
How will you convert
A. Propene to Propan -2-ol?
B. Phenol to 2, 4, 6- trinitrophenol?
Answer
527.5k+ views
Hint: We are already familiar with the rules of addition reactions of unsymmetrical alkenes. If we try to recall them, we can easily solve the given question.
2, 4, 6- trinitrophenol is also known as Picric acid. If we try to recall its structure we see it is but a phenol with nitro group added to its ortho and para positions. Hence, we can proceed keeping in mind this is a nitration reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We must first have a clear concept of Markonikov’s rule. It tells us where to add the nucleophile and hydrogen in an asymmetrical alkene addition reaction. This rule is simple, the nucleophile will add to the more substituted carbon. This leaves hydrogen to add to the less substituted carbon.
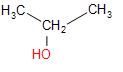
Hence if we simply add sulphuric acid we can obtain Propan-2-ol from Propene.
\[C{{H}_{3}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}\,+\,{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{boiling\,{{H}_{2}}O}\]
For the second part of the question,
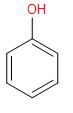
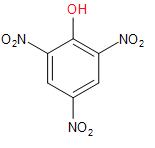
On adding concentrated Nitric acid to Phenol, we get Picric acid or
2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol. In this reaction, we see that electrophile nitronium ion substitute the hydrogen from all the ortho and para positions of phenol.
 \[+\,3HN{{O}_{3}}\xrightarrow{conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\]
\[+\,3HN{{O}_{3}}\xrightarrow{conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\]
 \[+\,3{{H}_{2}}O\]
\[+\,3{{H}_{2}}O\]
Additional Information:
The trick to recall Markovnikov’s reaction is the phrase: “The rich gets richer”. In an alkene addition reaction, the hydrogen will add to the less substituted carbon so that the nucleophile can attack the more substituted carbon.
We must conduct the reaction of production of Picric acid by sulphonation first as it is extremely exothermic. Direct addition of even dilute nitric acid to phenol is very vigorous.
Note: It is very important for us to learn the mechanism of Markovnikov’s rule since the addition of nucleophiles depends on the formation of stable intermediate like most reactions in organic chemistry. We might even come across certain reactions where no addition of hydrogen takes place.
Since the reaction is so exothermic we can guess the utilization of Picric acid. It finds the largest use in production of explosives like TNT and Dunnite(Explosive-D)
2, 4, 6- trinitrophenol is also known as Picric acid. If we try to recall its structure we see it is but a phenol with nitro group added to its ortho and para positions. Hence, we can proceed keeping in mind this is a nitration reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We must first have a clear concept of Markonikov’s rule. It tells us where to add the nucleophile and hydrogen in an asymmetrical alkene addition reaction. This rule is simple, the nucleophile will add to the more substituted carbon. This leaves hydrogen to add to the less substituted carbon.
Hence if we simply add sulphuric acid we can obtain Propan-2-ol from Propene.
\[C{{H}_{3}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}\,+\,{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{boiling\,{{H}_{2}}O}\]

For the second part of the question,
On adding concentrated Nitric acid to Phenol, we get Picric acid or
2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol. In this reaction, we see that electrophile nitronium ion substitute the hydrogen from all the ortho and para positions of phenol.


Additional Information:
The trick to recall Markovnikov’s reaction is the phrase: “The rich gets richer”. In an alkene addition reaction, the hydrogen will add to the less substituted carbon so that the nucleophile can attack the more substituted carbon.
We must conduct the reaction of production of Picric acid by sulphonation first as it is extremely exothermic. Direct addition of even dilute nitric acid to phenol is very vigorous.
Note: It is very important for us to learn the mechanism of Markovnikov’s rule since the addition of nucleophiles depends on the formation of stable intermediate like most reactions in organic chemistry. We might even come across certain reactions where no addition of hydrogen takes place.
Since the reaction is so exothermic we can guess the utilization of Picric acid. It finds the largest use in production of explosives like TNT and Dunnite(Explosive-D)
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




