
Consider the following bromides: The correct order of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reactivity is:
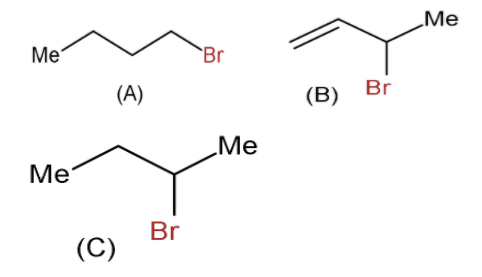
a) B ˃ C ˃ A
b) B ˃ A ˃ C
c) C ˃ B ˃ A
d) A ˃ B ˃ C

Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to make the product of each reactant when it will undergo ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$. Due to which it will form a carbocation as an intermediate and the compound which will be the most stable carbocation will be the most stable compound.
Complete step by step solution:
- In the given question, we have to explain the reactivity order of the bromide in the given three compounds.
- As we know that ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction because here the nucleophile attacks on the carbocation.
- But the attack of the nucleophile takes place from the front side due to which the stability of the tertiary carbocation is maximum and then secondary and then the tertiary carbocation.
- So, we can say that the order of the stability of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction will be:
\[\text{3}{}^\circ \text{C }\ge \text{ 2}{}^\circ \text{C }\ge \text{ 1}{}^\circ \text{C}\]
- Now, in the first structure when the bromine is removed then the carbocation formed is primary.
$\text{Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - Br }\to \text{ Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ CH}_{2}^{+}$
- Whereas in the second structure, after the removal of the bromine the carbocation formed is secondary but as we can see there is the presence of double bond as a conjugate pair.
- Due to which the carbocation undergoes the resonance and forms the most stable product.
$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}(\text{Br})\text{ - Me }\to \text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ CH}_{2}^{+}\text{ - Me}$
- Now, in the third structure, when the bromine will be removed the carbocation formed will be secondary but here it will not undergo the resonance and due to which it will be less stable less than the previous carbocation.
$\text{Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{(Br) - Me }\to \text{ Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}^{+}\ \text{- Me}$
- So, we can say the reactivity order will be B ˃ C ˃ A.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: The ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction is a slower process as compared to the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ as later is the one-step reaction and also the formation of the transition state takes place whereas in the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction the intermediate is carbocation instead of a transition state.
Complete step by step solution:
- In the given question, we have to explain the reactivity order of the bromide in the given three compounds.
- As we know that ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction because here the nucleophile attacks on the carbocation.
- But the attack of the nucleophile takes place from the front side due to which the stability of the tertiary carbocation is maximum and then secondary and then the tertiary carbocation.
- So, we can say that the order of the stability of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction will be:
\[\text{3}{}^\circ \text{C }\ge \text{ 2}{}^\circ \text{C }\ge \text{ 1}{}^\circ \text{C}\]
- Now, in the first structure when the bromine is removed then the carbocation formed is primary.
$\text{Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - Br }\to \text{ Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ CH}_{2}^{+}$
- Whereas in the second structure, after the removal of the bromine the carbocation formed is secondary but as we can see there is the presence of double bond as a conjugate pair.
- Due to which the carbocation undergoes the resonance and forms the most stable product.
$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}(\text{Br})\text{ - Me }\to \text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{ CH}_{2}^{+}\text{ - Me}$
- Now, in the third structure, when the bromine will be removed the carbocation formed will be secondary but here it will not undergo the resonance and due to which it will be less stable less than the previous carbocation.
$\text{Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{(Br) - Me }\to \text{ Me - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}^{+}\ \text{- Me}$
- So, we can say the reactivity order will be B ˃ C ˃ A.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: The ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction is a slower process as compared to the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ as later is the one-step reaction and also the formation of the transition state takes place whereas in the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction the intermediate is carbocation instead of a transition state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




