
Consider a uniform electric field $E = 3 \times {10^3}\,\hat iN{C^{ - 1}}$.
(a) What is the flux of this field through a square off $10\,cm$ on a side whose plane is parallel to the $yz$ plane?
(b) What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes an ${60^ \circ }$ angle with the $x$ axis?
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: Find the area of the square from the given length of one side. Use the formula of the electric flux, and substitute the known values in it to find the electric flux through the square parallel to the $yz$ plane and ${60^ \circ }$ from the $x$ axis by substituting the angles in the formula.
Formula used:
The formula of the electric flux is given by
$\Phi = EA\cos \theta $
Where $\Phi $ is the electric flux, $E$ is the electric field, $A$ is the area and $\theta $ is the angle of the normal with the coordinate axis.
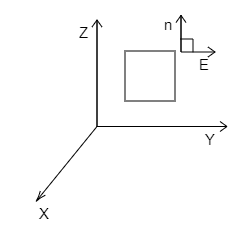
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
The uniform electric field, $E = 3 \times {10^3}\,\hat iN{C^{ - 1}}$
Side of the square, $a = 10\,cm$
The angle between the normal to the plane and the horizontal axis, $\theta = {60^ \circ }$
From the given side of the square, let us calculate the area of the square.
$A = 0.1 \times 0.1 = 0.01\,{m^2}$
(a) Let us use the formula of the electric flux,
$\Phi = EA\cos \theta $
Substitute the angle as the ${0^ \circ }$ since the plane is considered parallel to the $yz$ plane that is parallel to the $x$ axis, we get
$\Phi = 3 \times {10^3}\, \times 0.01 \times \cos {0^ \circ }$
By simplifying the above equation, we get
$\Phi = 30\,N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}$
(b) Substitute the angle of ${60^ \circ }$ in the formula of the electric flux to find the flux through the same square which is at the angle ${60^ \circ }$ with the horizontal $x$ axis.
$\Phi = EA\cos \theta $
$\Phi = 3 \times {10^3}\, \times 0.01 \times \cos {60^ \circ }$
By further simplification, we get
$\Phi = 15\,N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}$
Hence the electric flux through the square at an angle ${60^ \circ }$ from the $x$ axis is $15\,N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}$ .
Note: Electric flux measures the electric field in the region of the square. It depends on the electric field, area and the angle of the normal of the plane made with the horizontal. In the above solution, the square parallel to $yz$ plane is taken as ${0^ \circ }$ . This is because this square passes vertically in the horizontal and parallel to the $yz$ axis. Hence the normal to the horizontal is ${0^ \circ }$.
Formula used:
The formula of the electric flux is given by
$\Phi = EA\cos \theta $
Where $\Phi $ is the electric flux, $E$ is the electric field, $A$ is the area and $\theta $ is the angle of the normal with the coordinate axis.

Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
The uniform electric field, $E = 3 \times {10^3}\,\hat iN{C^{ - 1}}$
Side of the square, $a = 10\,cm$
The angle between the normal to the plane and the horizontal axis, $\theta = {60^ \circ }$
From the given side of the square, let us calculate the area of the square.
$A = 0.1 \times 0.1 = 0.01\,{m^2}$
(a) Let us use the formula of the electric flux,
$\Phi = EA\cos \theta $
Substitute the angle as the ${0^ \circ }$ since the plane is considered parallel to the $yz$ plane that is parallel to the $x$ axis, we get
$\Phi = 3 \times {10^3}\, \times 0.01 \times \cos {0^ \circ }$
By simplifying the above equation, we get
$\Phi = 30\,N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}$
(b) Substitute the angle of ${60^ \circ }$ in the formula of the electric flux to find the flux through the same square which is at the angle ${60^ \circ }$ with the horizontal $x$ axis.
$\Phi = EA\cos \theta $
$\Phi = 3 \times {10^3}\, \times 0.01 \times \cos {60^ \circ }$
By further simplification, we get
$\Phi = 15\,N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}$
Hence the electric flux through the square at an angle ${60^ \circ }$ from the $x$ axis is $15\,N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}$ .
Note: Electric flux measures the electric field in the region of the square. It depends on the electric field, area and the angle of the normal of the plane made with the horizontal. In the above solution, the square parallel to $yz$ plane is taken as ${0^ \circ }$ . This is because this square passes vertically in the horizontal and parallel to the $yz$ axis. Hence the normal to the horizontal is ${0^ \circ }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




