
Consider the condition mentioned in the diagram. The straight wire is kept constant but the loop will be able to move under a magnetic force. This time the loop will
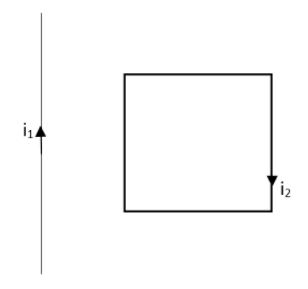
A. remain stationery
B. move towards the wire
C. move away from the wire
D. rotate about the wire

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Force acting on wire will be found by taking the ratio of the product of the permeability, current through the wire and current in the loop to twice the product of the value of the pi and the distance between them. The force is inversely proportional to distance. Find the force on each of the faces. Compare this. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step by step answer:
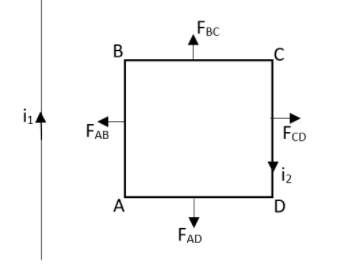
the force acting on the wire per unit length of a current carrying wire having a current ${{i}_{1}}$, due to another wire which is also carrying current ${{i}_{2}}$ at a distance $d$ can be written as,
$F=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{i}_{1}}{{i}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
This can be applied in each face of the loop.
The force on the surface AB can be found to be as,
${{F}_{AB}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{i}_{1}}{{i}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
This force will be acting towards the wire.
Now let us find the force on the surface BC which can be written as,
${{F}_{CD}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{i}_{1}}{{i}_{2}}}{2\pi \left( d+a \right)}$
This will be away from the wire. As the force is inversely proportional to distance, we can see that the force of the surface CD is less than force on the surface AB, we can write that,
${{\vec{F}}_{AB}}\rangle {{\vec{F}}_{CD}}$
From this we can understand that the resultant force will be towards the wire.
$\left| {{{\vec{F}}}_{BC}} \right|=\left| {{{\vec{F}}}_{DA}} \right|$
As they are at equal distance from the wire carrying current ${{i}_{1}}$. Even though their direction will be opposite. Therefore we can write that,
${{\vec{F}}_{BC}}=-{{\vec{F}}_{AD}}$
Therefore the net force will be towards the wire carrying current ${{i}_{1}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: A magnetic field is defined as a vector field which is defining the magnetic influence on electric charges, electric currents or magnetized particles which are in motion. The charge which is in motion in a magnetic field will be providing a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
the force acting on the wire per unit length of a current carrying wire having a current ${{i}_{1}}$, due to another wire which is also carrying current ${{i}_{2}}$ at a distance $d$ can be written as,
$F=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{i}_{1}}{{i}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
This can be applied in each face of the loop.
The force on the surface AB can be found to be as,
${{F}_{AB}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{i}_{1}}{{i}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
This force will be acting towards the wire.
Now let us find the force on the surface BC which can be written as,
${{F}_{CD}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{i}_{1}}{{i}_{2}}}{2\pi \left( d+a \right)}$
This will be away from the wire. As the force is inversely proportional to distance, we can see that the force of the surface CD is less than force on the surface AB, we can write that,
${{\vec{F}}_{AB}}\rangle {{\vec{F}}_{CD}}$
From this we can understand that the resultant force will be towards the wire.
$\left| {{{\vec{F}}}_{BC}} \right|=\left| {{{\vec{F}}}_{DA}} \right|$
As they are at equal distance from the wire carrying current ${{i}_{1}}$. Even though their direction will be opposite. Therefore we can write that,
${{\vec{F}}_{BC}}=-{{\vec{F}}_{AD}}$
Therefore the net force will be towards the wire carrying current ${{i}_{1}}$.

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: A magnetic field is defined as a vector field which is defining the magnetic influence on electric charges, electric currents or magnetized particles which are in motion. The charge which is in motion in a magnetic field will be providing a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




