
Consider an equiconvex lens of radius of curvature $R$ and focal length $f$. If $f>R$, refractive index $\mu $ of the material of the lens
A) is greater than zero but less than $1.5$
B) is greater than $1.5$ but less than $2.0$
C) is greater than $1.0$ but less than $1.5$
D) none of these
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: An equiconvex lens is nothing but a double convex lens which has two convex spherical surfaces of equal radii of curvature. Using the lens formula, an expression for focal length of the given equiconvex lens is derived. Applying the given condition to this expression, we can determine the satisfying condition from the given options.
Formula used:
$1)\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
$2)f>R$
Complete answer:
An equiconvex lens is nothing but a double convex lens which has two convex spherical surfaces of equal radii of curvature, as shown in the following diagram.
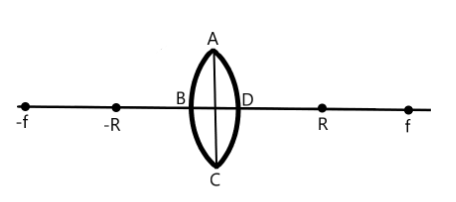
We are given that the radius of curvature and focal length of the equiconvex lens are $R$ and $f$, respectively.
We know by lens formula that
$\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
where
$f$ is the focal length of a lens.
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material of a lens.
${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ are the radii of curvature of spherical surfaces of the lens.
Let this be equation 1.
Using equation 1, focal length of the given equiconvex lens is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{-R} \right)$
where
$f$ is the focal length of equiconvex lens
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material of equiconvex lens
$R$ and $-R$ are the radii of curvature of spherical surfaces of the equiconvex lens
Let this be equation 2.
On simplifying equation 2, we have
$\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{-R} \right)\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\dfrac{2}{R}\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{R}{2(\mu -1)}$
Let this be equation 3.
Now, from the question, we are provided with the condition that
$f>R$
where
$f$ is the focal length of equiconvex lens
$R$ is the radius of curvature of equiconvex lens
Let this be expression 4.
Applying equation 3 in expression 4, we have
$f>R\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{2(\mu -1)}>R\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2(\mu -1)}>1\Rightarrow 2(\mu -1)<1\Rightarrow \mu -1<\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \mu <1+\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \mu <1.5$
where
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material of equiconvex lens
Let this be expression 5.
Now, from the question, we know that the value of $f$ is given as positive. Hence, it is clear from equation 2 that
$\mu >1$
Let this be expression 6
Therefore, from expression 5 and expression 6, it is clear that
$1<\mu <1.5$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Firstly, students need not get confused with the name ‘equiconvex lens’. This is nothing but a double convex lens or simply, convex lens having two convex spherical surfaces of equal radii of curvature. Secondly, the lens formula follows sign convention. Therefore, focal length and radius of curvature of convex spherical surface $(ADC)$ is taken as negative whereas those of the other convex spherical surface $(ABC)$ is taken as positive, as shown in the diagram.
Formula used:
$1)\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
$2)f>R$
Complete answer:
An equiconvex lens is nothing but a double convex lens which has two convex spherical surfaces of equal radii of curvature, as shown in the following diagram.

We are given that the radius of curvature and focal length of the equiconvex lens are $R$ and $f$, respectively.
We know by lens formula that
$\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
where
$f$ is the focal length of a lens.
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material of a lens.
${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ are the radii of curvature of spherical surfaces of the lens.
Let this be equation 1.
Using equation 1, focal length of the given equiconvex lens is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{-R} \right)$
where
$f$ is the focal length of equiconvex lens
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material of equiconvex lens
$R$ and $-R$ are the radii of curvature of spherical surfaces of the equiconvex lens
Let this be equation 2.
On simplifying equation 2, we have
$\dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{-R} \right)\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\dfrac{2}{R}\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{R}{2(\mu -1)}$
Let this be equation 3.
Now, from the question, we are provided with the condition that
$f>R$
where
$f$ is the focal length of equiconvex lens
$R$ is the radius of curvature of equiconvex lens
Let this be expression 4.
Applying equation 3 in expression 4, we have
$f>R\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{2(\mu -1)}>R\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2(\mu -1)}>1\Rightarrow 2(\mu -1)<1\Rightarrow \mu -1<\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \mu <1+\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \mu <1.5$
where
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material of equiconvex lens
Let this be expression 5.
Now, from the question, we know that the value of $f$ is given as positive. Hence, it is clear from equation 2 that
$\mu >1$
Let this be expression 6
Therefore, from expression 5 and expression 6, it is clear that
$1<\mu <1.5$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Firstly, students need not get confused with the name ‘equiconvex lens’. This is nothing but a double convex lens or simply, convex lens having two convex spherical surfaces of equal radii of curvature. Secondly, the lens formula follows sign convention. Therefore, focal length and radius of curvature of convex spherical surface $(ADC)$ is taken as negative whereas those of the other convex spherical surface $(ABC)$ is taken as positive, as shown in the diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




