
Consider the given reaction, the product ‘A’ is:
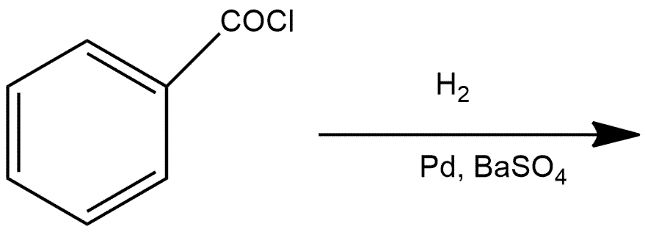
A. ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH$
B. ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$
C. ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}Cl$
D. ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CHO$

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:. Benzoyl chloride can also be known as benzene carbonyl chloride, it is an organochlorine compound with the formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COCl$. It is a colorless, fuming liquid with an irritating odor.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzoyl chloride is produced from benzotrichloride using either water or benzoic acid. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the preparation of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CC{{l}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COCl+2HCl$
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CC{{l}_{3}}+{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH\to 2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COCl+2HCl$
Reaction given in the question is example of Rosenmund reduction
The Rosenmund reduction is a hydrogenation process in which an acyl chloride is selectively reduced to an aldehyde. This reaction is generally a hydrogenolysis which is catalysed by palladium on barium sulfate which can be called the Rosenmund catalyst. Barium sulfate has a low surface area which reduces the activity of the palladium and prevents over-reduction. However, for certain reactive acyl chlorides the activity must be reduced further, by the addition of a poison. Originally this was thioquinanthrene although thiourea has also been used. Deactivation is required because the system must reduce the acyl chloride but not the subsequent aldehyde. If further reduction does take place it will create a primary alcohol which would then react with the remaining acyl chloride to form an ester. Rosenmund catalyst can be prepared by reduction of palladium (II) chloride solution in the presence of $BaS{{O}_{4}}$.
Thus the product A in this reaction is
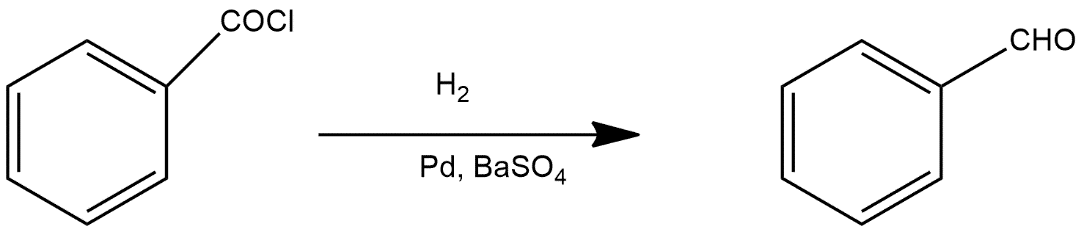
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: It reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and benzoic acid. Benzoyl chloride is a typical acyl chloride. It reacts with alcohols to give the corresponding esters. Similarly, it reacts with amines to give the amide.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzoyl chloride is produced from benzotrichloride using either water or benzoic acid. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the preparation of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CC{{l}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COCl+2HCl$
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CC{{l}_{3}}+{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH\to 2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COCl+2HCl$
Reaction given in the question is example of Rosenmund reduction
The Rosenmund reduction is a hydrogenation process in which an acyl chloride is selectively reduced to an aldehyde. This reaction is generally a hydrogenolysis which is catalysed by palladium on barium sulfate which can be called the Rosenmund catalyst. Barium sulfate has a low surface area which reduces the activity of the palladium and prevents over-reduction. However, for certain reactive acyl chlorides the activity must be reduced further, by the addition of a poison. Originally this was thioquinanthrene although thiourea has also been used. Deactivation is required because the system must reduce the acyl chloride but not the subsequent aldehyde. If further reduction does take place it will create a primary alcohol which would then react with the remaining acyl chloride to form an ester. Rosenmund catalyst can be prepared by reduction of palladium (II) chloride solution in the presence of $BaS{{O}_{4}}$.
Thus the product A in this reaction is

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: It reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and benzoic acid. Benzoyl chloride is a typical acyl chloride. It reacts with alcohols to give the corresponding esters. Similarly, it reacts with amines to give the amide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




