
Convert isopropyl alcohol to iodoform.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:To answer this question, you should recall the concept of oxidation of alcohol and iodoform reaction. Alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde with a methyl group in alpha position and then treated with a strong base and iodine to form iodoform.
Complete step by step solution:
This reaction is known as Jones oxidation which is used to oxidize alcohols using chromic trioxide and acid in water. A primary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde or all the way to a carboxylic acid, while a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
The mechanism begins with the reaction of \[Cr{O_3}\] with acid (often \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) to form chromic acid or dichromic acid in more concentrated solutions. The alcohol oxidation then occurs with chromic acid which in turn gets reduced in the process.
When Iodine in presence of a base like sodium hydroxide is added to a compound that contains either a methyl ketone or a secondary alcohol with a methyl group in the alpha position, a pale-yellow precipitate of iodoform or triiodomethane is formed. It can be used to identify aldehydes or ketones.
The reaction mechanism of the above described reaction can be written as:
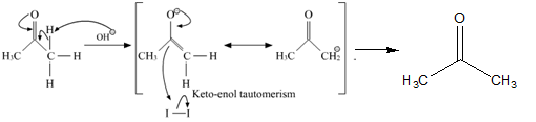
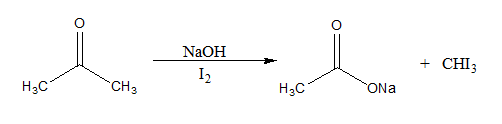
Here, the $CH{I_3}$ formed is a yellow precipitate known as iodoform.
Note:
If an aldehyde gives a positive iodoform test, then it must be acetaldehyde since it is the only aldehyde with a \[C{H_3}C = O\] group. First, the Hydroxide ion removes an acidic alpha hydrogen. This results in the formation of an enolate ion. The enolate anion then goes on to displace an iodide ion from the iodine molecule. This process repeats twice to give \[R - CO - C{I_3}\]. Now, a hydroxide ion forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon. This leads to the reformation of the carbonyl group and the elimination of \[C{I_3}^ - \] anion. A \[R - COOH\] group is also formed. The carboxylic acid group and the basic \[C{I_3}^ - \] ions neutralize each other. Thus, iodoform is precipitated.
Complete step by step solution:
This reaction is known as Jones oxidation which is used to oxidize alcohols using chromic trioxide and acid in water. A primary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde or all the way to a carboxylic acid, while a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
The mechanism begins with the reaction of \[Cr{O_3}\] with acid (often \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) to form chromic acid or dichromic acid in more concentrated solutions. The alcohol oxidation then occurs with chromic acid which in turn gets reduced in the process.
When Iodine in presence of a base like sodium hydroxide is added to a compound that contains either a methyl ketone or a secondary alcohol with a methyl group in the alpha position, a pale-yellow precipitate of iodoform or triiodomethane is formed. It can be used to identify aldehydes or ketones.
The reaction mechanism of the above described reaction can be written as:

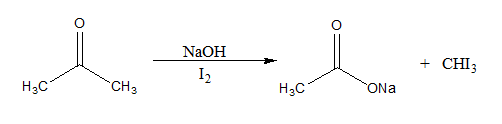
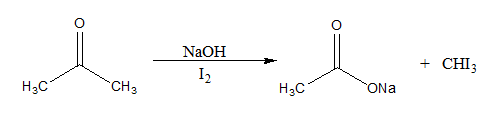
Here, the $CH{I_3}$ formed is a yellow precipitate known as iodoform.
Note:
If an aldehyde gives a positive iodoform test, then it must be acetaldehyde since it is the only aldehyde with a \[C{H_3}C = O\] group. First, the Hydroxide ion removes an acidic alpha hydrogen. This results in the formation of an enolate ion. The enolate anion then goes on to displace an iodide ion from the iodine molecule. This process repeats twice to give \[R - CO - C{I_3}\]. Now, a hydroxide ion forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon. This leads to the reformation of the carbonyl group and the elimination of \[C{I_3}^ - \] anion. A \[R - COOH\] group is also formed. The carboxylic acid group and the basic \[C{I_3}^ - \] ions neutralize each other. Thus, iodoform is precipitated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




