
What is the construction and working of dropping mercury electrodes?
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: The dropping mercury electrode (DME) is a working electrode made of mercury and used in polarography. Mercury drops form at the end of the capillary tube as a result of gravity. Experiments run with mercury electrodes are referred to as forms of polarography.
Complete answer:
The dropping mercury electrode is a working electrode made of mercury and used in polarography. It is designated as DME. In this electrode mercury continuously drops from a reservoir through a capillary tube (internal diameter\[0.03{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}0.05{\text{ }}mm\]) into the solution. The optimum interval between drops for most analyses is between\[2s{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}5s\].
Construction-
Capillary
The Mercury reservoir vessel; and
The stand tube with an adjoining stopcock. In the capillary tube a \[5.5{\text{ }}cm\]of corning marine barometer tubing is joined to \[6{\text{ }}mm\]soft glass tubing. Electrical contact to the mercury in the mercury reservoir vessel is made employing a tungsten contact mercury well.
Working-
The dropping mercury electrode (DME) is polarizable and can act as an anode as well as a cathode. The pool of mercury acts as a counter electrode, i.e., it will act as anode if DME is the cathode or it will act as cathode if DME is the anode. The counter electrode is non-polarizable. To the analyte solution placed in a glass beaker, supporting electrolyte like \[KCl\]is added i.e., \[50 - 100\]times of sample concentration. Pure nitrogen or hydrogen gas is bubbled through the solution, to expel (remove) oxygen. Then gradually increasing voltage is applied to the polarographic cell, typically by going to a more positive (more negative decomposing potential), and current is recorded. When the voltage becomes great enough, reduction occurs at the analytical electrode causing a current. The electrode is rapidly saturated so current production is limited based on the diffusion of the analyte to the small electrode. The reduced species alters the surface of the mercury electrode. The graph is plotted between the voltage applied and the current. This graph is called Polarography and the apparatus is known as Polarogram.
The polarography assembly with DME is arranged in the following manner:
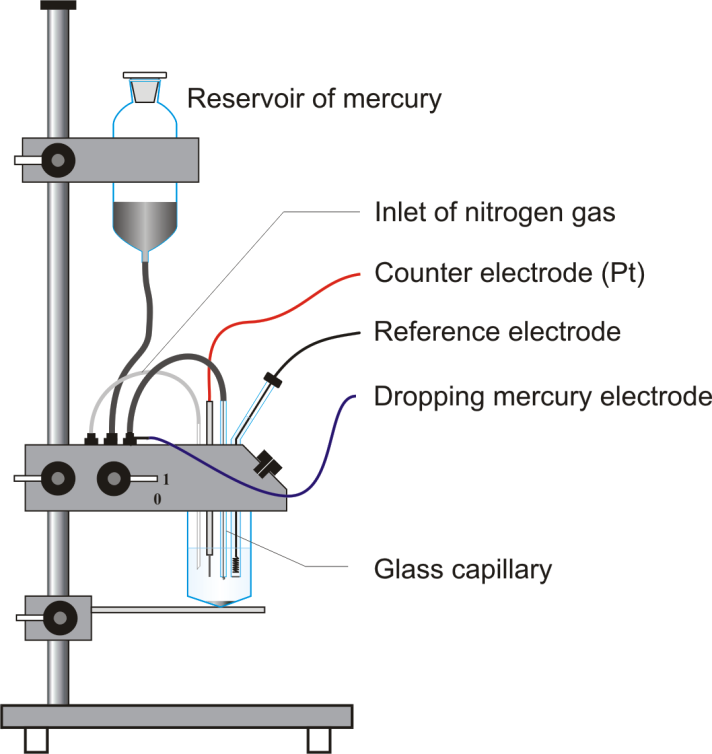
Note:
DME is used in polarography. It has several advantages as well as disadvantages. Care must be taken while using the DME. In DME only pure and triple distilled mercury should be used. The tip of DME should be always immersed in water when not in use and should be clean by dipping in the nitric acid. The entire assembly should be mounted vertically on a heavy stand to be free from vibrations.
Complete answer:
The dropping mercury electrode is a working electrode made of mercury and used in polarography. It is designated as DME. In this electrode mercury continuously drops from a reservoir through a capillary tube (internal diameter\[0.03{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}0.05{\text{ }}mm\]) into the solution. The optimum interval between drops for most analyses is between\[2s{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}5s\].
Construction-
Capillary
The Mercury reservoir vessel; and
The stand tube with an adjoining stopcock. In the capillary tube a \[5.5{\text{ }}cm\]of corning marine barometer tubing is joined to \[6{\text{ }}mm\]soft glass tubing. Electrical contact to the mercury in the mercury reservoir vessel is made employing a tungsten contact mercury well.
Working-
The dropping mercury electrode (DME) is polarizable and can act as an anode as well as a cathode. The pool of mercury acts as a counter electrode, i.e., it will act as anode if DME is the cathode or it will act as cathode if DME is the anode. The counter electrode is non-polarizable. To the analyte solution placed in a glass beaker, supporting electrolyte like \[KCl\]is added i.e., \[50 - 100\]times of sample concentration. Pure nitrogen or hydrogen gas is bubbled through the solution, to expel (remove) oxygen. Then gradually increasing voltage is applied to the polarographic cell, typically by going to a more positive (more negative decomposing potential), and current is recorded. When the voltage becomes great enough, reduction occurs at the analytical electrode causing a current. The electrode is rapidly saturated so current production is limited based on the diffusion of the analyte to the small electrode. The reduced species alters the surface of the mercury electrode. The graph is plotted between the voltage applied and the current. This graph is called Polarography and the apparatus is known as Polarogram.
The polarography assembly with DME is arranged in the following manner:

Note:
DME is used in polarography. It has several advantages as well as disadvantages. Care must be taken while using the DME. In DME only pure and triple distilled mercury should be used. The tip of DME should be always immersed in water when not in use and should be clean by dipping in the nitric acid. The entire assembly should be mounted vertically on a heavy stand to be free from vibrations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




