
Consider the following reaction:
$RCHO + N{H_2}N{H_2} \to RCH = N - N{H_2}$
What sort of reaction is this?
A) Free radical addition-elimination reaction
B) Electrophilic substitution-elimination reaction
C) Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
D) Electrophilic addition-elimination reaction
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: You must know that in a carbon-oxygen bond, the carbon centre is electrophilic while oxygen centre is nucleophilic in nature. Nitrogen contains lone pairs, so hydrazine ($N{H_2}N{H_2}$) in the given reaction will act as a nucleophile. It will attack the carbon centre of given aldehyde.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the following chemical reaction:
$RCHO + N{H_2}N{H_2} \to RCH = N - N{H_2}$
We can represent the above given reaction with mechanism as:
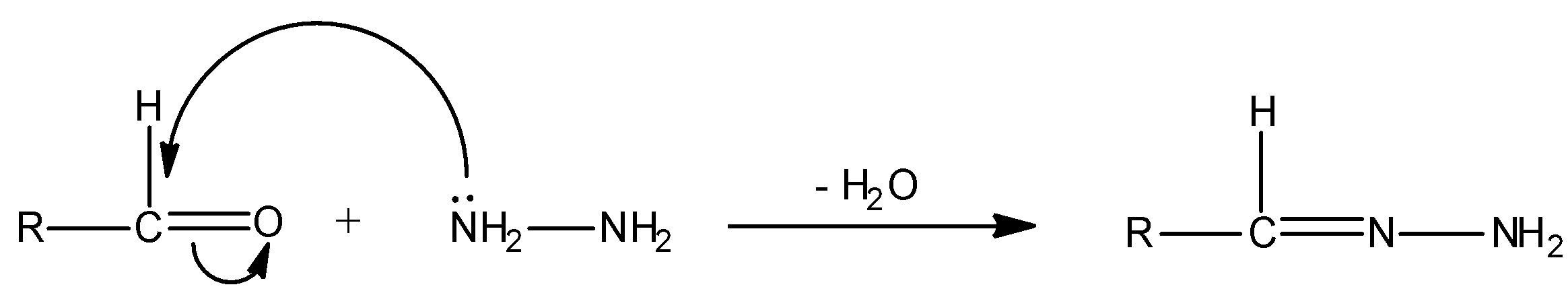
We all know that oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. So in a carbonyl bond i.e., carbon-oxygen bond, carbon is electron deficient always and oxygen is electron rich in nature. Thus, the carbon centre behaves as an electrophile. Here, hydrazine molecules ($N{H_2}N{H_2}$) are nucleophiles. This is because in hydrazine, nitrogen atoms contain lone pairs and hence it is electron rich or nucleophile. And, a nucleophile always attacks an electrophile. Hence, hydrazine molecules will attack the carbon centre (i.e., electrophile) of aldehyde ($RCHO$). When a nucleophile attacks on an electrophile, the reaction is termed as nucleophilic addition. So, when a molecule of hydrazine is added to the carbonyl group, this is the case of nucleophilic-addition reaction. Simultaneously, a water molecule is also eliminated in the given reaction. Thus, this is the case of elimination reaction. Hence, overall the given reaction is nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction.
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Aldehydes or ketones react with hydrazine to give hydrazones (hydrazine derivative) and further, hydrazones can be converted to corresponding alkanes by reaction with base and heat. These two steps can be converted into one reaction known as Wolff-Kishner reduction. In the first step, a water molecule is eliminated and in the second step, nitrogen gas is produced as the by-product in the reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the following chemical reaction:
$RCHO + N{H_2}N{H_2} \to RCH = N - N{H_2}$
We can represent the above given reaction with mechanism as:
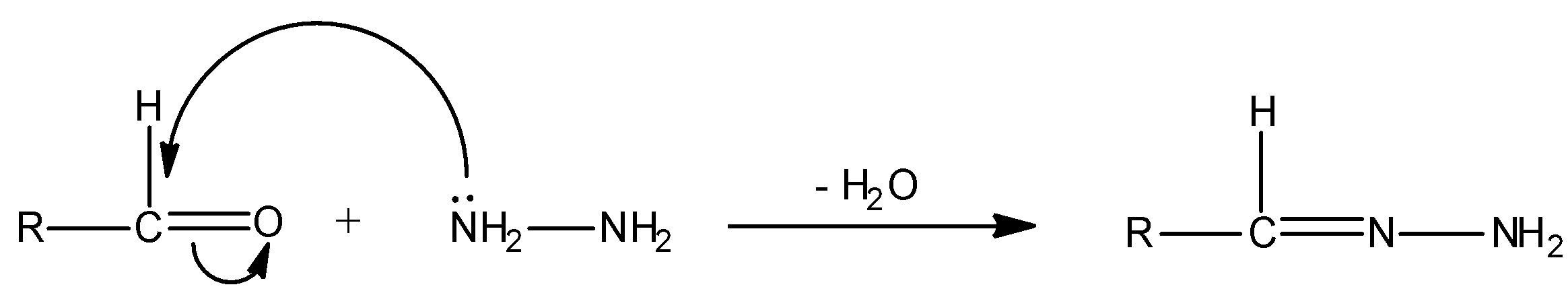
We all know that oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. So in a carbonyl bond i.e., carbon-oxygen bond, carbon is electron deficient always and oxygen is electron rich in nature. Thus, the carbon centre behaves as an electrophile. Here, hydrazine molecules ($N{H_2}N{H_2}$) are nucleophiles. This is because in hydrazine, nitrogen atoms contain lone pairs and hence it is electron rich or nucleophile. And, a nucleophile always attacks an electrophile. Hence, hydrazine molecules will attack the carbon centre (i.e., electrophile) of aldehyde ($RCHO$). When a nucleophile attacks on an electrophile, the reaction is termed as nucleophilic addition. So, when a molecule of hydrazine is added to the carbonyl group, this is the case of nucleophilic-addition reaction. Simultaneously, a water molecule is also eliminated in the given reaction. Thus, this is the case of elimination reaction. Hence, overall the given reaction is nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction.
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Aldehydes or ketones react with hydrazine to give hydrazones (hydrazine derivative) and further, hydrazones can be converted to corresponding alkanes by reaction with base and heat. These two steps can be converted into one reaction known as Wolff-Kishner reduction. In the first step, a water molecule is eliminated and in the second step, nitrogen gas is produced as the by-product in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




