
How will you convert?
Aniline to Chlorobenzene.
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: First you have to convert the aniline to benzene diazonium chloride. Then this benzene diazonium chloride can be converted into chlorobenzene either through Sandmeyer’s reaction or Gattermann reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Aniline is an aromatic compound whose formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$ and the structure is:
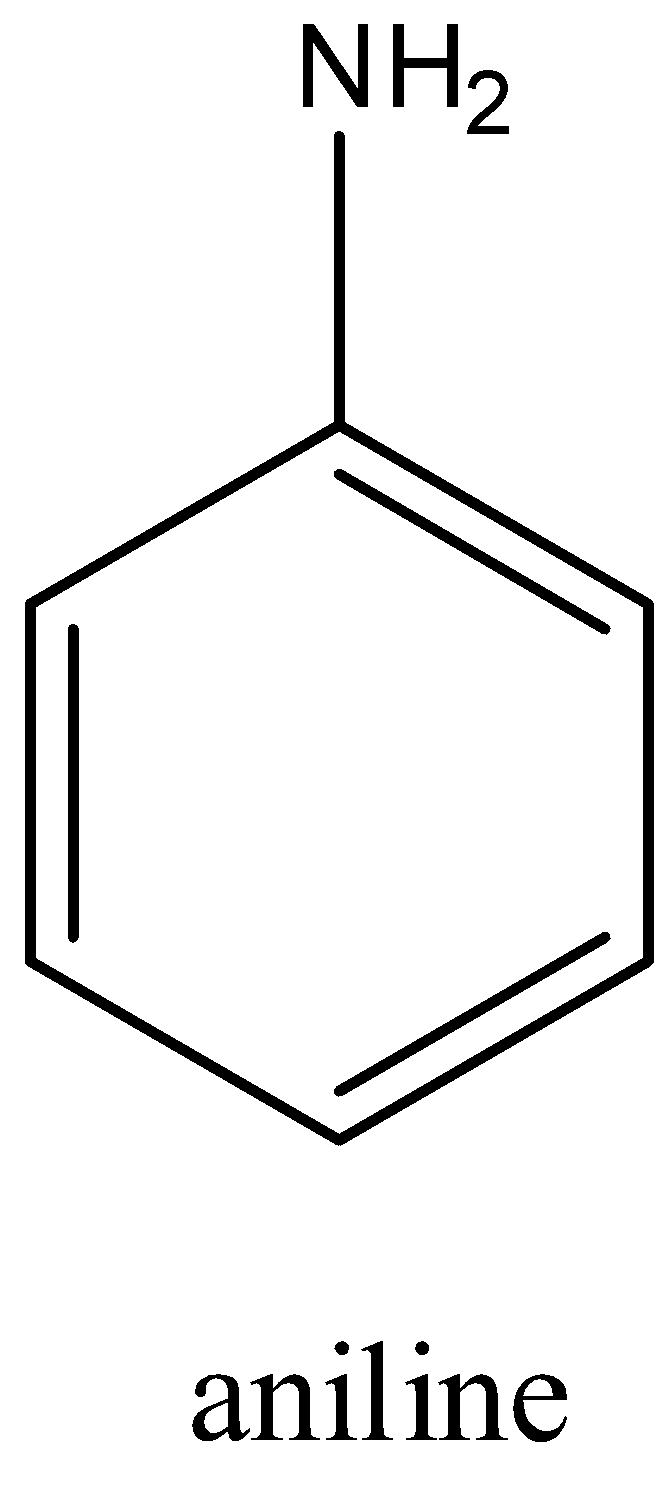
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic compound whose formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}Cl$ and the structure is:
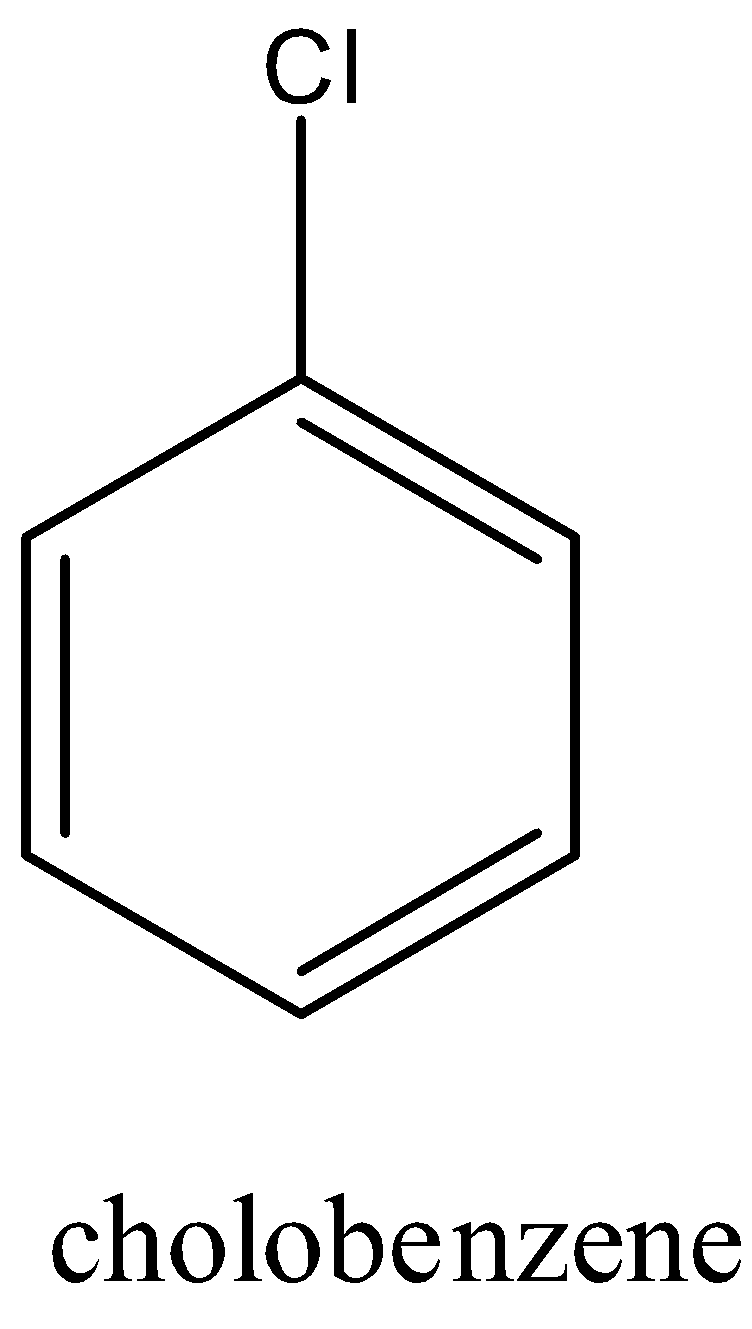
Aniline can be converted into chlorobenzene by the following steps:
First, the aniline is converted into benzene diazonium chloride. When the aniline is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrate we get benzene diazonium chloride. The reaction takes place at 273-278 K. The reaction is given below:
$NaN{{O}_{2}}+HCl\to HONO+NaCl$
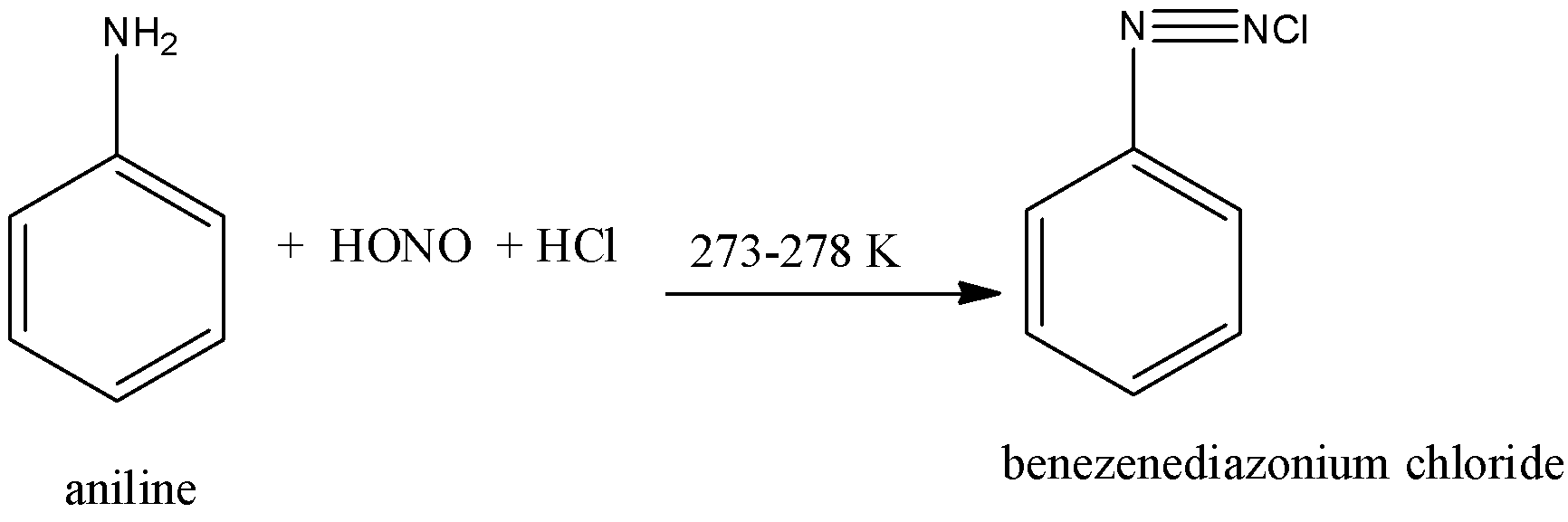
Now, this Benzenediazonium chloride is converted into chlorobenzene by one of the two processes explained below:
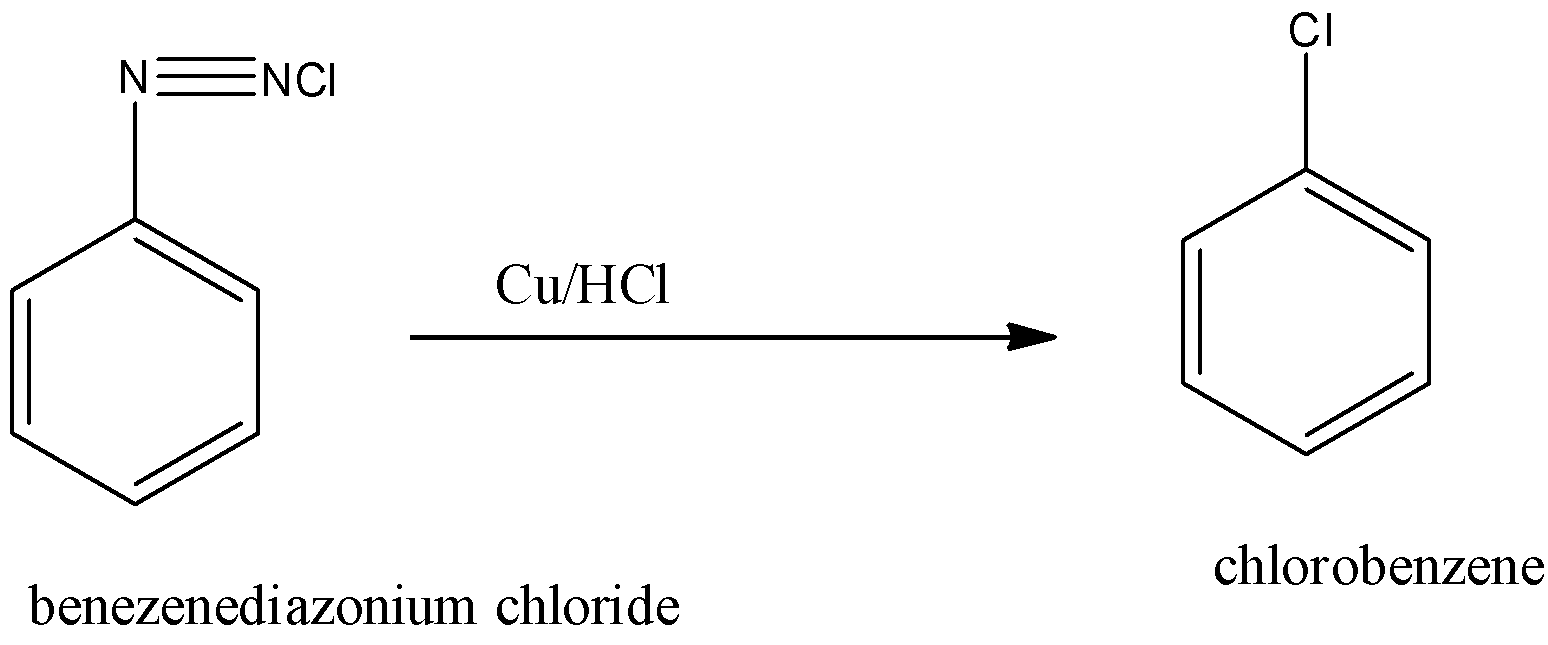
(i)- By Sandmeyer reaction: We can convert the benzene diazonium chloride to chlorobenzene by treating the diazonium salt with cuprous chloride $CuCl$ dissolved in $HCl$. This process is called a Sandmeyer reaction. The reaction is given below:
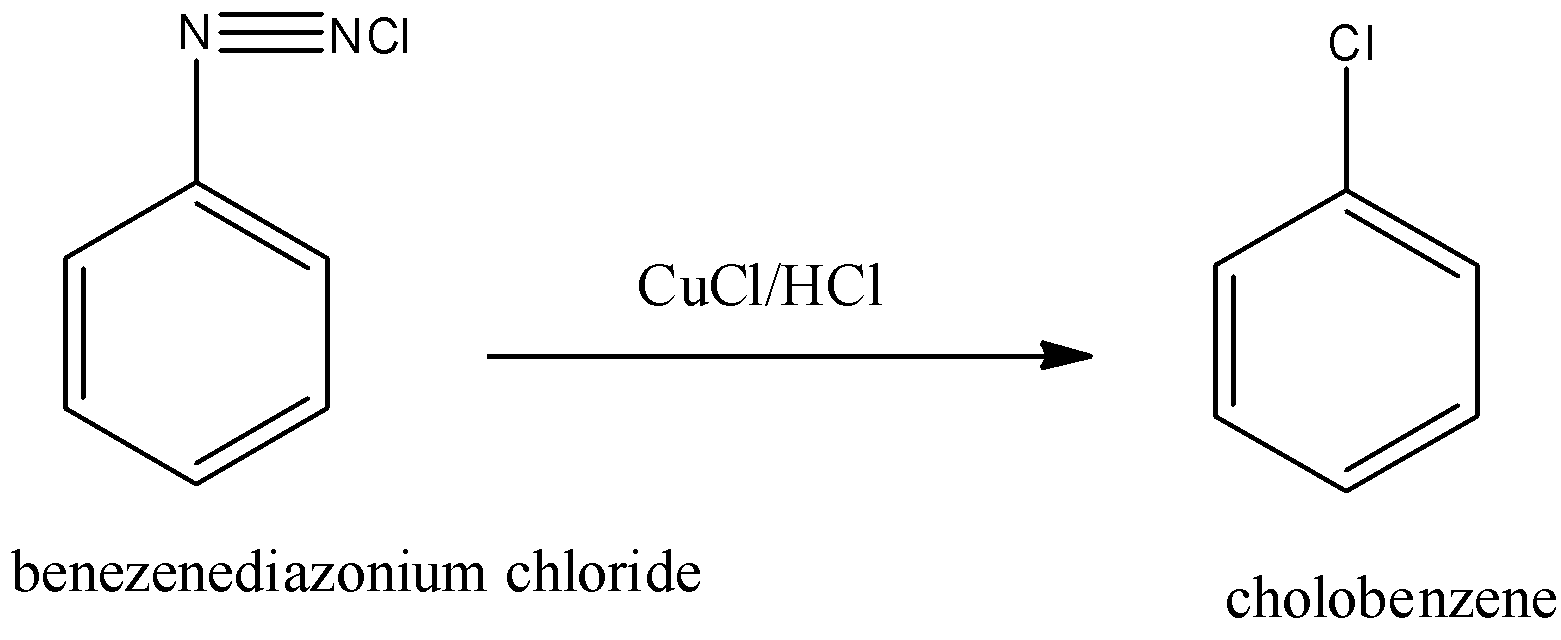
(ii)- By Gattermann reaction: Haloarenes like chlorobenzene can be prepared by Gattermann reaction. It is a modification of Sandmeyer’s reaction. In this reaction, a mixture of freshly prepared copper powder in the presence of corresponding haloacids (hydrogen chloride, because we have to form chlorobenzene) is used instead of cuprous halogen acid (here $CuCl/HCl$). The reaction is given below:
Note: In both the reactions i.e. Sandmeyer and Gattermann reaction instead of using hydrogen chloride and cuprous chloride, we can use hydrogen bromide and cuprous bromide, we can obtain bromobenzene. But these two reactions are not suitable for the formation of fluorobenzene and iodobenzene.
Complete step by step answer:
Aniline is an aromatic compound whose formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$ and the structure is:

Chlorobenzene is an aromatic compound whose formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}Cl$ and the structure is:

Aniline can be converted into chlorobenzene by the following steps:
First, the aniline is converted into benzene diazonium chloride. When the aniline is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrate we get benzene diazonium chloride. The reaction takes place at 273-278 K. The reaction is given below:
$NaN{{O}_{2}}+HCl\to HONO+NaCl$

Now, this Benzenediazonium chloride is converted into chlorobenzene by one of the two processes explained below:
(i)- By Sandmeyer reaction: We can convert the benzene diazonium chloride to chlorobenzene by treating the diazonium salt with cuprous chloride $CuCl$ dissolved in $HCl$. This process is called a Sandmeyer reaction. The reaction is given below:

(ii)- By Gattermann reaction: Haloarenes like chlorobenzene can be prepared by Gattermann reaction. It is a modification of Sandmeyer’s reaction. In this reaction, a mixture of freshly prepared copper powder in the presence of corresponding haloacids (hydrogen chloride, because we have to form chlorobenzene) is used instead of cuprous halogen acid (here $CuCl/HCl$). The reaction is given below:

Note: In both the reactions i.e. Sandmeyer and Gattermann reaction instead of using hydrogen chloride and cuprous chloride, we can use hydrogen bromide and cuprous bromide, we can obtain bromobenzene. But these two reactions are not suitable for the formation of fluorobenzene and iodobenzene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




