly customizable basic material for great synthetic chemistry.
-Aqueous \[{{KOH}}\] is alkaline, meaning it dissociates to produce hydroxide ion. As a strong nucleophile, these hydroxide ions replace the halogen atom in an alkyl halide. This reacts to give alcohol and the reaction is referred to as nucleophilic substitution.
Note:
Aniline reacts with acyl chlorides to give amides. Amides which are formed from anilines are often referred to as anilides. Propene, often called as propylene or methyl ethylene, has the chemical formula ${{{C}}_{{3}}}{{{H}}_{{6}}}$, which is unsaturated. It has only one double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
The chlorobenzene is reacted with alcoholic potassium hydroxide at approximately $400^oC$ to give phenol which is passed via zinc dust to form benzene.



Step 2:
The benzene is further reacted with sulfuric acid and nitric acid (nitration reaction), to form nitrobenzene which is treated with hydrochloric acid in presence of tin catalyst to form aniline.



Conversion ${{{C}}_{{2}}}{{{H}}_{{5}}}{{Br}}$to ethyl acetate:
Step 1:
The ethyl bromide reacts with aqueous potassium hydroxide to form ethyl alcohol.
Reaction involved:
${{{C}}_2}{{{H}}_5}{{Br + aq}}{{. KOH}} \to {{{C}}_2}{{{H}}_5}{{OH + HBr}}$
Step 2:
Then, the formed acid is oxidized in presence of ${{KMn}}{{{O}}_4}$to produce acetic acid or ethyl acetate.
${{{C}}_2}{{{H}}_5}{{OH}}\xrightarrow[{\left[ {{O}} \right]}]{{{{KMn}}{{{O}}_4}}}{{C}}{{{H}}_3}{{COOH}}$
Chloropropane to fluoropropane:
Step 1:
Chloropropane is first converted to propene by the use of alcoholic potassium hydroxide, which is a beta-elimination reaction.
${{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{Cl + alc}}{{.KOH}} \to {{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_6} + {{HCl}}$
Step 2:
Propene is converted to bromopropane by the addition of HBr in the presence of peroxide.
It follows Anti-Markovnikov's rule:
${{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_6}\xrightarrow[{{{peroxide}}}]{{{{HBr}}}}{{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{Br}}$
Step 3:
Alkyl fluoride is formed when an alkyl halide is treated with a fluorine compound namely \[{{AgF,Sb}}{{{F}}_{{3}}}{{,H}}{{{g}}_{{2}}}{{{F}}_{{2}}}{{ etc}}\].This is a Swartz reaction.
${{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{Br + AgF}} \to {{{C}}_3}{{{H}}_7}{{F + AgBr}}$
Additional Information:
-Aniline is an organic compound having phenyl groups attached to an amino group. It is a commodity chemical that is industrially important, as well as a highly customizable basic material for great synthetic chemistry.
-Aqueous \[{{KOH}}\] is alkaline, meaning it dissociates to produce hydroxide ion. As a strong nucleophile, these hydroxide ions replace the halogen atom in an alkyl halide. This reacts to give alcohol and the reaction is referred to as nucleophilic substitution.
Note:
Aniline reacts with acyl chlorides to give amides. Amides which are formed from anilines are often referred to as anilides. Propene, often called as propylene or methyl ethylene, has the chemical formula ${{{C}}_{{3}}}{{{H}}_{{6}}}$, which is unsaturated. It has only one double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




