
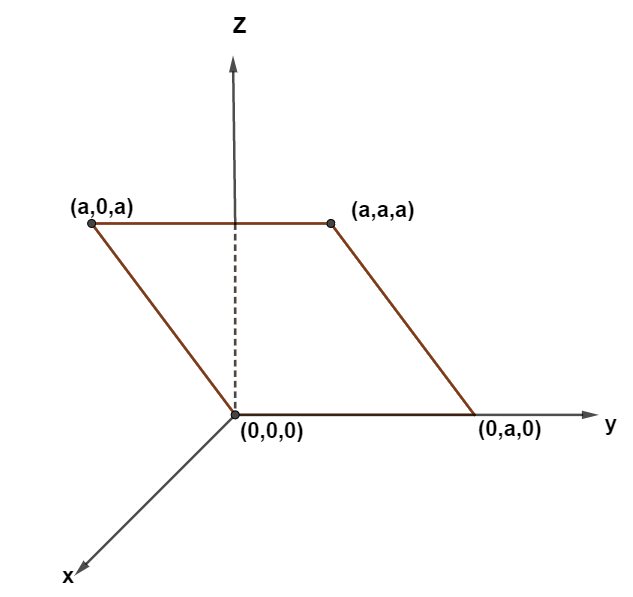
Consider an electric field $ \vec E = {E_ \circ }\hat x,{\text{ where }}{E_ \circ } $ is a constant. The flux through the shaded area ( as shown in the figure) due to this field is:
A. $ 2{{E}_{\circ }}{{a}^{2}} $
B. $ \sqrt{2}{{E}_{\circ }}{{a}^{2}} $
C. $ {{E}_{\circ }}{{a}^{2}} $
D. $ \dfrac{{{E}_{\circ }}{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}} $

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The electric flux through a given area held inside an electric field is the measure of the total number of electric lines of force passing through that area. Mathematically, it can be defined as the product of the normal component of the electric field and the surface area.
Formula Used:
Electric flux, $ \Delta {{\phi }_{E}}=E\Delta S\cos \theta =\vec{E}.\Delta \vec{S} $
where
$ \begin{align}
& E\text{ is the magnitude of electric field} \\
& \Delta \text{S is the surface area} \\
& \theta \text{ is the angle between the Electric field and the normal component of Surface}\text{.} \\
\end{align} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
The term flux implies some kind of flow. Flux is the property of any vector field. The electric flux is the property of the electric field. The electric flux through a given area held inside an electric field is the measure of the total number of electric lines of force passing through that area.
It is a scalar quantity, i.e., it only has magnitude associated with it and not direction. Its SI unit is $ N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}} $ .
Given that:
$ \vec{E}={{E}_{\circ }}\hat{x},\text{ where }{{E}_{\circ }} $ is constant.
Each side of the shaded region = a
So, $ \Delta S=\sqrt{2}{{a}^{2}} $
Additionally, it is clear from the diagram that the angle between the area vector and electric field will be $ {{45}^{\circ }} $
$ \Rightarrow \theta ={{45}^{\circ }} $
Substituting the values of the above in the formula for electric flux we get:
Electric flux,
$ \Delta {\phi _E} = \vec E.\Delta \vec S = E\Delta S\cos \theta $
$ \eqalign{
& E\Delta S\cos \theta = {E_ \circ }\left( {\sqrt 2 {a^2}} \right)\cos {45^ \circ } \cr
& \Rightarrow \Delta {\phi _E} = {E_ \circ }\left( {\sqrt 2 {a^2}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow \Delta {\phi _E} = {E_ \circ }{a^2}N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}} \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is C. i.e., Electric flux through the shaded portion in the diagram is $ \Delta {\phi _E} = {E_ \circ }{a^2}N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}} $ .
Additional Information:
i. Gauss’s theorem states that the total flux through a closed surface is $ \dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} $ times the net charge enclosed by the surface.
ii. Gauss’s law is based on the inverse square dependence on distance contained in Coulomb's law. It will not hold in case of any departure from inverse square law.
Note: The net flux through a closed surface due to a charge lying outside the enclosed surface is always zero. Additionally, if the net charge enclosed by a surface is zero $ \left( {q = 0} \right) $ , then the flux through it is also zero.
Formula Used:
Electric flux, $ \Delta {{\phi }_{E}}=E\Delta S\cos \theta =\vec{E}.\Delta \vec{S} $
where
$ \begin{align}
& E\text{ is the magnitude of electric field} \\
& \Delta \text{S is the surface area} \\
& \theta \text{ is the angle between the Electric field and the normal component of Surface}\text{.} \\
\end{align} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
The term flux implies some kind of flow. Flux is the property of any vector field. The electric flux is the property of the electric field. The electric flux through a given area held inside an electric field is the measure of the total number of electric lines of force passing through that area.
It is a scalar quantity, i.e., it only has magnitude associated with it and not direction. Its SI unit is $ N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}} $ .
Given that:
$ \vec{E}={{E}_{\circ }}\hat{x},\text{ where }{{E}_{\circ }} $ is constant.
Each side of the shaded region = a
So, $ \Delta S=\sqrt{2}{{a}^{2}} $
Additionally, it is clear from the diagram that the angle between the area vector and electric field will be $ {{45}^{\circ }} $
$ \Rightarrow \theta ={{45}^{\circ }} $
Substituting the values of the above in the formula for electric flux we get:
Electric flux,
$ \Delta {\phi _E} = \vec E.\Delta \vec S = E\Delta S\cos \theta $
$ \eqalign{
& E\Delta S\cos \theta = {E_ \circ }\left( {\sqrt 2 {a^2}} \right)\cos {45^ \circ } \cr
& \Rightarrow \Delta {\phi _E} = {E_ \circ }\left( {\sqrt 2 {a^2}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow \Delta {\phi _E} = {E_ \circ }{a^2}N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}} \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is C. i.e., Electric flux through the shaded portion in the diagram is $ \Delta {\phi _E} = {E_ \circ }{a^2}N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}} $ .
Additional Information:
i. Gauss’s theorem states that the total flux through a closed surface is $ \dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} $ times the net charge enclosed by the surface.
ii. Gauss’s law is based on the inverse square dependence on distance contained in Coulomb's law. It will not hold in case of any departure from inverse square law.
Note: The net flux through a closed surface due to a charge lying outside the enclosed surface is always zero. Additionally, if the net charge enclosed by a surface is zero $ \left( {q = 0} \right) $ , then the flux through it is also zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




