
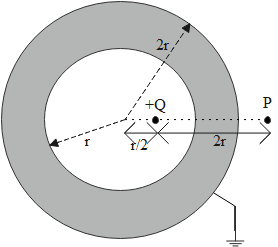
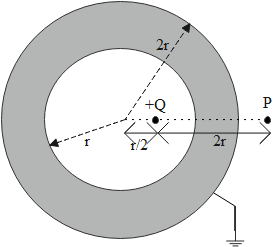
Consider an initially neutral hollow conducting spherical shell with their inner radius $r$ and outer radius $2r$. A point charge $+Q$ is now placed inside the shell at a distance of $\dfrac{r}{2}$ from the center of the center. The shell is then grounded by connecting the outer surface to the earth. $P$ is an external point at a distance $2r$ from the charge $+Q$ on the line passing through the center of the point charge $+Q$ as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the force on a test charge $+q$ is placed at point P.
A. $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{qQ}{4{{r}^{2}}}$
B. $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{9qQ}{100{{r}^{2}}}$
C. $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{4qQ}{25{{r}^{2}}}$
D. 0

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: When a charge is kept near a conducting material a charge of the same magnitude but opposite in direction gets induced on the surface of the object. This is known as the principle of induction. The ground is used to connect two terminals (electric setup and ground). The grounds act as the neutral terminal as the charge moves from higher potential to lower potential all the charge will be transferred to the ground.
Complete answer:
When we see the condition in the question concerning the diagram,
The shell is a conducting sphere, which initially has a zero electric field inside the shell.
When a $+Q$ charge is introduced in the inner shell. Due to the principle of charge induction, a charge of $-Q$ equal in magnitude $+Q$ will develop on the inner surface of the shell, such that the electric field is zero outside the inner surface.
Similarly, the unbalanced $+Q$ charge gets transferred to the outer surface of the shell. As it is mentioned in the question the outer surface is grounded, the unbalanced charge $+Q$ will get transferred to the Earth core.
So, the entire charge system acts as a no-charge (zero potential), for all the points outside the inner shell of the setup.
Here we can say that the force acting on the test charge placed at point P is \[0\]( zero) as the point P lies outside the inner surface of the shell.
Thus, for the above discussion, we can conclude that the correct option for the question is Option D.
Note:
There are two types of induction. Self-induction and mutual-induction. In mutual induction, two conductors participate in the setup whereas in self-induction only one conductor is present. The principle of induction is used in instruments like a transformer to step up or step down the voltage.
Complete answer:
When we see the condition in the question concerning the diagram,

The shell is a conducting sphere, which initially has a zero electric field inside the shell.
When a $+Q$ charge is introduced in the inner shell. Due to the principle of charge induction, a charge of $-Q$ equal in magnitude $+Q$ will develop on the inner surface of the shell, such that the electric field is zero outside the inner surface.
Similarly, the unbalanced $+Q$ charge gets transferred to the outer surface of the shell. As it is mentioned in the question the outer surface is grounded, the unbalanced charge $+Q$ will get transferred to the Earth core.
So, the entire charge system acts as a no-charge (zero potential), for all the points outside the inner shell of the setup.
Here we can say that the force acting on the test charge placed at point P is \[0\]( zero) as the point P lies outside the inner surface of the shell.
Thus, for the above discussion, we can conclude that the correct option for the question is Option D.
Note:
There are two types of induction. Self-induction and mutual-induction. In mutual induction, two conductors participate in the setup whereas in self-induction only one conductor is present. The principle of induction is used in instruments like a transformer to step up or step down the voltage.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

What is myopia and hypermetropia How are they corrected class 12 physics CBSE




