
Consider the following reaction and select the best choice that represents the reaction.
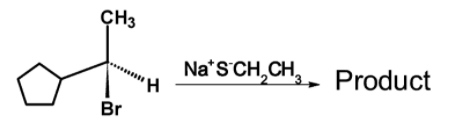


Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: The nucleophilic substitution reaction of alkyl halides takes place via two pathways: $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{1}}\text{2 }$or$\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$. Substitution bimolecular nucleophilic $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$reaction, the incoming nucleophile attacks on the partially positively charged carbon atom bearing a halogen atom. The reaction takes place via transition state. The product obtained has an inversion of configuration.
Complete step by step answer:
A nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate determining steps involves 2 components .i.e. the reaction is bimolecular which contains the simultaneously bond breaking and bond making is known as the $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ reaction.
Here, the strong nucleophile attacks on the partially positive charged carbon atom of the carbon halogen bond. the nucleophile attack in the direction which is $\text{ 18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{ }$ away from the leaving group.
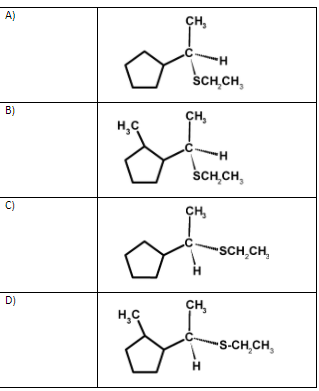
The sodium ethyl sulphide$\text{ NaSC}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ is a nucleophile. the nucleophile $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}^{-}}\text{ }$ attacks on the partially positive charge carbon atom of a carbon bromine bond $\text{ C}-\text{Br }$ . The carbon has a $\text{ }{{\delta }^{\text{+}}}\text{ }$ charge and the bromine acquires a partial $\text{ }{{\delta }^{-}}\text{ }$ charge. The nucleophile attacks on the carbon from the direction which is $\text{ 18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{ }$away from the bromine atoms i.e. from the backside. This leads to the partially bond formation between carbon and $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}^{-}}\text{ }$as $\text{ C}........\text{ SC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }$ and partially bond breaking between carbon and bromine$\text{ C}........\text{ Br }$.
This is a one-step reaction.in the transition state, the negative charge is shared by incoming nucleophiles as well as outgoing bromide.
The transition state is unstable because the carbon atom is simultaneously bonded to five atoms and therefore the bromide ion leaves and forming a $\text{ C}-\text{SC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }$bond. The reaction is as shown below,
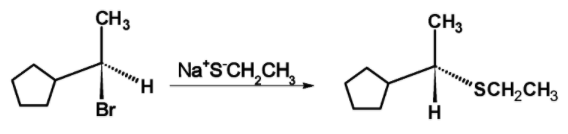
The mechanism of the nucleophilic substitution reaction is shown below,
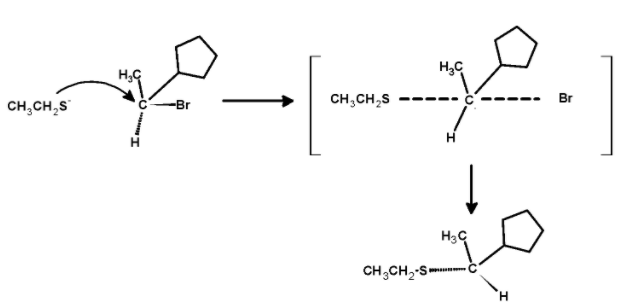
The sulphide nucleophilic backside attack on the carbon atom. Such that the bond which was initially towards the observer now changes to the bond away from the observer. Thus, the molecule undergoes the inversion of configuration.so the product is,
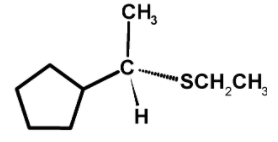
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note: Note that, in this reaction bond breaking and making occurs at the same time thus this is also known as the ‘concerted ‘mechanism. The nucleophilic reaction depends on the strength of a nucleophile. The ease at which the nucleophile is displaced or it’s leaving group ability depends on the capacity to accommodate a negative charge. Thus, here bromide leaves the molecule and inverts the configuration.
Complete step by step answer:
A nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate determining steps involves 2 components .i.e. the reaction is bimolecular which contains the simultaneously bond breaking and bond making is known as the $\text{ }{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2 }$ reaction.
Here, the strong nucleophile attacks on the partially positive charged carbon atom of the carbon halogen bond. the nucleophile attack in the direction which is $\text{ 18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{ }$ away from the leaving group.
The sodium ethyl sulphide$\text{ NaSC}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ is a nucleophile. the nucleophile $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}^{-}}\text{ }$ attacks on the partially positive charge carbon atom of a carbon bromine bond $\text{ C}-\text{Br }$ . The carbon has a $\text{ }{{\delta }^{\text{+}}}\text{ }$ charge and the bromine acquires a partial $\text{ }{{\delta }^{-}}\text{ }$ charge. The nucleophile attacks on the carbon from the direction which is $\text{ 18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{ }$away from the bromine atoms i.e. from the backside. This leads to the partially bond formation between carbon and $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}^{-}}\text{ }$as $\text{ C}........\text{ SC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }$ and partially bond breaking between carbon and bromine$\text{ C}........\text{ Br }$.
This is a one-step reaction.in the transition state, the negative charge is shared by incoming nucleophiles as well as outgoing bromide.
The transition state is unstable because the carbon atom is simultaneously bonded to five atoms and therefore the bromide ion leaves and forming a $\text{ C}-\text{SC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }$bond. The reaction is as shown below,

The mechanism of the nucleophilic substitution reaction is shown below,

The sulphide nucleophilic backside attack on the carbon atom. Such that the bond which was initially towards the observer now changes to the bond away from the observer. Thus, the molecule undergoes the inversion of configuration.so the product is,

Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note: Note that, in this reaction bond breaking and making occurs at the same time thus this is also known as the ‘concerted ‘mechanism. The nucleophilic reaction depends on the strength of a nucleophile. The ease at which the nucleophile is displaced or it’s leaving group ability depends on the capacity to accommodate a negative charge. Thus, here bromide leaves the molecule and inverts the configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




