
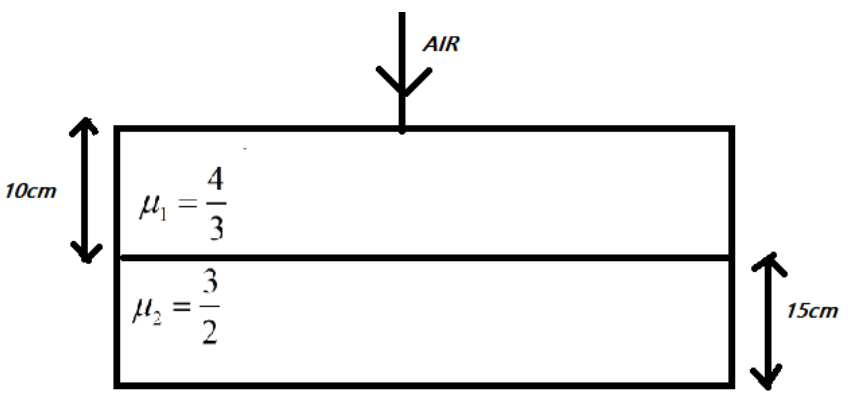
Considering the normal incidence of ray, the equivalent refractive index of the combination of two slabs as shown in the figure is:
\[\begin{align}
& A.1.8 \\
& B.1.43 \\
& C.2 \\
& D.\text{ None of these} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Refractive index is the measure of how much light bends when it passes from one medium to another. The bending of the light depends on the medium if it passes through. The Refractive index is a dimensionless number that has no units. And it is usually a constant for a given medium.
Formula used:
$\mu=\dfrac{sin( i)}{sin (r)}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that the refractive index of a material is given by the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction. Clearly, since this is the ratio of two similar quantities thus, it has no units.
$\mu=\dfrac{sin( i)}{sin (r)}$
This is derived from the Snell’s law which gives, that $\mu_{1}sin\theta_{1}=\mu_{2}sin\theta_{2}$
Where, $\theta_{1}$ and $\theta_{2}$ is the angle of incidence and refraction respectively. And $\mu_{1}$ and $\mu_{2}$ is the refractive index of the two mediums.
Here the angle of incidence $i=90^{\circ}$ for the combination, then we can say that, $t_{1}\mu_{1}sin(i)+t_{2}\mu_{2}sin (i)=(t_{1}+t_{2})sin(r)$
Then we get, $\dfrac{t_{1}\mu_{1}+t_{2}\mu_{2}}{t_{1}+t_{2}}=\dfrac{sin (r) }{sin(i)}=\mu$
Given that, thickness of first slab$t_{1}=10cm$, refractive index of first slab $\mu_{1}=\dfrac{4}{3}$, thickness of the second slab $t_{2}=15cm$ and refractive index of the second $\mu_{2}=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Then, we get,
$\dfrac{10\times\dfrac{4}{3}+15\times\dfrac{3}{2}}{10+15}=\mu$
Or,$\mu=\dfrac{10\times 8+15\times 9}{6\times 25}$
Or,$\mu=\dfrac{80+135}{150}=\dfrac{215}{150}=1.43$
Hence the refractive index of the combination is \[1.43\]
Thus the answer is \[B.1.43\]
Note: Here, even without the angle of the final refracted ray, we can still solve this sum. The refractive index of a material is a property of a material. It depends on the ratio the angle of incident ray to the angle of the refracted ray. It is also taken as the ratio of the speed of the light in medium to the speed of light in vacuum. It is also called the absolute refractive index, if one of the two mediums is air.
Formula used:
$\mu=\dfrac{sin( i)}{sin (r)}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that the refractive index of a material is given by the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction. Clearly, since this is the ratio of two similar quantities thus, it has no units.
$\mu=\dfrac{sin( i)}{sin (r)}$
This is derived from the Snell’s law which gives, that $\mu_{1}sin\theta_{1}=\mu_{2}sin\theta_{2}$
Where, $\theta_{1}$ and $\theta_{2}$ is the angle of incidence and refraction respectively. And $\mu_{1}$ and $\mu_{2}$ is the refractive index of the two mediums.
Here the angle of incidence $i=90^{\circ}$ for the combination, then we can say that, $t_{1}\mu_{1}sin(i)+t_{2}\mu_{2}sin (i)=(t_{1}+t_{2})sin(r)$
Then we get, $\dfrac{t_{1}\mu_{1}+t_{2}\mu_{2}}{t_{1}+t_{2}}=\dfrac{sin (r) }{sin(i)}=\mu$
Given that, thickness of first slab$t_{1}=10cm$, refractive index of first slab $\mu_{1}=\dfrac{4}{3}$, thickness of the second slab $t_{2}=15cm$ and refractive index of the second $\mu_{2}=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Then, we get,
$\dfrac{10\times\dfrac{4}{3}+15\times\dfrac{3}{2}}{10+15}=\mu$
Or,$\mu=\dfrac{10\times 8+15\times 9}{6\times 25}$
Or,$\mu=\dfrac{80+135}{150}=\dfrac{215}{150}=1.43$
Hence the refractive index of the combination is \[1.43\]
Thus the answer is \[B.1.43\]
Note: Here, even without the angle of the final refracted ray, we can still solve this sum. The refractive index of a material is a property of a material. It depends on the ratio the angle of incident ray to the angle of the refracted ray. It is also taken as the ratio of the speed of the light in medium to the speed of light in vacuum. It is also called the absolute refractive index, if one of the two mediums is air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




