
How will you convert benzene into aniline?
Answer
531.1k+ views
Hint:Benzene is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon. Aniline is the amino benzene in which an amine functional group is attached to a benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:Benzene is an organic compound which belongs to aromatic family of compounds. Benzene consists of six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. The molecular formula of benzene is \[{C_6}{H_6}\] .
The six carbon atoms of benzene molecules are joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon. Benzene is classified as a hydrocarbon as it has only carbon and hydrogen. The carbon atoms of benzene are joined by three double bonds which are delocalized. The structure is shown as:
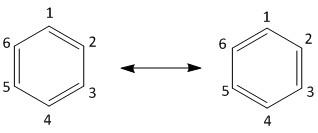
The reactivity of benzene is due to the presence of such delocalized electrons. The substitution of a proton of benzene by other groups is achieved easily in organic synthesis. The derivatization of benzene is performed by electrophilic aromatic substitution . The nucleophilic character of benzene ring is explored and utilized by substitution with electron deficient species like acylium ions, carbocations or other electron defiant groups like \[B{r^ + }\] , \[N{O_2}^ + \] etc.
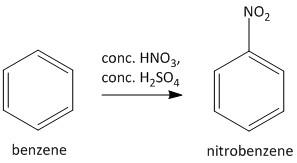
For the given transformation such a strategy is needed to introduce an amino group in the benzene ring. In the first step the benzene ring is treated with fuming nitric acid in presence of sulfuric acid to generate nitrobenzene. The active reagent in this case is \[N{O_2}^ + \] which substitutes a proton from the benzene ring.
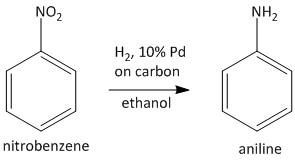
In the second step the nitrobenzene upon catalytic hydrogenation leads to generation of the desired aniline compound. The reagent used for this purpose in \[10\% Pd\] on carbon using ethanol solvent which acts as a hydrogen gas absorbent and leads to reduction of the nitro group into amino groups.
Note:
Generally for any compound synthesized from benzene nitrobenzene serves a useful intermediate. The reduction of nitrobenzene is also achieved using metal-acid based reduction. For this the reagents used are \[Fe - AcOH\] or \[Sn - HCl\].
Complete step by step answer:Benzene is an organic compound which belongs to aromatic family of compounds. Benzene consists of six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. The molecular formula of benzene is \[{C_6}{H_6}\] .
The six carbon atoms of benzene molecules are joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon. Benzene is classified as a hydrocarbon as it has only carbon and hydrogen. The carbon atoms of benzene are joined by three double bonds which are delocalized. The structure is shown as:

The reactivity of benzene is due to the presence of such delocalized electrons. The substitution of a proton of benzene by other groups is achieved easily in organic synthesis. The derivatization of benzene is performed by electrophilic aromatic substitution . The nucleophilic character of benzene ring is explored and utilized by substitution with electron deficient species like acylium ions, carbocations or other electron defiant groups like \[B{r^ + }\] , \[N{O_2}^ + \] etc.
For the given transformation such a strategy is needed to introduce an amino group in the benzene ring. In the first step the benzene ring is treated with fuming nitric acid in presence of sulfuric acid to generate nitrobenzene. The active reagent in this case is \[N{O_2}^ + \] which substitutes a proton from the benzene ring.

In the second step the nitrobenzene upon catalytic hydrogenation leads to generation of the desired aniline compound. The reagent used for this purpose in \[10\% Pd\] on carbon using ethanol solvent which acts as a hydrogen gas absorbent and leads to reduction of the nitro group into amino groups.

Note:
Generally for any compound synthesized from benzene nitrobenzene serves a useful intermediate. The reduction of nitrobenzene is also achieved using metal-acid based reduction. For this the reagents used are \[Fe - AcOH\] or \[Sn - HCl\].
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




